Parliamentary Committees & Comptroller And Auditor General | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Recent News
- The Parliamentary Committee on Subordinate Legislation recently convened to evaluate the fulfillment of legislative responsibilities and adherence to Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) standards.
- This committee is tasked with scrutinizing and presenting reports to the House on the proper exercise of authorities granted by the Constitution or delegated by Parliament to formulate regulations, rules, sub-rules, and bye-laws.
- Comprising 15 members from both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, individuals are nominated by the Speaker or Chairman as appropriate, with ministers ineligible to serve on this committee.
- The Committee's Chairman is selected from its members by the Speaker or Chairman, and in discussions, the Chairman holds only a casting vote.
Types of Parliamentary Committees
There exist two distinct types of committees, namely the AD HOC Committee and the Standing Committee. It is essential to delve into a detailed understanding of each.
An AD HOC Committee and a Standing Committee are the two primary categories of committees. Gaining comprehensive knowledge about each is crucial for a nuanced understanding.
Ad Hoc Committees
Ad hoc Committees are established periodically to investigate specific matters. They are not explicitly designated in the Rules of Procedure and disband once their designated task is concluded and a report is submitted.
These committees are temporary and fall into two main categories:
- Inquiry Committees: These are created by either house or the speaker to conduct thorough inquiries or reports on specific subjects. Examples include the joint committee on the maintenance of heritage and the committee on the violation of protocol norms.
- Advisory Committees: Appointed to provide reports on particular bills.
Explore the significant committees in the Indian Constituent Assembly for competitive exams here.
Standing Committees
Various types of standing committees exist, encompassing financial committees, departmental standing committees, committees for inquiry, scrutiny and control, housekeeping committees, and service committees. In the Indian Parliament, six distinct types of standing committees are recognized and outlined below.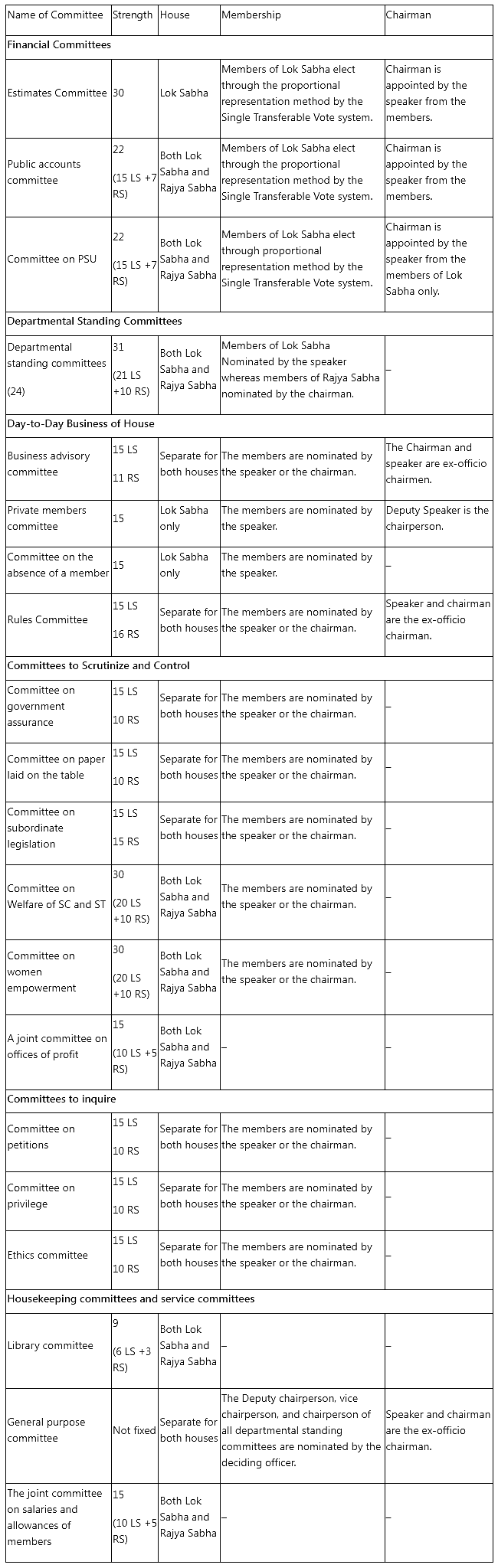
Functions of Parliamentary Committees
Financial Committees
- The Public Accounts Committee scrutinizes the annual reports of the government and the reports of the Comptroller and Auditor General, which the President presents to Parliament.
