Soaps & Detergents, Paints | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Heavy Metal Soaps (Metallic Soaps) |

|
| Detergents |

|
| Paints |

|
| Types of Paints |

|
Introduction
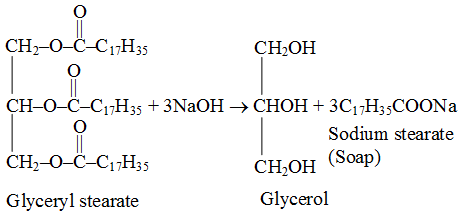
A soap is actually, a specific type of salt, the hydrogen alone of the fatty acid being replaced by a metal, which in common soaps is usually sodium. A typical commercial cleaning soap is prepared by reacting sodium hydroxide with a fatty acid. The lower the hydrogen content of the acid, the thinner the soap. The by-product of the reaction is glycerol. Many different carboxyl-containing substances are used, including, vegetable and animal oils, and fats, (stearic, palmitic, and oleic acids). Transparent soaps are made from decolourized fats.
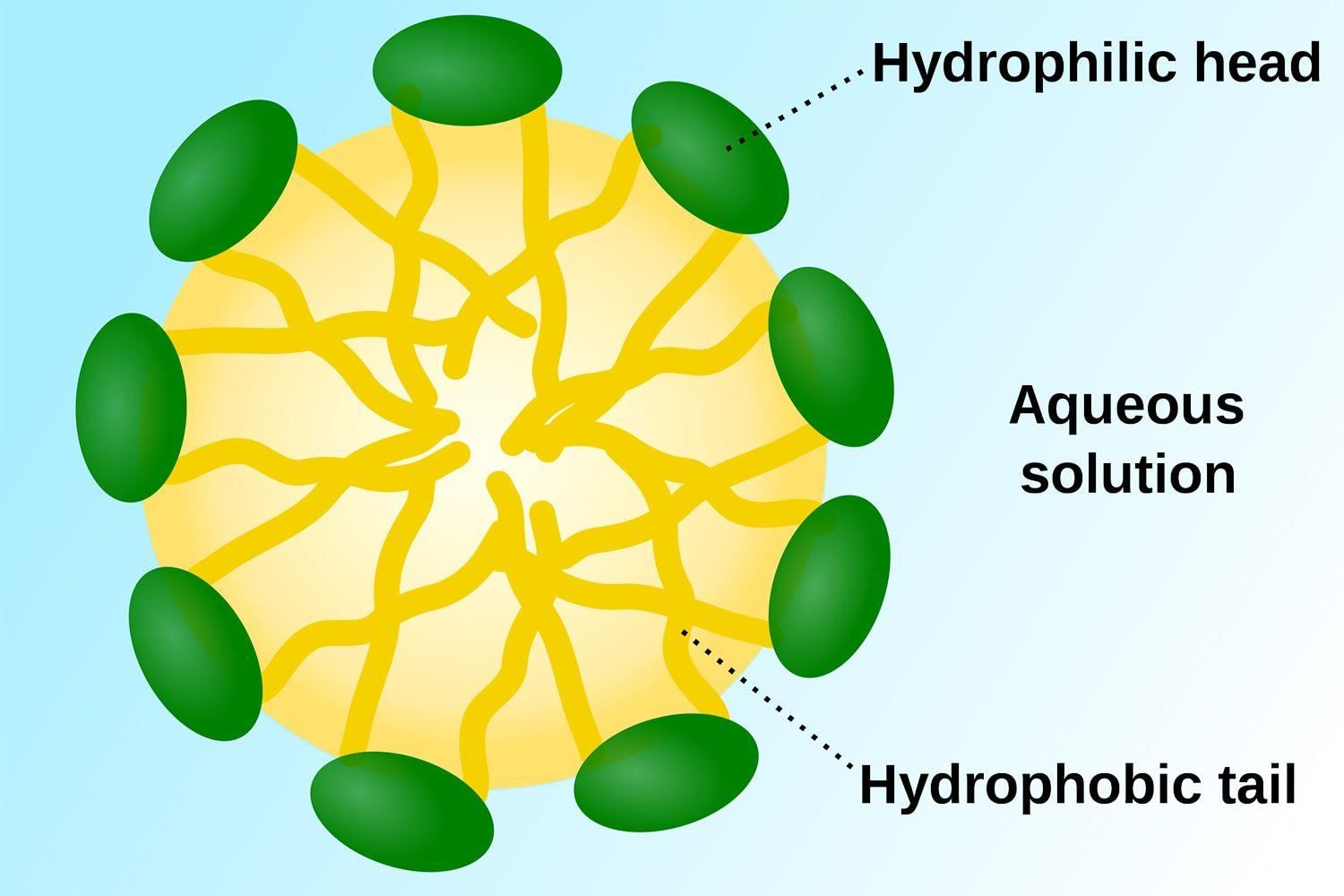 How Soap Works
How Soap Works
Heavy Metal Soaps (Metallic Soaps)
- These are soaps formed by metals heavier than sodium ,aluminium, calcium, cobalt, lead, zinc.
- These particular soaps do not dissolve in water. They are employed in the formulation of lubricating greases as thickeners and are also utilized in paints to serve as drying agents and agents that reduce gloss.
 Metallic Soaps
Metallic Soaps
- A detergent is a substance that diminishes the surface tension of water. It is typically a surfactant that accumulates at the interface between oil and water, facilitating the creation of emulsions and assisting in the removal of oils.
- Detergents are chemically distinct from soaps, which are salts of higher fatty acids.
Detergents
Synthetic detergents are preferred over soaps due to their economic and efficient cleaning properties, resistance to natural lime and magnesium salts, and consistent cleansing effectiveness.
 Synthetic Detergents are preferred over Soaps
Synthetic Detergents are preferred over Soaps
- Synthetic detergents maintain their cleaning power in the presence of lime and magnesium salts, minimizing wastage.
- Some synthetic detergents remain effective even in acidic solutions.
- Household use of synthetic detergents includes powdered forms for laundry and textile cleaning, while liquid detergents are employed for dishwashing, and floor, and wall cleaning.
