Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Coal and Petroleum
Q1: What is inexhaustible Natural Resource?
Ans: The resources which are present in unlimited quantity in nature and are not likely to be exhausted by human activities are known as inexhaustible Resources. For example: Sunlight, air
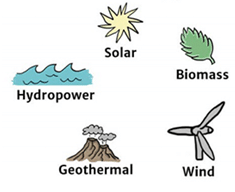 Inexhaustible Natural Resources
Inexhaustible Natural Resources
Q2: Define exhaustible resources with few examples.
Ans: All resources which are found in a limited quantity in nature are known as exhaustible resources. They can be exhausted by human activities. Example of these resources are forests, minerals, coal, petroleum, natural gas etc.
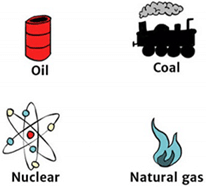 Exhaustible Natural Resources
Exhaustible Natural Resources
Q3: How was Coal formed?
Ans: Coal formed over millions of years from ancient plant remains. Around 300 million years ago, dense forests covered wetlands. As plants died, they accumulated and were buried under sediment. Pressure and heat from overlying layers transformed the plant matter into peat. With time, peat changed into lignite, then higher-grade coals like sub-bituminous, bituminous, and anthracite. This process occurred due to compression, heat, and biochemical changes, resulting in the diverse range of coal types we have today.
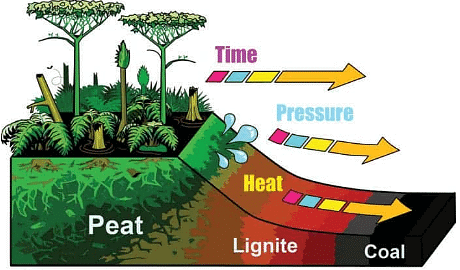 Formation of Coal
Formation of Coal
Q4: How was Petroleum formed?
Ans: Petroleum originated from marine organisms that perished millions of years ago. When these organisms died, their remains sank to the sea floor, becoming layered with sediment like sand and clay. Over immense spans of time, the absence of oxygen, coupled with elevated temperature and pressure, facilitated the conversion of these organic remnants into petroleum and natural gas. This process of transformation in the deep Earth gave rise to the valuable resources we use today.
Q5: What do you mean by refining and petroleum refinery?
Ans. Refining refers to the separation of different components or fractions within petroleum. This intricate process takes place at a petroleum refinery, where the raw crude oil is meticulously processed to extract its distinct parts, each with specific uses and properties.
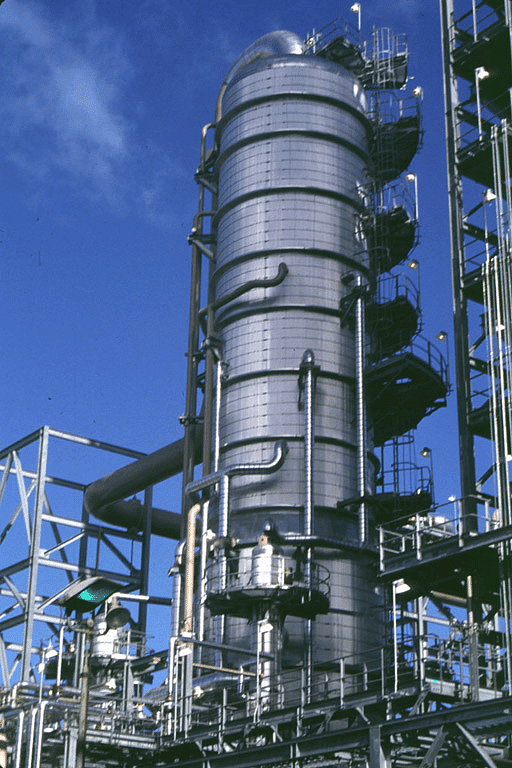 Refining crude oil
Refining crude oil
Q6: What do you understand by Petrochemical products. What are their uses?
Ans: Petrochemical products encompass a range of valuable substances derived from petroleum and natural gas. These materials find wide-ranging applications, such as in the production of detergents, synthetic fibers, polyethylene, and various other types of synthetic plastics.
Q7: Name various constituents of Petroleum and their uses.