- The Estimates Committee evaluates the government's proposed budget expenditure forecasts and provides recommendations for potential savings in government expenditures.
- The Committee on Public Undertakings examines the reports and accounts of public undertakings.
Departmental Standing Committee
Day to Day Business of House:
- The Business Advisory Committee manages the schedule of the House.
- The Private Members' Committee categorizes legislation and allocates time for debates on private member bills and resolutions.
- The Rules Committee proposes changes to the House rules when necessary.
- The Committee on Members' Absences examines all requests for leave submitted by members of the houses.
Committee to Scrutinize and Control
- The Committee on Government Assurance evaluates the implementation of promises, assurances, or undertakings made by ministers in the Lok Sabha. With 15 members in the Lok Sabha and 10 in the Rajya Sabha, it examines the extent to which these commitments have been fulfilled.
- The Committee on Subordinate Legislation scrutinizes whether the executive branch is appropriately exercising its powers to formulate regulations, rules, sub-rules, and bye-laws delegated by Parliament or the Constitution.
- The Committee for the Welfare of SCs and STs, comprised of 30 members (20 in the Lok Sabha and 10 in the Rajya Sabha), receives reports from the National Commission for SCs and the National Commission for STs.
- The Committee on Paper Laid on the Table, with 15 members in the Lok Sabha and 10 in the Rajya Sabha, assesses the validity and conformity of papers presented by ministers with the constitutional stipulations.
- The Committee on Women’s Empowerment reviews the report of the National Commission on Women.
- The Joint Committee on Office of Profit examines the composition and nature of committees and other bodies appointed by federal, state, and union territory administrations. It provides recommendations on whether individuals serving on these bodies should be disqualified from running for Parliament.
Committee to inquire:
- The Committee on Petitions reviews legislative petitions or matters of significant public concern.
- The Committee on Privileges, with a semi-judicial aspect, investigates and suggests appropriate actions if a member of the house breaches the code of conduct. It comprises 15 Lok Sabha members and ten Rajya Sabha members.
- The Ethics Committee probes instances of misbehavior or indiscipline by a member of the House of Representatives and imposes necessary sanctions.
House-keeping Committees and Service Committees
- The General Purposes Committee oversees matters that fall outside the purview of other legislative committees.
- The Library Committee is responsible for the management of the library and its associated facilities in the houses.
Consultative Committees:
- These committees are affiliated with different government departments or ministries.
- Ministers and committee members convene informally to deliberate on government policies, programs, and their implementation.
- The appointment of these committees falls under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Parliamentary Affairs.
- The committee's composition can range from a minimum of 10 members to a maximum of 30.
Consultative Committees:
- These committees are formed either through a resolution passed by both houses or upon the request of the speaker or chairman for a report on a specific subject.
- Functioning as bill select or joint committees, their mandate involves investigating and reporting on particular bills.
- These committees furnish details and insights regarding specific bills.
List of Parliamentary Committees
Standing Committees in Loksabha (Select)
- Business Advisory Committee
- Committee for General Purposes
- Committee on Government Assurances
- House Affairs Committee
- Committee for the Library
- Committee on Rules
- Committee on Members' Absence from House Sessions
Standing Committees in Rajya Sabha (Select)
- Committee on Petitions
- Committee of Privileges
- Ethics Committee.
- Business Advisory Committee
- Committee on Government Assurances
- Committee on Subordinate Legislation
Department Related Standing Committees (LS)
- Committee on External Affairs
- Committee on Finance
- Committee on Food, Consumer Affairs & Public Distribution
- Committee on Information Technology
- Committee on Petroleum & Natural Gas
- Committee on Social Justice & Empowerment
- Committee on Chemicals & Fertilizers
Department Related Standing Committees (RS)
- Committee on Industry
- Committee on Personnel, Public Grievances, Law and Justice
- Committee on Science & Technology, Environment & Forests
- Committee on Transport, Tourism and Culture
- Committee on Commerce
- Committee on Health and Family Welfare
- Committee on Home Affairs
- Committee on Human Resource Development
Joint Parliamentary Committees (JPCs)
- Joint Parliamentary Committees (JPCs) can be formed to examine a specific bill, such as the joint committee to discuss legislation, or to investigate financial irregularities. These committees’ members are selected from both Houses.
