Structure of Human Heart - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Human Heart? |

|
| External Structure of Human Heart |

|
| Blood Vessels Present in Heart |

|
| Internal Structure of Human Heart |

|
| Working of Human Heart |

|
Explain about internal structure of heart?
Ref: https://edurev.in/question/568153/Explain-about-internal-structure-of-heart-
What is Human Heart?
The human heart is a vital organ that functions to pump blood throughout the body. It is a muscular organ located in the chest cavity between the lungs and is responsible for the circulation of oxygen and nutrients to all the cells of the body.
In this EduRev document of Class 10 Science, we will provide a detailed overview of the structure of the human heart.
External Structure of Human Heart
The external structure of the human heart refers to its physical appearance and location within the body. The heart is a conical-shaped muscular organ that is roughly the size of a closed fist. It is located within the thoracic cavity, between the two lungs, and is protected by the sternum in front and the spine at the back.
- Four Chambers of the Heart: The heart is divided into four chambers: the right atrium, the left atrium, the right ventricle, and the left ventricle. The atria are the two upper chambers of the heart and the ventricles are the two lower chambers. These chambers are separated by a thick muscular wall called the septum. The right side of the heart is responsible for pumping deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation, while the left side of the heart is responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
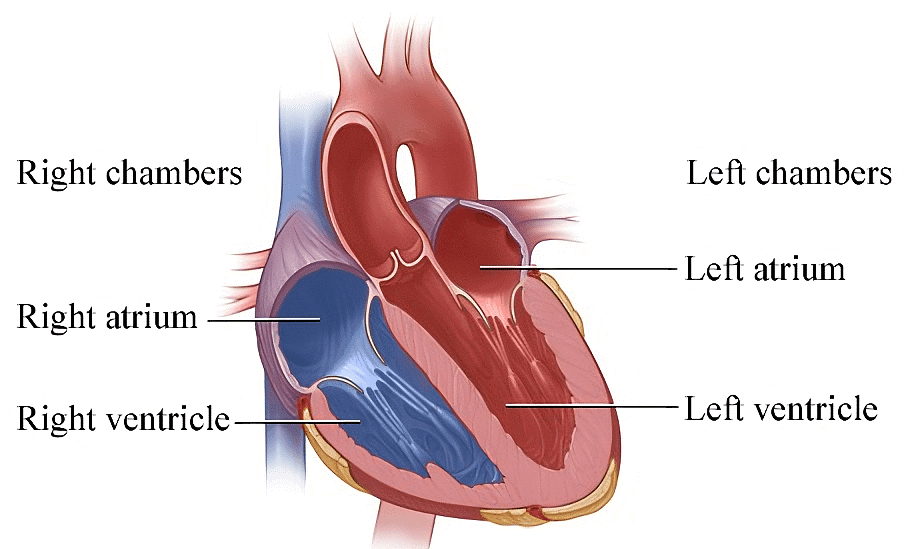 Four Chambers of Heart
Four Chambers of Heart
- Role of Pericardium: The heart is surrounded by a protective sac called the pericardium, which consists of two layers: the outer fibrous layer and the inner serous layer. The fibrous pericardium is a tough, inelastic sac that encloses the heart and attaches it to the surrounding structures, including the diaphragm and the sternum. The serous pericardium is a thin, double-layered membrane that covers the heart and forms a closed sac around it. The space between the two layers of the serous pericardium is called the pericardial cavity, which contains a small amount of fluid that lubricates the heart as it beats.
 Diagram of The Heart
Diagram of The Heart
Major Blood Vessels of Heart: The external structure of the heart also includes the major blood vessels that enter and exit the heart. The superior and inferior vena cava are two large veins that bring deoxygenated blood from the body into the right atrium. The pulmonary veins are four small veins that carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium. The pulmonary artery is a large artery that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs, where it is oxygenated. The aorta is the largest artery in the body and carries oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body.
Blood Vessels Present in Heart
The circulatory system of human beings comprises various components, including the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. The blood vessels present in the heart play a crucial role in the transportation of blood throughout the body.
 Blood Vessels
Blood Vessels
- Arteries: Arteries are responsible for carrying blood away from the heart and towards various organs of the body. They do this at a high pressure and transport only oxygenated blood, except for the pulmonary artery. Arteries are characterized by a narrow lumen, which means that they have a smaller space for blood flow, and they lack valves.
Veins: Veins, on the other hand, transport blood towards the heart from different organs of the body at a lower pressure. They carry only deoxygenated blood, except for the pulmonary vein. Veins have a wider lumen than arteries, allowing for more blood flow, and are equipped with valves to prevent the backward flow of blood.
Capillaries: Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels in the body and play a crucial role in exchanging gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as other substances like water and salts, between the blood and the surrounding tissues. They carry blood from the arteries to the veins and are characterized by their very narrow lumen, which enables efficient exchange of substances between the blood and the tissues. Unlike arteries and veins, capillaries do not have valves.
Internal Structure of Human Heart
- Atria: The two upper chambers of the heart are called the atria. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava, while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins. The atria contract together and push blood into the ventricles.
- Ventricles: The two lower chambers of the heart are called the ventricles. The right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery, while the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta. The ventricles have thicker walls than the atria because they need to pump blood out of the heart.
