Atmospheric Circulation & Weather Systems - 1 Class 11 Geography
| Table of contents |

|
| Overview |

|
| Atmospheric Pressure |

|
| World Distribution of Sea Level Pressure |

|
| General circulation of the atmosphere |

|
Overview
Atmospheric circulation refers to the movement of air around the Earth driven by differences in temperature and pressure. This circulation influences weather patterns and the formation of weather systems. In the context of chaptr, understanding atmospheric circulation helps explain the Indian monsoon, which is crucial for agriculture and livelihoods across the country. The monsoon is influenced by seasonal changes in atmospheric pressure and wind patterns, bringing heavy rainfall to different parts of India at specific times of the year.
Atmospheric Pressure
- Air expands when heated and gets compressed when cooled. This results in variations in the atmospheric pressure.
- The result is that it causes the movement of air from high pressure to low pressure, setting the air in motion. air in horizontal motion is wind.
- Atmospheric pressure also determines when the air will rise or sink.
- The wind redistributes the heat and moisture across the planet, thereby, maintaining a constant temperature for the planet as a whole. The vertical rising of moist air cools it down to form the clouds and bring precipitation.
- The weight of a column of air contained in a unit area from the mean sea level to the top of the atmosphere is called the atmospheric pressure.
- The atmospheric pressure is expressed in units of milibar. At sea level the average atmospheric pressure is 1,013.2 milibar. Due to gravity the air at the surface is denser and hence has higher pressure.
- Air pressure is measured with the help of a mercurybarometer or the aneroidbarometer
- The pressure decreases with height.
- At any elevation it varies from place to place and its variation is the primary cause of air motion, i.e. wind which moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.
Vertical Variation of Pressure
- In the lower atmosphere the pressure decreases rapidly with height. The decrease amounts to about 1 mb for each 10 m increase in elevation. It does not always decrease at the same rate.
- The vertical pressure gradient force is much larger than that of the horizontal pressure gradient. But, it is generally balanced by a nearly equal but opposite gravitational force. Hence, we do not experience strong upward winds.
Horizontal Distribution of Pressure
- Small differences in pressure are highly significant in terms of the wind direction and velocity.
- Horizontal distribution of pressure is studied by drawing isobars at constant levels.
- Isobars are lines connecting places having equal pressure. In order to eliminate the effect of altitude on pressure, it is measured at any station after being reduced to sea level for purposes of comparison.
- Low-pressure system is enclosed by one or more isobars with the lowest pressure in the centre.
- High-pressure system is also enclosed by one or more isobars with the highest pressure in the centre.
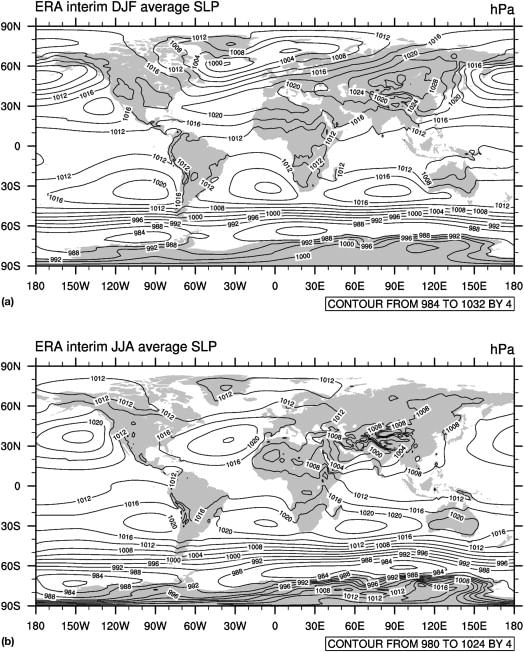
World Distribution of Sea Level Pressure
- Near the equator the sea level pressure is low and the area is known as equatorial low.
- Along 30° N and 30° S are found the high-pressure areas known as the subtropical highs.