Ans: Products obtained by refining of petroleum are petroleum gas, petrol, diesel, kerosene, paraffin wax and lubricating oil.
| Constituents of Petroleum | Uses |
Petroleum Gas in Liquid form | Fuel for home and Industry |
Petrol | Motor fuel, Aviation fuel, solvent for dry cleaning |
Kerosene | Fuel for stoves, lamps and for jet aircrafts |
Diesel | Fuel for heavy motor vehicles, electric generators |
Lubricating oil | Lubrication of bearings in moving parts of machines |
Paraffin wax | Ointments, candles, Vaseline etc. |
Bitumen | Paints, Road surfacing |
Q8: Name few places where Natural Gas has been found in India.
Ans: In our country Natural Gas has been found in Tripura, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra and in the Krishna & Godavari Delta.
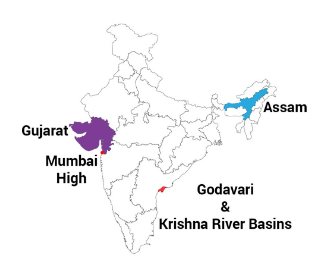 Map of India showing the places where petroleum reserves are found
Map of India showing the places where petroleum reserves are found
Q9: Why should we use some resources like coal and petroleum in limit?
Ans: As we know Coal and petroleum are fossil fuels. The dead organisms takes millions of years to get converted into these fuels, On the other hand the known reserves of these will last almost a few hundred years. A part from this since these products are not environmental friendly as burning of these fuels is a major cause of air pollution and their use is also linked to global warming therefore we should use these resources only when it is actually required.
Q10: What are the advices of PCRA to save petrol/diesel while driving?
Ans: The advices of PCRA to save petrol/diesel while driving:
- Drive at a constant and moderate speed as far as possible.
- Switch off the engine at traffic lights or at a place where you have to wait.
- Ensure correct type pressure.
- Ensure regular maintenance of the vehicle.
Q12: What does CNG stand for and what are the benefits of using CNG as fuels?
Ans: CNG stands for Compressed Natural gas. In CNG compressed gas (which is mainly methane gas) is stored under high pressure as compressed natural Gas.
Advantages of CNG:
- CNG is a very important fossil fuel because it is easy to transport through pipes.
- It is a cleaner fuel.
- CNG-powered vehicles have lower maintenance costs when compared with other fossil fuel-powered vehicles.
- CNG fuel systems are sealed, which prevents any spill or evaporation losses.
- CNG mixes easily and evenly in air being a gaseous fuel.
Q13: What does LPG Stand for and its uses?
Ans: LPG stands for "Liquefied Petroleum Gas." It serves as a clean-burning fuel for both household and industrial purposes. Notably eco-friendly, LPG is favored for its convenience in transportation and utilization.
Q14: Why Coal is called Fossil fuel?
Ans: Coal is referred to as a fossil fuel due to its origin from the remains of ancient plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. These organic materials underwent a natural transformation process, resulting in coal formation. This connection to prehistoric life and its fossilized components gives coal its classification as a fossil fuel.
Q15: Why the layer containing petroleum and Gas is above the water?
Ans:
The layer containing petroleum and gas is positioned above water because oil and gas have lower densities than water, preventing them from mixing. Due to their lighter nature, these hydrocarbons naturally rise and accumulate above the denser water layer.
Q16: Why Coal, Petroleum and Natural Gas can't be prepared in Laboratory?
Ans: These natural resources can't be prepared in laboratory because their formation is a very slow process and it is not possible to create the conditions for their formation in the laboratory.
Q17: Explain the uses of coal.
Ans: Coal serves various purposes due to its energy-rich properties:
- Electricity Generation: Coal is a crucial source for generating electricity in power plants.
- Heating Homes: It's used for heating homes and water in many households.
- Industrial Fuel: Industries use coal to power machines and for various processes.
- Making Goods: Coal helps make products like iron, steel, and cement in factories.
- Historical Significance: Traditionally, it was used for cooking and heating in homes.
Q18: What is the main reason for coal to be used to generate electricity?
Ans: Coal is used to generate the electricity because it is reliable and low cost energy source.
Q19: Explain few advantages and disadvantages of using petroleum.
Ans: Few advantages and disadvantages of using petroleum are:
Advantages:
- Storage and transportation are simple.
- Spills and leaks are controllable using existing technology.
- As raw material in chemical synthesis it is extremely flexible.
Disadvantages:
- Over use can create local and global problems.
- It is limited resource which can be used up by wasteful procedures.
Q20: What could be the potential risk using oil as fuel or source of energy?
Ans: Burning oil for energy can release large amounts of carbon dioxide, which can contribute to global warming. In addition the risk of dependence on oil as energy source is that supplies are eventually going to be depleted.
Q21: Why is Petroleum known as Black gold?