- The main types of synthetic detergents are anionic, non-ionic, and ampholytic.
- Anionic detergents, such as sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate, are popular for their cleaning abilities.
- Non-ionic detergents, like nonylphenol polyethylene oxide, are derived from ethylene oxide.
- Ampholytic detergents, such as N-alkyl amino propionates, act as cations in acidic solutions and anions in alkaline solutions.
- Linear alkyl benzene (LAB) is the most widely used group of synthetic detergents.
Paints
- Paints are composed of a mechanical mixture, comprising pigments and extenders suspended in a vehicle.
- To achieve dilution or thinning, additional volatile liquids like turpentine or acetone are incorporated.
 Paints
Paints
- Extenders serve as low-density substances within the paint, effectively raising the pigment volume concentration while reducing gloss.
- The vehicle refers to the liquid component of paint, encompassing drying oil or resin, solvent, and thinner, in which the solid elements are either dissolved or dispersed.
Types of Paints
(A) Latex Paint: Latex paint is composed of dry powders, with the principal components being latex paints, styrene-butadiene, polyvinyl acetate, and acrylic resins.
(B) Inorganic Paint: Inorganic paint is a type of paint based on potassium silicate, which provides corrosion resistance. It is suitable for use on bridges and other metal structures exposed to marine environments.
(C) Metallic Paint: Metallic paint is a paint variety where the primary pigment consists of finely divided metal particles dispersed in a vehicle. One of the most common forms of metallic paint is aluminium paint.
|
90 videos|491 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Soaps & Detergents, Paints - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are heavy metal soaps? |  |
| 2. How are heavy metal soaps used in detergents? |  |
| 3. What role do heavy metal soaps play in paints? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of paints? |  |
| 5. How do soaps and detergents differ from each other? |  |




