- Further pole wards along 60° N and 60° S, the low-pressure belts are termed as the sub polar lows.
- Near the poles the pressure is high and it is known as the polar high.
- These pressure belts are not permanent in nature. They oscillate with the apparent movement of the sun.
- In the northern hemisphere in winter they move southwards and in the summer northwards.
Forces Affecting the Velocity and Direction of Wind
- The air is set in motion due to the differences in atmospheric pressure.
- The air in motion is called wind. The wind blows from high pressure to low pressure, addition, rotation of the earth also affects the wind movement.
- The force exerted by the rotation of the earth is known as the Coriolis force.
- The horizontal winds near the earth surface respond to the combined effect of three forces - the pressure gradient force, the frictional force and the Coriolis force. In addition, the gravitational force acts downward.
Pressure Gradient Force
- The differences in atmospheric pressure produces a force.
- The rate of change of pressure with respect to distance is the pressure gradient.
- The pressure gradient is strong where the isobars are close to each other and is weak where the isobars are apart.
Frictional Force
- It affects the speed of the wind.
- It is greatest at the surface and its influence generally extends up to an elevation of 1 - 3 km. Over the sea surface the friction is minimal.
Coriolis Force
- The rotation of the earth about its axis affects the direction of the wind. This force is called the Coriolis force after the French physicist who described it in 1844.
- It deflects the wind to the right direction in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere.
- The deflection is more when the wind velocity is high.
- The Coriolis force is directly proportional to the angle of latitude. It is maximum at the poles and is absent at the equator.
- The Coriolis force acts perpendicular to the pressure gradient force. The pressure gradient force is perpendicular to an isobar.
- The higher the pressure gradient force, the more is the velocity of the wind and the larger is the deflection in the direction of wind.
- As a result of these two forces operating perpendicular to each other, in the low-pressure areas the wind blows around it.
- At the equator, the Coriolis force is zero and the wind blows perpendicular to the isobars.
- The low pressure gets filled instead of getting intensified. That is the reason why tropical cyclones are not formed near the equator.
Pressure and Wind
- The winds in the upper atmosphere, 2 - 3 km above the surface, are free from frictional effect of the surface and are controlled mainly by the pressure gradient and the Coriolis force.
- When isobars are straight and when there is no friction, the pressure gradient force is balanced by the Coriolis force and the resultant wind blows parallel to the isobar. This wind is known as the geostrophic wind (Figure 10.4).
- The wind circulation around a low is called cyclonic circulation.
- Around a high it is called anti-cyclonic circulation. The direction of winds around such systems changes according to their location in different hemispheres.
- The wind circulation at the earth’s surface around low and high on many occasions is closely related to the wind circulation at higher level. Generally, over low pressure area the air will converge and rise.
- Over high pressure area the air will subside from above and diverge at the surface (Figure10.5).
- Apart from convergence, some eddies, convection currents, orographic uplift and uplift along fronts cause the rising of air, which is essential for the formation of clouds and precipitation.
General circulation of the atmosphere
- The pattern of planetary winds largely depends on :
- latitudinal variation of atmospheric heating
- emergence of pressure belts
- migration of belts following apparent path of the sun
- distribution of continents and oceans
- rotation of earth
- The pattern of the movement of the planetary winds is called the general circulation of the atmosphere.
- The general circulation of the atmosphere also sets in motion the ocean water circulation which influences the earth's climate.
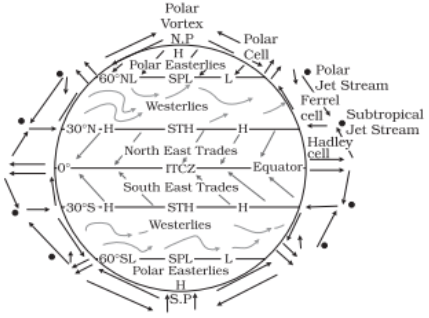
- The air at the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) rises because of convection caused by high insolation and a low pressure is created.
