Irodov Solutions: Electric Oscillations- 3 | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q.131. A series circuit consisting of a capacitor and a coil with active resistance is connected to a source of harmonic voltage whose frequency can be varied, keeping the voltage amplitude constant. At frequencies ω1 and ω2 the current amplitudes are n times less than the resonance amplitude. Find:
(a) the resonance frequency;
(b) the quality factor of the circuit.
Ans. At resonance
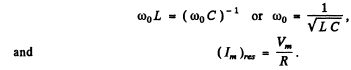
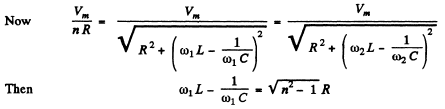
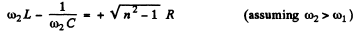
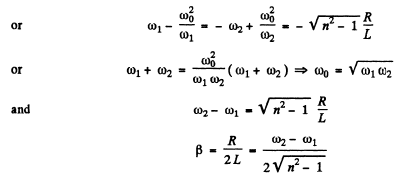
and
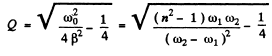
Q.132. Demonstrate that at low damping the quality factor Q of a circuit maintaining forced oscillations is approximately equal to ωo/Δ ω, where ωo is the natural oscillation frequency, Δω is the width of the resonance curve I (ω) at the "height" which is 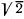 times less than the resonance current amplitude.
times less than the resonance current amplitude.
Ans.
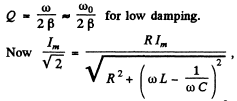 Im = current amplitude at resouance.
Im = current amplitude at resouance.
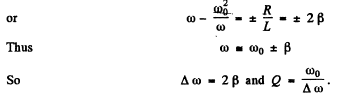
Q.133. A circuit consisting of a capacitor and a coil connected in series is fed two alternating voltages of equal amplitudes but different frequencies. The frequency of one voltage is equal to the natural oscillation frequency (ωo) of the circuit, the frequency of the other voltage is η times higher. Find the ratio of the current amplitudes (l0/l) generated by the two voltages if the quality factor of the system is equal to Q. Calculate this ratio for Q = 10 and 100, if η = 1.10.
Ans. At resonance
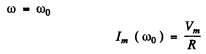
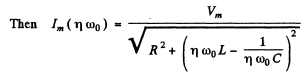
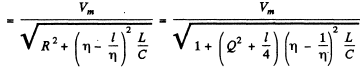
Q.134. It takes to hours for a direct current l0 to charge a storage battery. How long will it take to charge such a battery from the mains using a half-wave rectifier, if the effective current value is also equal to l0?
Ans. The a.c. current must be
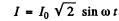
Then D.C. component of the rectified current is
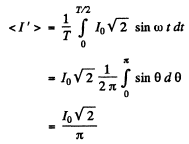
Since the charge deposited must be the same
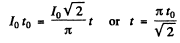
The answer is incorrect.
Q.135. Find the effective value of current if its mean value is l0 and its time dependence is
(a) shown in Fig. 4.34; 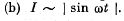
Ans. (a)
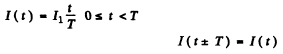
Now mean current
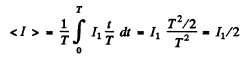
Then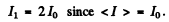
Now mean square current
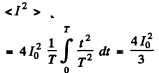
so effective current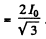
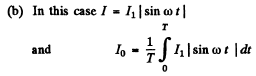
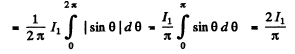
so 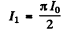
Then, mean square current 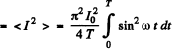
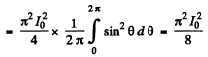
so effective current 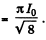
Q.136. A solenoid with inductance L = 7 mH and active resistance R = 44Ω is first connected to a source of direct voltage Vo and then to a source of sinusoidal voltage with effective value V = V0. At what frequency of the oscillator will the power consumed by the solenoid be η = 5.0 times less than in the former case?
Ans.
