Industry & Trade- 2 | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Petroleum Industry
- In 1956, Digboi (Assam) was the only oil producing area of the country.
- At present a number of regions having oil reserves have been identified and the oil is being extrac-ted in these regions.
- Oil regions in India are Assam, Tripura, Manipur, West Bengal, Mumbai, Gujarat, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Coastal area of Kerala and Andman & Nicobar Islands.
- According to India 2015, 22 refineries-17 in the public sector, 3 in the private sector and two in joint venture-the domestic refining capacity as on end-December 2012 was 213-66 million tonnes per annum (MMPTA)
- Out of 17 public sector refineries, 8 are owned by Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. (IOCL), 2 each by Chennai Petroleum Corporation Ltd. (a subsidiary of IOCL), Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Ltd. (HPCL), Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd. (BPCL) and Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Ltd. (ONGC). Numaligarh Refinery Limited (a subsidiary of BPCL) and Manglore Refinery and Petro Chemicals Ltd. have one each.
Oil and Gas Production
- Oil and gas constitute around 45 per cent of total energy consumption.
- At the same time, the dependence on imports of petroleum and petroleum products continues to be around 80 per cent of total oil consumption in the country.
- In order to meet the ever-growing demand for petroleum products, the government has consistently end-eavoured to enhance exploration and exploitation of petroleum resources, along with developing a concrete and structured distribution and marketing system.
- Despite this, crude oil production for 2013-14 remained stagnant at around 37.8 million metric tonnes (MMT) as against 37.9 MMT in 2012-13, showing a marginal decrease of about 0.20 per cent.
- The bulk of crude oil production is from ageing fields, with the exception of the Krishna Godavari (KG) deep-water and Rajasthan blocks.
- The average natural gas production for 2013-14 was about 35.4 BCM as against 40.7 BCM for 2012-13, showing a decline of about 13 percent.
- India has an estimated sedimentary area of 3.14 million sq. km, comprising 26 sedimentary basins.
| Maharatna and Navratna Companies |
|
|
Green Fuels
- In order to reduce pollution, unleaded petrol is being supplied throughout the country from February 1, 2000.
- Supply of diesel with 0.05 per cent (maximum) sulphur content and also unleaded petrol with sulphur content of 0.05 per cent (maximum) hitherto supplied in the National Capital Region (NCR), is now being supplied in all the four metropolitan cities.
- Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) has already been established as a clean and environment friendly fuel.
- The retail network of CNG dispensing stations is being expanded in Mumbai and Delhi.
- Di-Methyl Ether (DME) is another environment friendly fuel, manufactured from natural gas, and has been recognized as a fuel for the future in the India Hydrocarbon Vision 2025 document.
- An Indian combine consisting of IOC, GAIL and Indian Institute of Petroleum have entered into a Joint Collaboration Agreement (JCA) with Amoco (now BP-Amoco) on a 50 : 50 basis to develop an integrated value chain to bring DME to India and to develop it as a power generation fuel, as an alternative to LPG and as an auto fuel for diesel engines.
| Top Trade Unions of India | ||||
| Trade Union | Year of Establishment | H.Q. | Political Affiliation | Membership (Million) |
| All India Trade Union Congress (AITUC) | 1920 | New Delhi | CPI | 14.2 |
| Indian National Trade Union Congress (INTUC) | May 3,1947 | New Delhi | Indian National Congress | 33.3 |
| Bhartiya Mazdoor Sangh (BMS) | July 27,1955 | New Delhi | BJP | 17.1 |
| Centre for Indian Trade Unions (CITU) | 1970 | New Delhi | CPM | 5.7 |
| Hind Mazdoor Sabha (HMS) | Dec. 24,1948 | New Delhi | Samajvadi | 9.1 |
| All India Trade Union Centre (AIUTUC) | April 26-27, 1958 | Kolkata | Socialist Unity Centre of India (Marxist) | 4.7 |
| Self-employed Women’s Association of India (SEWA) | 1972 | Ahmedabad | 1.3 | |
| Trade Union Co-ordination Centre | 1970 | NA | AIFB | 1.6 |
| All India Central Council of Trade Union | May-89 | NA | CPI (M-L) | 2.5 |
Mini Ratna
The Government had introduced the Miniratna scheme in 1997 in pursuance of the policy objective to make the public sector more efficient and competitive and to grant enhanced autonomy and delegation of powers to the profit making public sector enterprises. The enhanced powers given to Miniratna CPSEs include the power to The administrative Ministries are empowered to declare a CPSE as a Miniratna if it fulfils the eligibility conditions. Presently, there are 61 Miniratna CPSEs (47 category-I and 14 category-II). As on October 26, 2014, 54 Miniratna Category-I CPSEs and 18 Category-II CPSEs have been granted Miniratna Status.