- The winds from the tropics converge at this low pressure zone. The converged air rises along with the convective cell. It reaches the top of the troposphere up to an altitude of 14 km. and moves towards the poles. This causes accumulation of air at about 30o N and S.
- Another reason for sinking is the cooling of air when it reaches 30o N and S latitudes. Down below near the land surface the air flows towards the equator as the easterlies. The easterlies from either side of the equator converge in the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Such circulations from the surface upwards and vice-versa are called cells. Such a cell in the tropics is called Hadley Cell.
- In the middle latitudes the circulation is that of sinking cold air that comes from the poles and the rising warm air that blows from the subtropical high.
- At the surface these winds are called westerlies and the cell is known as the Ferrel cell.
- At polar latitudes the cold dense air subsides near the poles and blows towards middle latitudes as the polar easterlies. This cell is called the polar cell.
- These three cells set the pattern for the general circulation of the atmosphere. The transfer of heat energy from lower latitudes to higher latitudes maintains the general circulation.
- The general circulation of the atmosphere also affects the oceans. The large-scale winds of the atmosphere initiate large and slow moving currents of the ocean. Oceans in turn provide input of energy and water vapour into the air. These interactions take place rather slowly over a large part of the ocean.
General Atmospheric Circulation and its Effects on Oceans
- Warming and cooling of the Pacific Ocean is most important in terms of general atmospheric circulation. The warm water of the central Pacific Ocean slowly drifts towards South American coast and replaces the cool Peruvian current.
- Such appearance of warm water off the coast of Peru is known as the El Nino.
- The El Nino event is closely associated with the pressure changes in the Central Pacific and Australia. This change in pressure condition over Pacific is known as the southern oscillation.
- The combined phenomenon of southern oscillation and El Nino is known as ENSO.
- In the years when the ENSO is strong, large-scale variations in weather occur over the world.
- The arid west coast of South America receives heavy rainfall, drought occurs in Australia and sometimes in India and floods in China. This phenomenon is closely monitored and is used for long range forecasting in major parts of the world.
Seasonal Winds:
- Seasonal wind patterns change based on how hot different areas get and how air moves around because of it.
- This change is really noticeable during monsoons in southeast Asia.
- The book you are studying talks about this in detail.
- Wind patterns change throughout the year because some places get hotter than others and this affects how air moves.
- In monsoons in southeast Asia, this change is very strong.
Local Winds:
When parts of the Earth heat up or cool down at different rates every day or every year, it can create winds that are specific to certain areas.
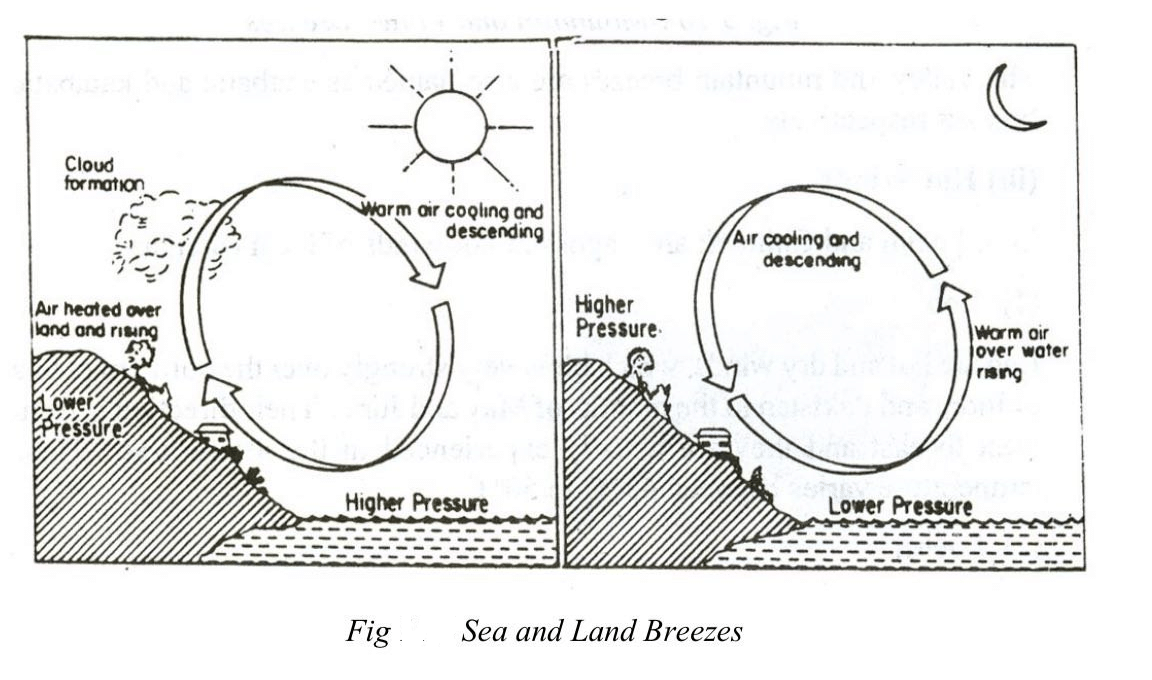
Land and Sea Breezes:
- During the day, land heats up faster than the sea.