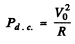
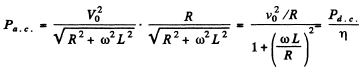
Thus 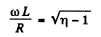
or 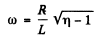
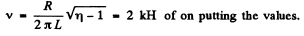
Q.137. A coil with inductive resistance XL = 30Ω and impedance Z = 50Ω is connected to the mains with effective voltage value V = 100 V. Find the phase difference between the current and the voltage, as well as the heat power generated in the coil.
Ans.
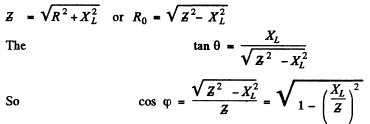
The current lags by φ behind the voltage.
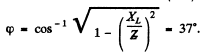
also 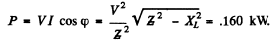
Q.138. A coil with inductance L =- 0.70 H and active resistance r = 20Ω is connected in series with an inductance-free resistance R. An alternating voltage with effective value V = 220 V and frequency w = 314 s-1 i s applied across the terminals of this circuit. At what value of the resistance R will the maximum heat power be generated in the circuit? What is it equal to?
Ans.
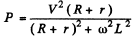
This is maximum when R + r = ωL for
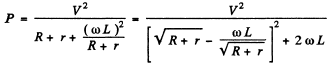
Thus R = ωL - r for maximum power and 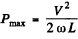
Substituting the values, we get 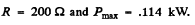
Q.139. A circuit consisting of a capacitor and a coil in series is connected to the mains. Varying the capacitance of the capacitor, the heat power generated in the coil was increased n = 1.7 times. How much (in per cent) was the value of cos 11) changed in the process?
Ans.
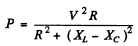
Varying the capacitor does not change R so if P increases n times
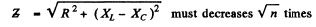
Thus

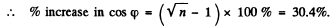
Q.140. A source of sinusoidal emf with constant voltage is connected in series with an oscillating circuit with quality factor Q = 100. At a certain frequency of the external voltage the heat power generated in the circuit reaches the maximum value. How much (in per cent) should this frequency be shifted to decrease the power generated n = 2.0 times?
Ans.
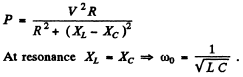
Power generated will decrease n times when
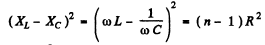
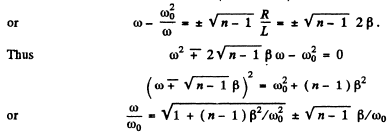
(taking only the positive sign in the first term to ensure positive value for 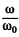 )
)
Now
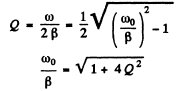
Thus
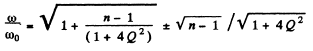
For large Q
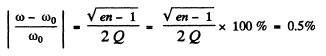
Q.141. A series circuit consisting of an inductance-free resistance R = 0.16 kΩ and a coil with active resistance is connected to the mains with effective voltage V = 220 V, Find the heat power generated in the coil if the effective voltage values across the resistance R and the coil are equal to V1 = 80 V and V2 = 180 V respectively.
Ans. We have
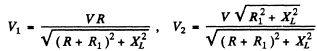
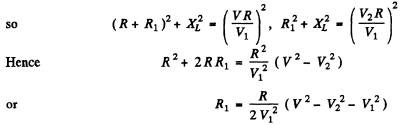
Heat generated in the coil 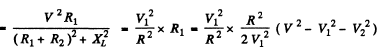
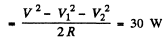
Q.142. A coil and an inductance-free resistance R = 25Ω are connected in parallel to the ac mains. Find the heat power generated in the coil provided a current I = 0.90 A is drawn from the mains. The coil and the resistance R carry currents I1 = 0.50 A and l2 = = 0.60 A respectively.
Ans. Here
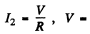 effective voltage
effective voltage
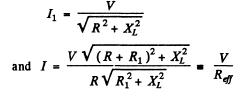
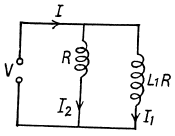
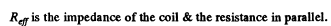
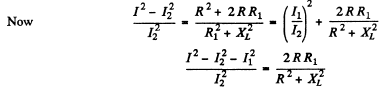
Now mean power consumed in the coil
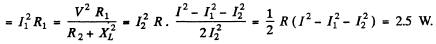
Q.143. An alternating current of frequency ω = 314 s- 1 is fed to a circuit consisting of a capacitor of capacitance C = 73 ηF and an active resistance R = 100Ω connected in parallel. Find the impedance of the circuit.