- incur capital expenditure,
- enter into joint ventures,
- set up technological and strategic alliances and
- formulate schemes of human resources management.
Grant of Maharatna Status
- Having Navratna status.
- Listed on Indian stock exchange with minimum prescribed public shareholding under SEBI regulations.
- An average annual turnover of more than Rs. 25,000 crore during the last 3 years.
- An average annual net worth of more than Rs. 15,000 crore during the last 3 years.
- An average annual net profit after tax of more than Rs. 5,000 crore during the last 3 years.
- Should have significant global presence/international operations.
Grant of Navaratna Status
The Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs) fulfilling the following criteria are eligible to be considered for grant of Navaratna status :
- Having Schedule 'A' and Miniratna Category-1 status.
- Having atleast three 'Excellent' or ‘Very Good’ Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) ratings during the last five years.
- Having a composite score of 60 or above out of 100 marks based on its performance during the last
New Competition Act, 2013
The salient features of the Act are followings:
- Companies are required to spend at least two per cent of their net profit on Corporate Social Responsibility.
- To help in curbing a major source of corporate delinquency, introduces punishment for falsely inducing a person to enter into any agreement with a bank or financial institution to obtain credit facilities.
- The limit of the maximum number of companies in which a person may be appointed as auditor has been pegged at 20.
- Appointment of auditors for 5 years shall be subject to ratifica-tion at every Annual General Meeting.
- Independent directors to be excluded for the purpose of computing one-third of retiring directors.
- Whole-time director has been included in the definition of the term key managerial personnel.
- Maximum number of directors in a private company increased from 12 to 15 which can be further increased by a special resolution.
- The term private placement has been defined to bring clarity.
- Financial year of any company can only end on March 31.
- The only exception is for companies which are a holding/subsidiary of a foreign entity requiring consolidation outside India.
Trade
India’s Foreign Traded
- In 1950, the Indian share in the total world trade was 1.78%, which came down to 0.6% in 1995.
- India's merchandise trade has been growing in importance over the years with the share in world exports and imports increasing, though gradually, from 0.7 per cent and 0.8 per cent respectively in 2000 to 1.7 per cent and 2.5 per cent respectively in 2013.
- India's ranking in the top merchandise exporters and importers in the world has also improved from 30th in 2000 to 19th in 2013 in exports and from 23rd to 12th for imports in the same years, as per the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- There has also been marked improvement in India's total merchandise trade to GDP ratio from 21.8 per cent in 2000-01 to 41-8 per cent in 2013-14.
- India's merchandise exports as a proportion of GDP was 12.1% in 2004-05 which became 17.0% in 2013-14.
| Foreign Trade in India (in Million $) | |||
| Year | Export | Import | Trade Deficit |
| 2000-01 | 44560 | 50536 | 5976 |
| 2001-02 | 43827 | 51413 | 7586 |
| 2002-03 | 52719 | 61412 | 8693 |
| 2003-04 | 63843 | 78150 | 1407 |
| 2004-05 | 83536 | 111518 | 27982 |
| 2005-06 | 100607 | 140238 | 39631 |
| 2006-07 | 126413 | 185735 | 59321 |
| 2007-08 | 163132 | 251654 | 88522 |
| 2008-09 | 185295 | 303696 | 118401 |
| 2009-10 | 178751 | 288373 | 109621 |
| 2010-11 | 251136 | 369769 | 118633 |
| 2011-12 | 305964 | 489319 | 183356 |
| 2012-13 | 300401 | 490737 | 190336 |
| 2013-14 | 314405 | 450200 | 135795 |
| 2014-15 | 310534 | 447548 | 134014 |
Exports:
- Exports during March 2015 were valued at US $ 23951.16 million (Rs. 149574.53 crore) which was 21.06 per cent lower in Dollar terms (19.20 per cent lower in Rupee terms) than the level of US $ 30341.04 million (Rs. 185122.83 crore) during March 2014.