- This makes the air over the land rise, creating low pressure, while the sea remains cooler with higher pressure.
- This pressure difference causes wind to blow from the sea to the land, known as sea breeze.
- At night, the land cools faster than the sea, creating a pressure difference that results in wind blowing from the land to the sea, known as land breeze.
Mountain and Valley Winds:
- Valley Breeze and Mountain Wind: In hilly areas, during the day, the slopes heat up, causing air to rise up the mountain slopes. This creates a gap that is filled by air moving up the valley, known as the valley breeze. At night, the slopes cool down, leading to dense air descending into the valley as the mountain wind.
- Katabatic Wind: Cold air from high plateaus and ice fields flows down into the valley, known as katabatic wind.
- Leeward Warm Wind: On the leeward side of mountains, warm winds can occur. As moist air crosses the mountains, it cools, condenses, and precipitates. When it descends on the leeward side, the dry air warms up due to an adiabatic process. This warm, dry air can melt snow quickly.
Air Masses:
An air mass is a large body of air that stays over a uniform area for a long time, taking on the characteristics of that region in terms of temperature and humidity. It has little variation in temperature and moisture horizontally.
Air masses are classified based on their source regions. There are five main source regions which determine the type of air mass: warm tropical and subtropical oceans, subtropical hot deserts, relatively cold high-latitude oceans, very cold snow-covered continents in high latitudes, and permanently ice-covered continents in the Arctic and Antarctica.
Based on the source regions, different types of air masses are recognized: Maritime tropical (mT), Continental tropical (cT), Maritime polar (mP), Continental polar (cP), and Continental arctic (cA). Tropical air masses are warm, while polar air masses are cold.
Fronts:
- When two different air masses meet, the boundary zone is called a front.
- Frontogenesis is the process of front formation.
- There are four types of fronts: Cold, Warm, Stationary, and Occluded.
- Cold front occurs when cold air moves towards warm air, creating a contact zone.
- Warm front occurs when warm air moves towards cold air, forming a contact zone.
- Stationary front remains in place without much movement.
- Occluded front happens when an air mass is fully lifted above the surface.
- Fronts occur in middle latitudes and have steep temperature and pressure gradients.
- They lead to abrupt changes in temperature, cloud formation, and precipitation.
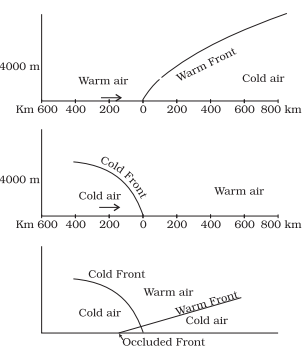
Vertical Sections of : (a) Warm Front; (b) Cold Front; (c) Occluded Front
Extra Tropical Cyclones:
- These cyclones develop in mid and high latitudes outside the tropics.