Ans.
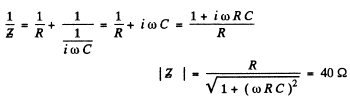
Q.144. Draw the approximate vector diagrams of currents in the circuits shown in Fig. 4.35. The voltage applied across the points A and B is assumed to be sinusoidal; the parameters of each circuit are so chosen that the total current l0 lags in phase behind the external voltage by an angle φ.
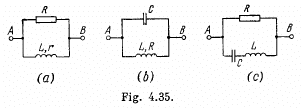
Ans. (a) For the resistance, the voltage and the current are in phase. For the coil the voltage is ahead of the current by less than 90°. The current is obtained by addition because the elements are in parallel
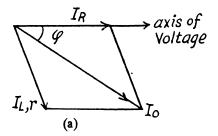
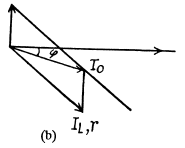
(b) Ic is ahead of the voltage by 90°.
(c) The coil has no resistance so Ih is 90° behind the voltage.
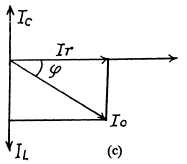
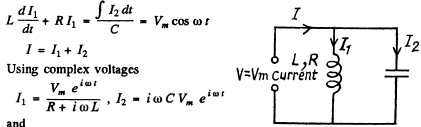
Q.145. A capacitor with capacitance C = 1.0 μF and a coil with active resistance R = 0.10Ω and inductance L = 1.0 mH are connected in parallel to a source of sinusoidal voltage V = 31 V. Find:
(a) the frequency ω at which the resonance sets in;
(b) the effective value of the fed current in resonance, as well as the corresponding currents flowing through the coil and through the capacitor.
Ans. When the coil and the condenser are in parallel, the equation is
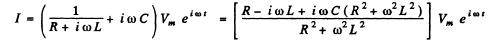
Thus, taking real parts 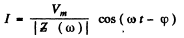
where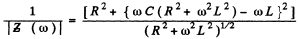
and 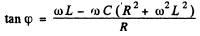
(a) To get the frequency of resonance we must define what we mean by resouance. One definition requires the extremum (maximum or minimum) of current amplitude. The other definition requires rapid change of phase with φ passing through zero at resonance. For the series circuit.
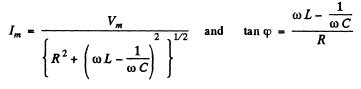
both definitions give 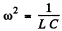 at resonance. In the present case the two definitions do not agree (except when R = 0 ). The definition that has been adopted in the answer given in the book is the vanishing of phase. This requires
at resonance. In the present case the two definitions do not agree (except when R = 0 ). The definition that has been adopted in the answer given in the book is the vanishing of phase. This requires
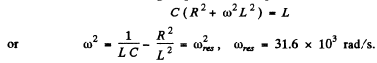
Note that for small R , φ rapidly changes from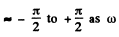 passes through
passes through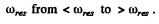
(b) At resonance
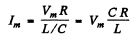
so l = effective value of total current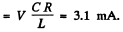
similarly 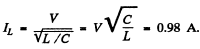
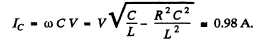
Note :- The vanishing of phase (its passing through zero) is considered a more basic definition of resonance.
Q.146. A capacitor with capacitance C and a coil with active resistance R and inductance L are connected in parallel to a source of sinusoidal voltage of frequency ω. Find the phase difference between the current fed to the circuit and the source voltage.
Ans. We use the method of complex voltage
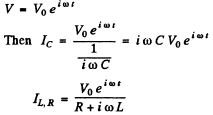
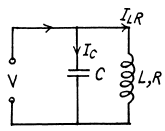
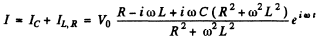
Then taking the real part
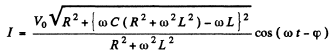
where 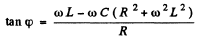
Q.147. A circuit consists of a capacitor with capacitance C and a coil with active resistance R and inductance L connected in parallel. Find the impedance of the circuit at frequency ω of alternating voltage.