- Cumulative value of exports for the period April-March 2014-15 was US $ 310533.87 million (Rs. 1897025.85 crore) as against US $314415.73 million (Rs. 1905011.08 crore) registering a growth of – 1.23 per cent in Dollar terms and growth of – 0.42 per cent in Rupee terms over the same period last year.
Imports:
- Imports during March 2015 were valued at US $ 35744.68 (Rs. 223224.83 crore) which was 13.44 per cent lower in Dollar terms and 11.40 per cent lower in Rupee terms over the level of imports valued at US $ 41294.41 million (Rs. 251953.73 crore) in March 2014. Cumulative value of imports for the period April-March 2014-15 was US $ 447548.33 million (Rs. 2734049.06 crore) as against US $ 450213.63 million (Rs. 2715433.89 crore) registering a growth of – 0.59 per cent in Dollar terms and growth of 0.69 per cent in Rupee terms over the same period last year.
Crude Oil and Non-Oil Imports:
- Oil imports during March 2015 were valued at US $ 7413.30 million which was 52.68 per cent lower than oil imports valued at US $ 15667.12 million in the corresponding period last year.
- Oil imports during April-March 2014-15 were valued at US $ 138261.66 million which was 16.09 per cent lower than the oil imports of US $ 164770.33 million in the corresponding period last year.
- Non-oil imports during March 2015 were estimated at US $ 28331.38 million which was 10.55 per cent higher than non-oil imports of US $ 25627.29 million in March 2014.
- Non-oil imports during April-March 2014-15 were valued at US $ 309286.67 million which was 8.35 per cent higher than the level of such imports valued at US $ 285443.30 million in April-March 2013-14.
Trade Balance:
- The trade deficit for April-March 2014-15 was estimated at US $ 137014.46 million which was higher than the deficit of US $ 135797.90 million during April-March 2013-14.
- Manufactured goods constitute the bulk of exports-over 63 per cent in recent years, followed by crude and petroleum products (including coal) with a 20 per cent share, and agriculture and allied products with a share of 13.7 per cent share.
- The top seven product groups accounting for nearly 80.9 per cent of India's total exports in 2014-15 (April-December) were; petroleum products (19.4 per cent share); gems and jewellery (13.0 per cent share); agriculture and allied products (12.0 per cent share); textiles and allied products (11.6 per cent share); chemicals and related products (10.1 per cent share); transport equipment (8.5 per cent share) and machinery (6.3 per cent share).
- Growth in exports of petroleum and agriculture and allied products which had been in positive territory for the last four years, turned negative in 2014-15 (April-January).
- Gems and jewellery exports which exhibited a declining trend in 2012-13 and 2013-14, continued to register a declining trend in 2014-15 (April-January).
- In the case of electronic goods, there has been continuous decline in exports since 2012-13.
| Exports of India (Value in US $ Million) 2013-14 | |
| $ Million | |
| Agricultural and Allied Products : | 43133 |
| ♦ Coffee | 793 |
| ♦ Tea and Mate | 806 |
| ♦ Oil Cakes | 2822 |
| ♦ Tobacoo | 1014 |
| ♦ Cashew kernels | 849 |
| ♦ Spices | 2504 |
| ♦ Sugar and Molasses | 1211 |
| ♦ Raw cotton | 3692 |
| ♦ Rice | 7783 |
| ♦ Fish and fish preparations | 5062 |
| ♦ Meat and meat preparations | 4490 |
| ♦ Fruits, vege tables and pulses (excl. cashew kernels, processed fruits & juices) | 1782 |
| ♦Miscellaneous processed foods (incl. processed fruits and juices) | 1916 |
| Ores and Minerals (excl. coal) : | 5762 |
| ♦ Mica | 51 |
| ♦ Iron ore (million tonne) | 1567 |
| Manufactured goods : | 199648 |
| ♦ Cotton yarn, fabrics, made-ups etc. | 9696 |
| ♦ Readymade garments of all textile materials | 14995 |
| ♦ Coir yarn and manufactures | 231 |
| ♦ Jute manufactures incl. twist & yarn | 401 |
| ♦ Leather & leather, manufactures incl. leather footwear, leather travel goods & leather garments | 5741 |
| Handicrafts (incl. carpets hand-made) : | 2685 |
| ♦ Gems and Jewellery | 41381 |
| ♦ Chemicals and Allied products | 35877 |
| ♦ Machinery, transport and Metal manufactures including iron and Steel | 61976 |
| ♦ Mineral fuels and Lubricants (incl. coal) | 64831 |
India’s Service Trade
- In commercial services trade, India was the sixth largest exporter with 3.4 per cent share of world exports and seventh largest importer with 30 per cent share of world imports in 2012.
