Friedel Crafts Alkylation and Acylation | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Friedel Crafts alkylation reaction
When benzene is treated with an alkyl halide in the presence of a Lewis acid such as anhydrous aluminium chloride, alkyl benzene is formed. This reaction is popularly known as Friedel Crafts alkylation reaction.
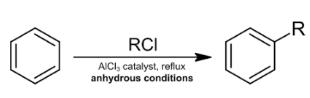
Friedel Crafts acylation reaction:
When benzene is treated with an acyl halide in the presence of Lewis acids such as anhydrous aluminium chloride, acyl benzene is formed. This reaction is popularly known as Friedel Crafts acylation reaction.
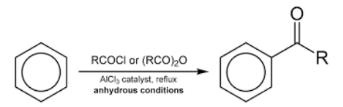
The mechanism for Friedel Crafts alkylation and acylation reactions of benzene:
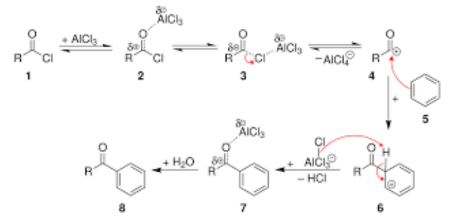
Friedel Crafts alkylation and acylation reactions involve a three-step mechanism:
Generation of electrophile:
Due to the presence of a Lewis acid, generation of electrophile takes place. As Lewis acid accepts the electron pair from the attacking reagent.
Formation of arenium ion:
The electrophiles generated attacks on the benzene ring to form positively charged cyclohexadienyl cation better called arenium ion containing one sp3 hybridized carbon atom. The positive charge is effectively distributed over three carbon atoms due to resonance which makes it partially stable.
As delocalization of electrons stops at sp3 hybridized carbon atom, the arenium ion is not aromatic in nature.
Removal of positive charge from the carbo-cation intermediate:
The arenium ion finally loses its proton from sp3 hybridized carbon to a Lewis base restoring the aromaticity.
A general mechanism for Friedel Craft’s acylation is depicted below:
|
334 videos|660 docs|300 tests
|
FAQs on Friedel Crafts Alkylation and Acylation - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is Friedel Crafts alkylation and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What is the purpose of using a Lewis acid catalyst in Friedel Crafts alkylation? |  |
| 3. What are the limitations of Friedel Crafts alkylation? |  |
| 4. How is Friedel Crafts acylation different from Friedel Crafts alkylation? |  |
| 5. What are some common applications of Friedel Crafts alkylation and acylation reactions? |  |

