Ans. From the previous problem
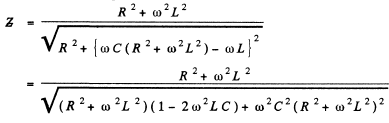
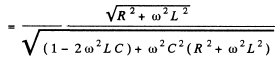
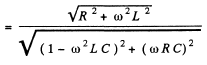
Q.148. A ring of thin wire with active resistance R and inductance L rotates with constant angular velocity ω in the external uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the rotation axis. In the process, the flux of magnetic induction of external field across the ring varies with time as 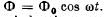 Demonstrate that
Demonstrate that
(a) the inductive current in the ring varies with time as I =
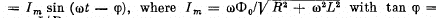
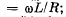
(b) the mean mechanical power developed by external forces to maintain rotation is defined by the formula

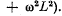
Ans. (a) We have
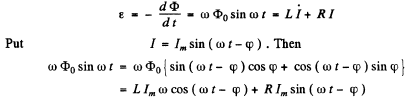
(b) Mean mechanical power required to maintain rotation = energy loss per unit time
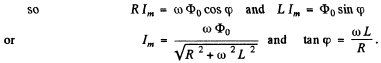
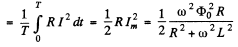
Q.149. A wooden core (Fig. 4.36) supports two coils: coil 1 with inductance L1 a nd short-circuited coil 2 with active resistance R and inductance L2. The mutual inductance of the coils depends on
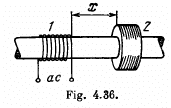
the distance x between them according to the law L12 (x). Find the mean (averaged over time) value of the interaction force between the coils when coil 1 carries an alternating current 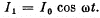
Ans. We consider the force  that a circuit 1 exerts on another closed circuit 2 :-
that a circuit 1 exerts on another closed circuit 2 :-
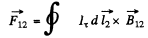
Here 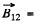 magnetic field at the site of the current element
magnetic field at the site of the current element 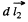 due to the current I1 flowing in 1.
due to the current I1 flowing in 1.
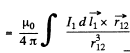
where 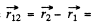 vector, from current element
vector, from current element 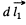 to the current element
to the current element 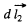
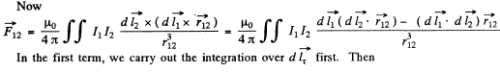
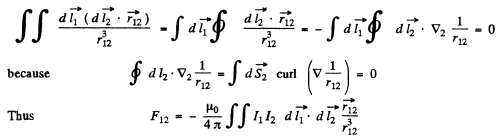
The integral involved will depend on the vector 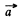 that defines the separation of the (suitably chosen )centre of the coils. Let C1 and C2 be the centres of the two coil suitably defined.
that defines the separation of the (suitably chosen )centre of the coils. Let C1 and C2 be the centres of the two coil suitably defined.
Write
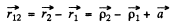
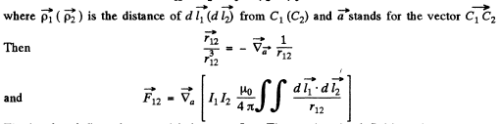
The bracket defines the mutual inductance L12. Thus noting the definition of x
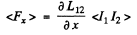
where < > denotes time average. Now
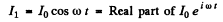
The current in the coil 2 satisfies 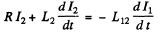
or 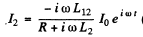 ( in the com plex case )
( in the com plex case )
taking the real part
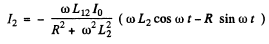
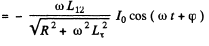
Where tan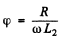 . Taking time average, we get
. Taking time average, we get
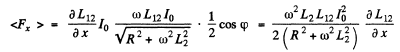
The repulsive nature of the force is also consistent with Lenz’s law, assuming, of comse, that L12 decreases with x.





