- The 2008 global financial crisis gave a big jolt to India’s service exports.
- In the five years prior to 2008 (i.e., 2003-04 to 2007-08) service export growth (CAGR) at 35.4 per cent was faster and way above the merchandise export growth at 25.8 per cent.
- In the five years post crisis (2008-09 to 2012-13), service export growth at 8.3 per cent was below the 12.8 per cent merchandise export growth.
- In 2012-13, service exports at US $ 145.7 billion showed a lower growth of 2.4 per cent compared to the 14.2 per cent in the preceding year.
- They improved slightly in 2013-14 with a 4 per cent growth, the same as merchandise export growth.
- While export of software services with 45.8 per cent share and non-software with 29.1 per cent share grew by 5.4 per cent and 5.9 per cent respectively, all other major categories had negative or very low growth.
- Service imports which grew by a small 3.2 per cent in 2012-13 fell to a negative –2.8 per cent in 2013-14 with all major categories registering negative growth.
| Imports of India (Value in US $ Million) 2013-14 | |
| $ Million | |
| ♦Cereals and cereal preparations | 91 |
| ♦ Cashewnuts (unprocessed) | 756 |
| ♦ Crude rubber (including synthetic and reclaimed) | 2125 |
| ♦ Synthetic and regenerated fibres (man-made fibres) | 312 |
| ♦ Raw wool | 325 |
| ♦ Raw cotton | 394 |
| ♦ Raw Jute | 26 |
| ♦ Petroleum, oil and lubricants | 164770 |
| ♦ Edible oils | 9346 |
| ♦ Fertilizers and fertilizer mfg | 6264 |
| ♦Chemical elements and compounds | 3725 |
| ♦Dyeing, tanning and colouring material | 1503 |
| ♦Medicinal and pharmaceutical products | 2973 |
| ♦Plastic material, regenerated cellulose and artificial resins | 9096 |
| ♦ Pulp and waste paper | 1385 |
| ♦Paper, paper board and manufactures thereof | 2485 |
| ♦ Pearls, precious and semiprecious stones, unworked or worked | 23968 |
| ♦ Iron and steel | 7947 |
| ♦ Non-ferrous metals | 201100 |
| ♦ Capital goods | 54379 |
| ♦ Manufactures of metals | 4065 |
| ♦Non-electrical machinery apparatus and applicances including machine tools | 25680 |
| ♦Electrical machinery, apparatus and appliances | 4345 |
| ♦ Transport equipment | 15738 |
India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2015–20
- India aims to increase India's exports of merchandise and services from US$ 465.9 billion in 2013-14 to approximately US$ 900 billion by 2019-20 and to raise India's share in world exports from 2 per cent to 3.5 per cent.
- Unveiling the first trade policy of the National Democratic Alliance (NDA) government, Commerce Minister Nirmala Sitharaman said the FTP (2015-20) will introduce Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) and Services Exports from India Scheme (SEIS) to boost outward shipments.
- Besides, higher level of incentives will be provided for export of agriculture products under the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP), which seeks to integrate with Make in India and Digital India initiatives of the government.
- The FTP also seeks to establish an Export Promotion Mission to provide an institutional framework to work with State Governments to boost India's exports.
FDI Inflow in India
- An investor-friendly FDI policy has been put in place, whereby FDI up to 100 per cent is permitted under the automatic route in most sectors/ activities.
- In 2014, FDI policy has been further liberalized. FDI up to 49 per cent through the government route has been permitted in the defence industry. Higher FDI has also been allowed on a case-to-case basis.
- FDI up to 100per cent through the automatic route has been permitted in construction, opera-tion, and maintenance of identified railway transport infrastructure. Norms related to minimum land area, capitalization and repatriation of funds for FDI in construction development projects have been further liberalized.
- During April-February 2014-15, total FDI inflows (including equity inflows, reinvested earnings, and other capital) were US$ 41.22 billion, while FDI equity inflows were US$ 28.81 billion. Cumulative FDI inflows from April 2000 to February 2015 were US $ 364.79 billion.
