Multipurpose Projects | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multipurpose River Valley Projects |

|
| Various Multipurpose River Valley Projects of India |

|
| Advantages of Multipurpose Projects |

|
| Disadvantages of Multipurpose Projects |

|
Multipurpose River Valley Projects
These projects aim to develop irrigation for agriculture and generate electricity by building dams. Originally, dams were built mainly to store rainwater and prevent flooding. However, now they serve multiple purposes. Modern multipurpose river valley projects are designed for various uses, including:
Modern multipurpose river valley projects are designed for various uses, including:
- Irrigation
- Hydropower generation
- Drinking and industrial water supply
- Flood control
- Navigation
Various Multipurpose River Valley Projects of India
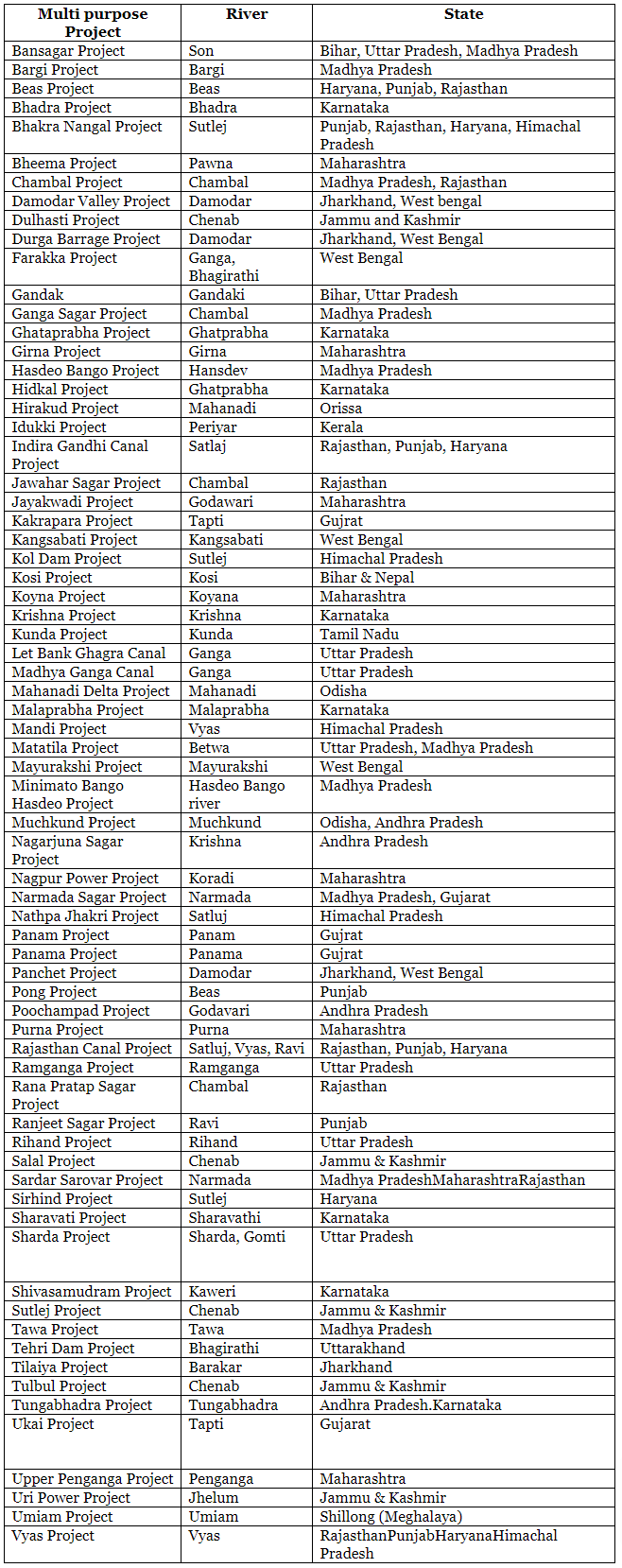
Chambal Project:
- The Chambal Valley Project aims to control soil erosion and manage the Chambal River, which flows through Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- The primary objective of the project is to regulate the river flow from northwest Madhya Pradesh.