- They form along the polar front, characterized by warm air moving north and cold air moving south.
- When pressure drops, a cyclonic circulation begins, leading to an extra tropical cyclone.
- A well-developed cyclone has a warm front, cold front, and pockets of warm air.
- Warm air glides over cold air, creating clouds and precipitation.
- The cold front pushes warm air up, forming cumulus clouds.
- Eventually, the cold front overtakes the warm front, leading to occlusion and cyclone dissipation.
- Extra tropical cyclones differ from tropical cyclones in terms of frontal systems, origin, area coverage, and movement direction.
- Extra tropical cyclones are larger, cover both land and sea, and move from west to east.
- Tropical cyclones originate over seas, move from east to west, and are more destructive
Tropical Cyclones:
Tropical tag cyclones are powerful storms that form over warm ocean waters in tropical regions. They bring destructive winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surges, posing significant threats to coastal areas.
- Naming: These storms are called Cyclones in the Indian Ocean, Hurricanes in the Atlantic, Typhoons in the Western Pacific and South China Sea, and Willy-willies in Western Australia.
- Formation Conditions: Tropical cyclones require warm ocean temperatures above 27°C, the Coriolis force, stable vertical wind speed, a pre-existing low-pressure area, and upper-level divergence to form and strengthen.
- Energy Source: The storm's energy comes from condensation in towering cumulonimbus clouds, fueled by moisture from the warm ocean. When it makes landfall, the storm weakens due to lack of moisture supply.
- Landfall: The point where a tropical cyclone hits land is known as its landfall. Cyclones crossing 20°N latitude often recurve and tend to be more destructive.
- Structure: A mature tropical cyclone features a calm center called the eye, surrounded by the eye wall where the strongest winds and heaviest rains occur. The storm's diameter can range from 150 to 250 km.
- Movement: These storms move slowly at about 300-500 km per day and cover a large area, with diameters ranging from 600 to 1200 km over oceans like the Bay of Bengal, Arabian Sea, and Indian Ocean.
- Impact: Tropical cyclones create storm surges that flood coastal low-lying areas, causing significant damage before dissipating over land.
Introduction: Thunderstorms and tornadoes are extreme weather events that can cause significant damage in a short period. They are both forms of severe local storms that occur under specific conditions.
Thunderstorms and Tornadoes
Thunderstorms:
- Thunderstorms are short-lived weather phenomena that happen in small areas but can be intense.
- They are triggered by strong upward movement of hot, moist air on warm days.
- A thunderstorm is identified by a large cumulonimbus cloud that produces thunder and lightning.
- When these clouds reach high altitudes with sub-zero temperatures, they can produce hailstorms.
- In cases of low moisture, a thunderstorm can lead to dust storms.
- Key feature: Thunderstorms have a powerful updraft of warm air that causes clouds to grow and release precipitation.
- The precipitation eventually falls due to a downdraft of cool air.
Tornadoes:
- Tornadoes are violent windstorms that can cause massive destruction.
- They are often a result of severe thunderstorms and are characterized by spiraling winds.
- Tornadoes have a low-pressure center and can be as powerful as an elephant's trunk in force.
- They typically occur in regions with middle latitudes and are known as waterspouts when they form over the sea.
Significance:
- These storms showcase how the atmosphere adjusts to changes in energy distribution.
- Potential and heat energies in the atmosphere transform into kinetic energy during these events.
- After the storm, the atmosphere stabilizes as the energy is released.
|
70 videos|339 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Atmospheric Circulation & Weather Systems - 1 Class 11 Geography
| 1. What is atmospheric pressure and how does it affect weather patterns? |  |
| 2. How is sea level pressure distributed around the world? |  |
| 3. What is the general circulation of the atmosphere and how does it impact weather systems? |  |
| 4. How does atmospheric circulation affect climate patterns on a global scale? |  |
| 5. What are some key factors that influence atmospheric pressure and wind patterns? |  |
