- Services construction. telecommunications, computer software and hardware, drugs and phar-maceuticals, the automobile industry, chemicals, and power have attracted a proportionately high share of total inflows.
FDI Relaxsation
In a bid to boost the economy, me UPA government at the centre is giving top most priority to attract FDI in a big way. Union Cabinet approved a slew of following relaxsation in FDI policy :
- As a big relief to global retailers, the new policy measure allows multibrand retailer to procure at least 30% of procurement value from Indian small industries with upto US $ 2 million investment in plant and machinery. Earlier the limit was US $ 1 million.
- ‘Small Industry’ requirement only at the time of first engagement.
- Such industries will qualify for sourcing even if it outgrows investment of US $ 2 million.
- States are free to decide on the city for the location of front-end stones irrespective of population.
- Earlier the limit was over 10 lakh population.
- A new definition of ‘control’ for calculating direct and indirect foreign investment in a company to avoid controversies, such as created by the proposed Jet-Etehad deal.
India’s Exports & Imports
- India has a viable economic relationship with many countries in the world.
- As a result, India exports huge amounts of commodities to foreign countries and vice versa.
- The countries with which India is engaged in foreign trade activities are termed as India’s trading partners.
Exports
Major items accounting for the country’s exports are:
- Engineering goods
- Handicrafts
- Chemicals and allied products
- Iron ore
- Rice
- Fish
- Leather
- Fruits and vegetables
- Cotton yarn
- Readymade garments
Countries, where India’s exports reach, are:
- France
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- China
- Hong Kong
- Singapore
- United Arab Emirates
- Iran
- United States of America
- Certain African/ Latin American countries
Imports
- Petroleum and lubricants are the foremost items that account for India’s imports from the OPEC (Oil and Petroleum Exporting Countries) of Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates
- India also imports capital goods, fertilizer, electrical and non-electrical machinery, transport equipment, etc.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in India
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is an investment made by a firm or an individual in one country into business interests located in another nation.
- FDI in India is a major source of money for India’s economic development
- Foreign companies invest directly in fast-growing private businesses in India to reap the benefits of cheaper wages and an ever-dynamic business environment.
- Economic liberalization started in India during the 1991 economic crisis and since then the FDI activities have been on the rise generating employment opportunities.
FDI Routes in India
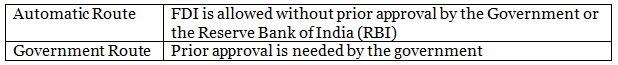 FDI Permissible Sectors & their Limits
FDI Permissible Sectors & their Limits
FDI Prohibited Sectors
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is prohibited in the following sectors:
- Lottery business including government/ pirate lottery, online lottery, etc.
- Gambling and betting including casinos, etc
- Chit funds
- Nidhi Company
- Trading in Transferable Development Rights (TDRs)
- Real estate business or construction of farmhouses
- Manufacturing of cigars, cigarillos, tobacco substitutes, cigarillos, etc.
- activities/ sectors not open to private sector investment like Atomic Energy or Railway operations
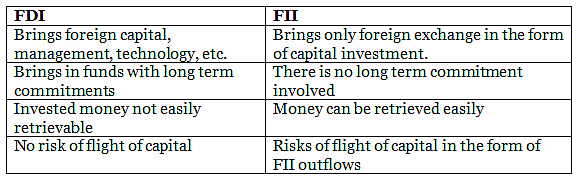
Foreign Institutional Investors in India (FII)
- Foreign institutional investors (FII) are investors or investment funds registered in a country outside of the one in which it is investing.
- Generally, institutional investors include insurance companies, mutual funds, pension funds, and hedge funds.
- FII is most commonly used in India and refers to the companies abroad investing in the financial markets of the country.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) vs Foreign Institutional Investors (FII)
Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI)
- The FPI is an investment made by non-residents in Indian securities such as shares, corporate bonds, infrastructure securities, government bonds, etc.
- The class of investors who make such investments in these categories of securities is known as Foreign Portfolio Investors.
|
173 videos|487 docs|159 tests
|
FAQs on Industry & Trade- 2 - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the impact of international trade on the economy? |  |
| 2. How does the World Trade Organization (WTO) regulate international trade? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of free trade? |  |
| 4. How does protectionism impact international trade? |  |
| 5. What role do trade agreements play in international trade? |  |