- The project includes the construction of several dams and power plants in different stages:
- First Stage: Gandhi Sagar Dam, with a 115 MW power plant, and the Kota Barrage.
- Second Stage: Rana Pratap Sagar Dam, featuring a 172 MW power plant.
- Third Stage: Jawahar Sagar Dam and a 99 MW power plant.
- Once completed, the project will generate a total of 386 Megawatts of electricity.
Damodar Valley Project:
- The Damodar Valley Project is a multipurpose initiative aimed at promoting the development of West Bengal and Jharkhand through irrigation, flood management, and electricity generation.
- Established in 1948, the project is managed by the Damodar Valley Corporation and is one of India’s earliest multipurpose ventures.
- The project has the potential to irrigate 5.51 lakh hectares and has an installed power generation capacity of 1181 Megawatts.
- It is modeled after the American Tennessee Valley Authority.
Hirakund Dam:
- The Hirakund Dam is located on the Mahanadi River near Hirakud in Sambalpur, Odisha.
- At 4801.2 meters, it is the longest dam in the world.
- The dam primarily serves to control floods and irrigate the coastal plains of Odisha upstream of the Mahanadi River.
- Additionally, it has a power generation capacity of 27.2 MW.
Nagarjuna Sagar Project
- The Nagarjuna Sagar Project, initiated by the Andhra Pradesh government, aims to utilize water from the Krishna River.
- The project was inaugurated on August 4, 1967, and is situated in the Nalgonda district.
- The dam stands 92 meters high and stretches 1450 meters in length.
- Once completed, the project is expected to irrigate approximately 8.95 lakh hectares of land.
Ranjit Sagar Dam:
- Completed in 2001, the Ranjit Sagar Dam is part of a hydroelectric project by the Punjab state government.
- Also known as the Thein Dam, it is built on the Ravi River.
- The dam is situated about 24 kilometers upstream of Madhopur Headworks and 600 MW of power generation capacity.
Project Kakrapara:
- Project Kakrapara is located 80 km upstream of Surat, Gujarat, on the Tapti River.
- The project involves the construction of a weir that is 14 meters high and 621 meters long.
- Completed in 1963, Project Kakrapara is situated in the Kakrapara area of Surat district.
Bhakra Nangal Initiative:
- The Bhakra Nangal Initiative is a collaboration between the states of Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan.
- It is the largest multipurpose river valley project in India, featuring a gravity dam on the Sutlej River at Bhakra.
- The dam is 518 meters long and 226 meters high.
- The project’s canal system irrigates 14.8 lakh hectares of land and generates 1204 Megawatts of electricity.
Project Koyna:
- Project Koyna, managed by the Maharashtra State Electricity Board, is the largest completed hydroelectric power project in India.
- With an overall generation capacity of 1,960 MW, the project includes four dams, with the Koyna River dam being the largest.
- The project involves the construction of a dam that is 208 feet high.
Farakka Barrage:
- The Farakka Barrage system consists of two barrages: one across the Ganga River at Farakka and another across the Bhagirathi River at Jangipur.
- It includes a 39 km long feeder canal that diverts water from the Ganga at Farakka to the Bhagirathi below the Jangipur Barrage.
- One of the main connection lines crosses the Farakka barrage via a road-rail bridge.
- The primary purpose of the Farakka barrage is to protect and maintain the Kolkata port by improving the navigability of the Hooghly River and reducing silt buildup at the port.
Canal Indira Gandhi Canal:
- The Indira Gandhi Canal is one of the largest irrigation projects in India, originally initiated as the Rajasthan Canal in 1958.
- The project aims to provide irrigation to the northwestern region of Rajasthan, which is part of the Thar Desert.
