Irrigation Development, Irrigation Engineering | Irrigation Engineering Notes - Agricultural Engineering PDF Download
Irrigation Development
Irrigated agriculture has developed most extensively in the arid and semi-arid regions and areas having prolonged dry spells. The practice is essentially to supplement the available rainfall in an area. The principle irrigation practice of ancient times was building of temporary bunds across streams and then diverting their flow to the fields. The practice of storing water in tanks was developed at a later stage. Modern well designed large scale irrigation system with reservoirs and delivery systems developed mainly after 18thcentury.
Vedas, Ancient Indian writers and ancient Indian scriptures have made references to wells, canals, tanks and dams. These irrigation technologies were in the form of small and minor works, which could be operated by small households to irrigate small patches of land. In the south, perennial irrigation may have begun with construction of the Grand Anicut by the Cholas as early as second century to provide irrigation from the Cauvery River. The entire landscape in the central and southern India is studded with numerous irrigation tanks which have been traced back to many centuries before the beginning of the Christian era. In northern India also there are a number of small canals in the upper valleys of rivers which are very old.
2.1.1 Irrigation during Medieval India
Irrigation is said to be one of the major reasons for the growth and expansion of the Vijayanagar Empire in southern India in the fifteenth century. Babur, in his memoirs called ‘Baburnamah’ gave a vivid description of prevalent modes of irrigation practices in India at that time. The Gabar Bunds captured and stored annual runoff from surrounding mountains to be made available to tracts under cultivation.
2.1.2 Irrigation Development under British rule
According to sources of irrigation close to nineteenth century; canals irrigated 45 %, wells 35 %, tanks 15 % and other sources 5 %. Famines of 1897-98 and 1899-1900 necessitated British to appoint first irrigation commission in 1901, especially to report on irrigation as a means of protection against famine in India. As a result of recommendations of the first irrigation commission total irrigated area by public and private works increased to 16 Mha in 1921. From the beginning of 19th century to 1921 there was no significant increase in tube well irrigated area. During 1910 to 1950 growths rate of irrigation was estimated at 2.0 % per annum for government canal irrigation, 0.54 % per annum for well irrigation and 0.98 % per annum in respect of irrigation from all sources.
2.1.3 Irrigation Development at Time of Independence
At time of independence net irrigated area of India under British rule which include Bangladesh and Pakistan was 28.2 M ha. After partition net irrigated area in India and Pakistan being 19.4 Mha and 8.8 Mha respectively.
Irrigation development in Indiawas taken up in a big way after independence through major, medium and minor irrigation schemes. The irrigation potential has gone up from 22.6 Mha (9.76 Mha through Major and Medium and 12.84 Mha through Minor) prior to Plan period to 93.95 Mha by the end of IX Plan and further to 97.15 Mha (38.87 Mha through Major & Medium and 58.28 Mha through Minor) up to March 2004 against the Ultimate Irrigation Potential of 139.91 Mha (58.49 Mha through Major & Medium and 81.42 Mha through Minor). This development of irrigation facilities has largely contributed to country’s self-sufficiency in food grains which has gone up from 51 Million tons in 1950 to 210 million tons in 2000. Additional Irrigation Potential of 10.50 Mha (6.5 through Major and Medium and 4.00 Mha. through Minor) is planned to be created during the X Plan totalling to 104.45 Mha by the end of the Xth Plan (MoWR, 2007).
2.2 Plan Development
a) Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP)
b) Command Area Development and Water Management Programme (CADWM)
c) Bharat Nirman
a) Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme (AIBP)
The Accelerated Irrigation Benefits Programme (AIBP) was launched during 1996-97 to provide loan assistance to the states to complete some of the incomplete major/medium irrigation projects, which were in an advanced stage of completion. The criteria for AIBP was further relaxed from April 2005 to include minor irrigation schemes of non-special category States with potential of more than 100 ha with preference to Tribal Areas and drought-prone areas. After commencement of this programme 50 major/medium and 3480 Surface minor irrigation schemes have been completed. An additional irrigation potential for 3.25 million hectare has been created through major/medium irrigation projects up to March 2005 and an irrigation potential of 123,000 hectare has been created through surface minor irrigation schemes up to March 2006 (GoI, 2006).
b) Command Area Development and Water Management Programme (CADWM)
The Centrally sponsored Command Area Development (CAD) Programme was launched in 1974-75 with the objective of bridging the gap between irrigation potential created and that utilized through efficient utilization of created irrigation potential.The other aim was optimizing agricultural production from irrigated lands on a sustainable basis. The CAD programmewas initiated with 60 major and medium irrigation projects. So far 310 irrigation projects with a Culturable Command Area (CCA) of about 28.45 Mha have been included under the programme, out of which 133 projects are currently under implementation (GOI, 2005). However, there have been certain constraints which are:
- Unreliability of water supply from the government sources mainly due to system deficiency, Water logging, non-availability of drainage system and unscientific water use,
- Gap between scientific technologies of efficient water use and the technologies adopted at the farm level,
- Lack of participation of farmers in water management,
- Lack of conjunctive use of surface and groundwater, f) Non-inclusion of corrective measuresfor system deficiencies
- Lack of matching budgetary support by State Governments to execute the programme.