- Valves: The heart has four valves that ensure that blood flows in the correct direction. The atrioventricular valves (AV) are located between the atria and ventricles and prevent backflow of blood into the atria when the ventricles contract.
 The tricuspid valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the mitral valve is located on the left side of the heart. The semilunar valves (SL) are located between the ventricles and the arteries and prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles when they relax. The pulmonary valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the aortic valve is located on the left side of the heart.
The tricuspid valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the mitral valve is located on the left side of the heart. The semilunar valves (SL) are located between the ventricles and the arteries and prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles when they relax. The pulmonary valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the aortic valve is located on the left side of the heart. - Coronary arteries: The heart has its own blood supply through the coronary arteries. These arteries branch off from the aorta and supply blood to the heart muscle.
- Electrical conduction system: The heart has an electrical conduction system that controls the rhythm of the heartbeat. The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, is the natural pacemaker of the heart. It generates electrical impulses that spread throughout the atria, causing them to contract. The atrioventricular (AV) node is located between the atria and ventricles and delays the electrical impulses before they reach the ventricles. The bundle of His and Purkinje fibers then distribute the electrical impulses to the ventricles, causing them to contract.
Working of Human Heart
The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood to all parts of the body. It works tirelessly to ensure that oxygen and nutrients are delivered to the cells of the body, and waste products are removed. Here's how it works:
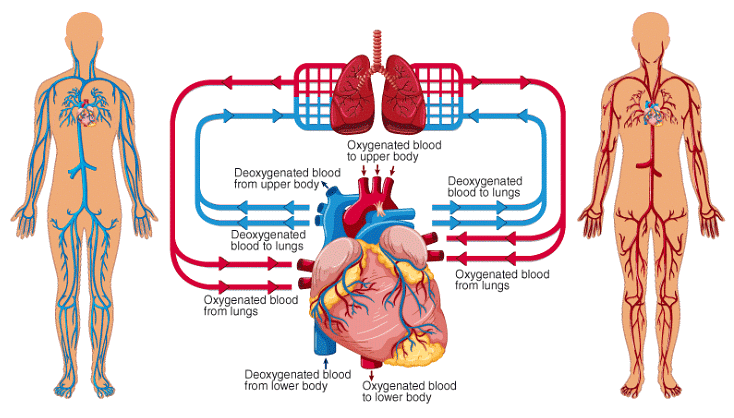
- Role of four chambers of heart: The heart is divided into four chambers - the right atrium, the left atrium, the right ventricle, and the left ventricle. Blood enters the heart through the two atria, which are the upper chambers. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body, while the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
- Pushing of Blood (Function of Atria and Ventricles): When the atria contract, they push the blood into the ventricles, which are the lower chambers of the heart. The right ventricle pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where it gets oxygenated. The left ventricle pumps the oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
- Conduction System of the Heart: The heart has a specialized network of cells called the conduction system, which helps regulate its rhythm. The sinoatrial node, also known as the pacemaker, sends out electrical signals that cause the heart muscle to contract and pump blood.
- Valves of the Heart: The heart has valves that open and close to ensure that blood flows in only one direction. The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle, while the mitral valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle. The pulmonary valve separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary artery, while the aortic valve separates the left ventricle from the aorta.
- Heartbeat and Rhythm: The heart works non-stop to ensure that the body receives a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients. It beats approximately 60 to 100 times per minute, depending on the person's age and level of physical activity.
If you want to make the most of your studies and get the grades you deserve, then EduRev is a perfect Choice!
FAQs on Structure of Human Heart - Class 10
| 1. What is the human heart? |  |
| 2. What is the external structure of the human heart? |  |
| 3. What are the blood vessels present in the heart? |  |
| 4. What is the internal structure of the human heart? |  |
| 5. How does the human heart work? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
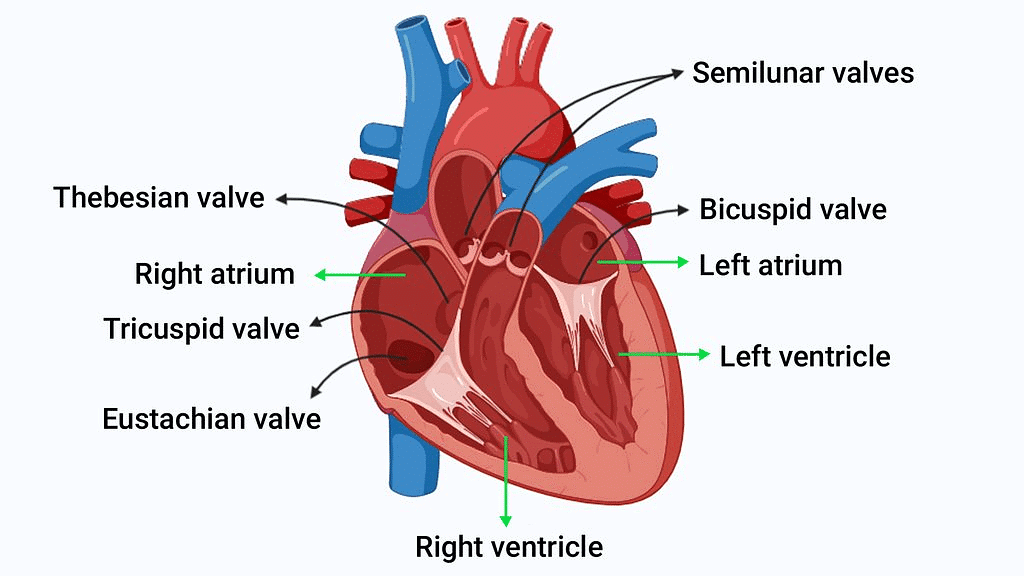 The tricuspid valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the mitral valve is located on the left side of the heart. The semilunar valves (SL) are located between the ventricles and the arteries and prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles when they relax. The pulmonary valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the aortic valve is located on the left side of the heart.
The tricuspid valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the mitral valve is located on the left side of the heart. The semilunar valves (SL) are located between the ventricles and the arteries and prevent backflow of blood into the ventricles when they relax. The pulmonary valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the aortic valve is located on the left side of the heart.

