- A JPC may seek evidence from experts, governmental entities, associations, individuals, or interested parties on its own initiative or upon their request. If a witness fails to appear before a JPC in answer to a summons, he is in contempt of the House.
- JPCs are a type of panel that can be “appointed by the House or the Speaker or the Presiding Officers of both Houses as the case may be from time to time on an ad hoc basis as and when appropriate for a particular purpose.”
- Committee on the Welfare of Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- Committee on Offices of Profit.
- Committee on Empowerment of Women.
- Library Committee.
- Committee on Food Management in Parliament House Complex.
- Committee on Installation of Portraits/Statues of National Leaders and Parliamentarians in the Parliament House Complex.
- Committee on Security Matters in Parliament House Complex.
Regulation of Parliament by itself
- Parliamentary Committees are constituted to deal with many sorts of issues that the parliament cannot deal with owing to their volume.
- They play an important role not only in law-making but also in the day-to-day work of the House.
- The parliament executes all of its critical tasks through discussions, which must be meaningful and orderly in order for the Parliament’s functions to be carried out smoothly and with dignity.
- The real Constitution has set special provisions to ensure that commerce runs smoothly.
- The assembly’s directing official is the last expert on matters pertaining to council control.
- Another method for controlling member behavior.
Importance of Parliamentary Committees in Indian democracy
- Parliament engages in discussions on intricate issues that often require technical expertise for a thorough understanding.
- Committees play a crucial role in facilitating this understanding by providing a platform for Members to engage with domain experts and government officials during their deliberations.
- Prior to finalizing their reports, Committees actively seek input from various stakeholders, including the National Commission for Women, medical professionals, and government officials.
- Moreover, Committees serve as a forum for political parties to find common ground. While parliamentary sessions are televised, with MPs generally adhering to their party positions, Committees conduct closed-door sessions where open questioning and discussions take place, allowing for a more candid exploration of issues and the potential for consensus.
- The primary aim of parliamentary committees is to foster open dialogue among members, enabling the development of a cohesive framework for addressing pertinent issues.
Way Forward:
- Establishing New Committees: Given the growing intricacy of economic and technological matters, the creation of fresh legislative committees becomes imperative.
- One such example is the Standing Committee on National Economy, tasked with conducting economic analyses and availing resources for advisory expertise, data collection, and research.
- A Standing Constitution Committee will scrutinize constitutional amendment bills before their introduction in Parliament.
- To streamline legislative plans, the Legislative Standing Committee will monitor and coordinate them.
- Crucial reports from all committees should be given due consideration in Parliament, particularly in instances of disagreement between the Committee and the administration.
- The ideas put forth by the Public Accounts Committee should carry significant weight, recognizing them as the country's "financial conscience-keepers."
- As per the National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (NCRWC), the periodic review of DRSCs is crucial. This ensures that committees that have become obsolete can be replaced with new, relevant ones.
- Additionally, revising the rules of procedure in both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha is essential. This would ensure that all key bills are referred to DRSCs, which would then oversee the Committee's second reading stage.
- In any democratic organization, deliberation, debate, and reconsideration are fundamental functions of Parliament. Given the complexity of the issues Parliament deals with, technical knowledge is vital for a comprehensive understanding. Parliamentary committees enable Members of Parliament to engage with domain experts and government officials during their research.
- For the preservation of parliamentary democracy, rather than circumventing parliamentary committees, it is imperative to bolster their role and influence.
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Parliamentary Committees & Comptroller And Auditor General - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are parliamentary committees? |  |
| 2. What is the role of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) in parliamentary committees? |  |
| 3. How do parliamentary committees contribute to bank exams? |  |
| 4. What are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) about parliamentary committees and the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)? |  |
| 5. How can one prepare for bank exams with a focus on parliamentary committees and the role of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)? |  |






