The restructured Command Area Development and Water Management Program (CADWM) from 2002, considered almost all aspects of the water resources management. The programme covers a great deal of activities responsible for bringing in greater efficiencies in land water and crop management. The success of the programme would, however, depend on the CADAs/State agencies that are implementing the program through coordination of the concerned organizations and other related inputs.
c) Bharat Nirman
Under the irrigation component of Bharat Nirman, the target of creation of additional irrigation potential of 10 M ha in 4 years (2005-06 to 2008-09) is planned to be meet largely through expeditious completion of identified ongoing major and medium irrigation projects. Irrigation potential of 42 lakh hectare is planned to be created by expeditiously completing such on-going major and medium projects (GOI, 2005).
2.3 Irrigation Potential Created and Utilized
Ultimate Irrigation Potential (UIP): This term refers to the gross area that could be irrigated theoretically if all available land and water resources would be used for irrigation.
Irrigation Potential Created (IPC): This term refers to the total gross area proposed to be irrigated under different crops during a year by a scheme. The area proposed to be irrigated under more than one crop during the same year is counted as many times as the number of crops grown and irrigated.
Irrigation Potential Utilized (IPU): This term is defined as the gross area actually irrigated during the reference year out of the gross proposed area to be irrigated by the scheme.
Irrigation Potential Creation: Expansion of irrigation facilities, along with consolidation of the existing systems, has been the main part of the strategy for increasing production of food grains. With sustained and systematic development of irrigation, the irrigation potential through major, medium and minor irrigation projects has increased from 22.6 Mha in 1951, when the process of planning began in India, to about 98.84 Mha at the end of the year 2004-05. Plan wise irrigation potential created and utilized through major, medium and minor irrigation projects in the country is shown in Table 2.1 and Figure 2.1.
Table 2.1.Irrigation potential created and utilized during Plan periods in India
| Plan Period | Potential (cumulative) created (Mha) | Potential (cumulative) utilized (Mha) |
| Pre-Plan period | 22.60 | 22.60 |
| First Plan (1951-56) | 26.26 | 25.04 |
| Second Plan (1956-61) | 29.08 | 27.80 |
| Third Plan (1961-66) | 33.57 | 32.17 |
| Annual Plans (1966-69) | 37.10 | 35.75 |
| Fourth Plan (1969-74) | 44.20 | 42.19 |
| Fifth Plan (1974-78) | 52.02 | 48.46 |
| Annual Plans (1978-80) | 56.61 | 52.64 |
| Sixth Plan (1980-85) | 65.22 | 58.82 |
| Seventh Plan (1985-90) | 76.53 | 68.59 |
| Annual Plans (1990-92) | 81.09 | 72.86 |
| Eighth Plan (1992-97) | 86.26 | 77.24 |
| Ninth Plan (1997-2002) | 93.95 | 80.06 |
| Tenth Plan (upto 2004-05) | 98.84 | 83.56 |
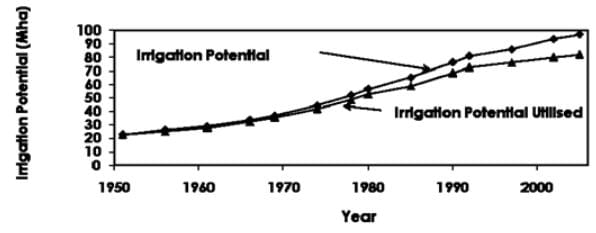
Fig. 2.1. Irrigation potential created and utilized.
2.4 Causes for gap in potential Created and Utilized (Ramanayya et al., 2008)
2.4.1 Measurement Problems
- The estimates made by the Irrigation Department do not take into accountthe unauthorized irrigation and pilferages of water.
- The Revenue Department goes by the revenue collected and not by actualarea irrigated.
- The meaning of IPU is similar to the meaning of the GIA, but the statistics are collected and published by the Ministry of Water Resources instead of the Ministry of Agriculture. The differences between the most recent reported IPU (80.06 Mha) and GIA (75.87 Mha for 2000/2001) can be explained by the difference in the data collection and sampling strategies adopted to calculate the two quantities and by considering minor irrigation schemes inside the command area of major or medium irrigation schemes.
2.4.2 Design Problems
There are certain assumptions made at the time of designing the project. It is necessary to verify andvalidate these assumptions after completingthe project and redefine the quantum of potential created.
- The average rainfall in the area over a period of 30 years or so isconsidered while designing the project and calculating the dependableyield. It does not make any allowances for variations.
- The assumption made about the cropping pattern at the time of estimatingthe irrigation potential created may not hold good after implementation of theproject.
- Availability of water at the beginning of each agricultural season shouldbe the criterion for defining the potential created. In other words, thepotential is based on the availability of water in a particular season andvaries every year.
- The estimation of potential utilized should also take into account the canalbreaches and unauthorized irrigation
FAQs on Irrigation Development, Irrigation Engineering - Irrigation Engineering Notes - Agricultural Engineering
| 1. What is irrigation development? |  |
| 2. What is the role of irrigation engineering in agricultural engineering? |  |
| 3. How does irrigation development contribute to sustainable agriculture? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of irrigation systems used in agricultural engineering? |  |
| 5. What are the key challenges in irrigation development and how can they be addressed? |  |
