- The canal system includes a 215 km Rajasthan feeder canal, drawing water from the Pong dam, and a 445 km Rajasthan Main Canal, which spans the entire state of Rajasthan.
- The project aims to irrigate 14.5 lakh hectares of land.
Project Rihand:
- Project Rihand involves the construction of a concrete gravity dam across the Rihand River at Sonbhadra, Uttar Pradesh.
- The project includes essential transmission infrastructure and a power plant located in Pipri.
- The installed capacity of Project Rihand is 300 Megawatts.
Tungabhadra Hydroelectric Project:
- The Tungabhadra Hydroelectric Project is a multipurpose dam situated in the Ballari district of Karnataka, across the Tungabhadra River.
- The dam is used for flood control, energy production, and irrigation.
- The reservoir has a storage capacity of 101 TMC and a catchment area of 28000 square kilometers.
- The dam is 49.5 meters tall and has an installed power generation capacity of 72 MW.
Pong Dam:
- The Pong Dam is a 116-meter-high dam located on the Beas River in the Dhaoladhar Mountains near Pong village in Himachal Pradesh.
- The dam primarily serves irrigation purposes in Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan, covering over 21 lakh hectares.
- The Hydroelectric Power (HEP) project at the Beas complex has a total installed capacity of 1020 MW.
Nizamuddin Sagar:
- The Nizamuddin Sagar project is an irrigation and hydroelectric power project located on the Manjra River in Nizamabad, Andhra Pradesh.
- The project supplies water to Nizamabad and Hyderabad and was built in 1923 by Nizam-Ul-Mulk, the ruler of the former Nizam empire.
- The dam features a brick structure with a motorable road that is fourteen feet wide, making it a popular tourist destination.
Advantages of Multipurpose Projects
- Power Generation: Multipurpose river projects generate cheap and clean energy, contributing significantly to the power supply. For instance, they produced over 30,000 MW of power, as noted in a 2005-2006 economic survey.
- Flood Prevention: These projects help prevent flooding by storing water and regulating its flow. They have transformed problematic rivers, like the Kosi, into manageable waterways, protecting soil and reducing water flow.
- Irrigation: During dry seasons, these projects provide irrigation to agricultural areas through a network of canals, aiding in the cultivation of previously arid lands.
- Afforestation: Trees are deliberately planted around reservoirs, supporting wildlife conservation and preserving natural habitats.
- Inland Water Navigation: These projects facilitate cost-effective inland water navigation, allowing for the transportation of large goods via principal rivers or canals.
- Fisheries: The projects create ideal conditions for fish breeding, promoting the growth of specific fish populations.
- Tourism: Well-planned multipurpose projects become major tourist attractions, boosting local tourism.
Disadvantages of Multipurpose Projects
- Loss of Fertile Land: River water often submerges fertile agricultural land, impacting food production.
- Environmental Degradation: Forestland is either cleared or flooded, causing significant harm to the environment and biodiversity.
- Displacement of People: Large-scale projects displace numerous individuals, forcing them to vacate their homes and properties.
- Dam Siltation: The accumulation of silt reduces the lifespan and efficiency of the dam, impacting its functionality.
- Induced Seismic Activity: Complex and large-scale projects may trigger minor earthquakes due to changes in land and water pressure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, multipurpose river projects in India offer a range of benefits, including power generation, flood control, irrigation, and tourism. However, they also come with significant challenges such as environmental degradation and displacement of communities. To ensure the success of these projects, it is crucial to involve all stakeholders in the planning process and address their concerns effectively.
|
264 videos|875 docs|232 tests
|
FAQs on Multipurpose Projects - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are multipurpose projects? |  |
| 2. How do multipurpose projects contribute to economic development? |  |
| 3. What are the environmental impacts of multipurpose projects? |  |
| 4. How are multipurpose projects managed and operated? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of successful multipurpose projects? |  |
