Ans: Petroleum is called "Black gold" due to its immense economic value and significance in various industries, resembling the preciousness of gold.
Q22: Name the material by which Plastics are made?
Ans: Petroleum
Q23: What is Coal gas?
Ans: Coal gas is obtained during the processing of Coal to get coke. It is used as a fuel in many industries situated near the coal processing plants.
Q24: What is PCRA?
Ans: PCRA stands for Petroleum Conservation Research Association, it advices people how to save petrol and diesel while driving by giving following tips:
- Drive at a constant and moderate speed as far as possible
- Switch off the engine at traffic lights or at a place where you have to wait
- Ensure correct tyre pressure
- Ensure regular maintenance of the vehicle
Q25: How burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution?
Ans: Pollutants that come from the combustion of fossil fuels include sulphur dioxide (SO2),nitrogen oxides (NOx), ground-level ozone, particulate matter (PM), carbon monoxide(CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), volatile organic compounds (VOC) including benzene, some heavy metals and a number of other pollutants which contribute to smog, acid rain, climate change, and health, environmental and economic concerns.
Q26: What are natural resources? Explain with examples.
Ans. The resources provided by nature or obtained from the nature are called natural resources. For example: air, water, soil and sunlight etc.
Q27: Classify the natural resources on the basis of their availability.
Ans. On the basis of the availability various, natural resources in nature can be classified in the following two groups:
(i) Inexhaustible natural resources: Air, Water, Soil, Sunlight, etc.
(ii) Exhaustible natural resources: Forests, Wildlife, Minerals and Coal etc.
Q28: What are fossil fuels? Name the main fossil fuels.
Ans. The remains of dead plants and animals are called fossils. The fuels formed by the remains of dead plants and animals are called fossil fuels. Main fossil fuels are: coal petroleum and natural gas.
Q29: What is coke? Write its uses.
Ans. Coke is a tough porous and black substance. It is almost the purest form of carbon. It is formed by heating coal in the absence of air.
Uses:
(i) It is used in manufacture of steel.
(ii) It is used in the extraction of metals.
Q30: What is coal tar? What are its uses?
Ans. Coal tar is a black thick liquid. It is a mixture of about 200 substances.
Uses:
(i) It is used as a source of various useful substances.
(ii) It is used to get naphthaline which is used to repel moths and other insects.
(iii) It is used to make road surface.
Q31: What is coal gas? Write the uses of coal gas.
Ans. Coal gas is a by-product formed when coal is heated in absence of air.
Uses:
(i) It is used as fuel in many industries.
(ii) Previously it was used for street lighting in London in 1810.
Q.32: What is petroleum? Why is it called black gold?
Ans. Petroleum is a dark oily liquid. It is a mixture of various constituents. Its constituents are very useful. Due to its great commercial importance petroleum is also called black gold.
Q33: Where and when was the first oil well drilled? (i) in world and (ii) in India.
Ans. (i) The world’s first oil well was drilled in Pennsylvania, (U.S.A.), in 1859.
(ii) In India, the first oil well was drilled at Makum (Assam) in 1867.
Q34: Why is natural gas called a very important fossil fuel in these days?
Ans. Natural gas is a very important fossil fuel because it is easy to transport through pipes. It is used in the form of CNG as fuel and generation of power.
Q35: Why is CNG called a clean fuel?
Ans. CNG is called a clean fuel because:
(i) It does not produce any pollution.
(ii) No residue is left after burning of CNG.
(iii) It burns completely in the air.
Q36: What are the harmful effects of using fossil fuels?
Ans. Harmful effects of burning fossil fuels are as following:
(i) Burning of fossil fuels cause air pollution.
(ii) They also cause global warming because they produce greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide on burning.
Q37: Make a list of various materials used by us in daily life and classify them as natural and man-made materials (Refer to Activity 5.1).
Ans.
Natural material | Man-made material |
1. Air | 1. Table |
2. Soil | 2. Chair |
3. Water | 3. Car |
4. Sunlight | 4. Bus |
5. CNG | 5. TV |
6. LPG | 6. Plastic |
7. Coal | 7. Rubber |
8. Petrol | 8. Food |
9. Fruits | 9. Bed |
10. Minerals | 10. Blackboard |
|
92 videos|419 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Coal and Petroleum
| 1. What is coal and how is it formed? |  |
| 2. How is coal mined and what are the different methods used? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of using coal as a source of energy? |  |
| 4. What are the environmental impacts of burning coal for energy production? |  |
| 5. How is petroleum formed and what are its uses? |  |

















