Irodov Solutions: Electromagnetic Induction: Maxwell’s Equations | I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE PDF Download
Q. 288. A wire bent as a parabola y = ax2 is located in a uniform magnetic field of induction B, the vector B being perpendicular to the plane x, y. At the moment t = 0 a connector starts sliding translationwise from the parabola apex with a constant acceleration w (Fig. 3.78). Find the emf of electromagnetic induction in the loop thus formed as a function of y.
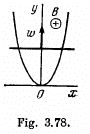
Solution. 288. Obviously, from Lenz's law, the induced current and hence the induced e.m.f. in the loop is anticlockwise.
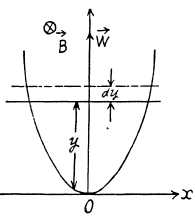
From Faraday's law of electromagnetic indcution,
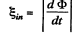
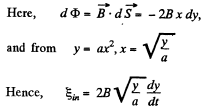
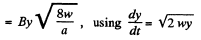
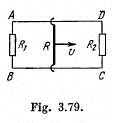
Q. 289. A rectangular loop with a sliding connector of length l is located in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the loop plane (Fig. 3.79). The magnetic induction is equal to B. The connector has an electric resistance R, the sides AB and CD have resistances R1 and R2 respectively. Neglecting the self-inductance of the loop, find the current flowing in the connector during its motion with a constant velocity v.
Solution. 289. Let us assume,  directed into the plane of the loop. Then the motional e.m.f.
directed into the plane of the loop. Then the motional e.m.f.
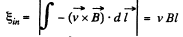
and directed in the same of 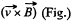
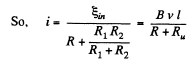
As R1 and R2 are in parallel connections.
Q. 290. A metal disc of radius a = 25 cm rotates with a constant angular velocity ω = 130 rad/s about its axis. Find the potential difference between the centre and the rim of the disc if
(a) the external magnetic field is absent;
(b) the external uniform magnetic field of induction B = 5.0 mT is directed perpendicular to the disc.
Solution. 290. (a) As the metal disc rotates, any free electron also rotates with it with same angular velocity ω, and that's why an electron must have an acceleration ω2r directed towards the disc's centre, where r is separation of the electron from the centre of the disc. We know from Newton's second law that if a particle has some acceleration then there must be a net effecetive force on it in the direction of acceleration. We also know that a charged particle can be influenced by two fields electric and magnetic. In our problem magnetic field is absent hence we reach at the conslusion that there is an electric field near any electron and is directed opposite to the acceleration of the electron.
If E be the electric field strength at a distance r from the centre of the disc, we have from Newton's second law.
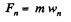
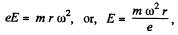
and the notential difference
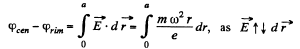
Thus 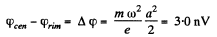
(b) When field 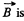 present, by definition, of motional e.m.f.
present, by definition, of motional e.m.f.
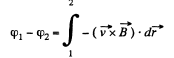
Hence the sought potential difference,
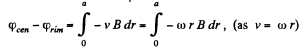
Thus 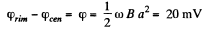
(In general 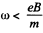 so we can neglect the effect discussed in (1) here).
so we can neglect the effect discussed in (1) here).
Q. 291. A thin wire AC shaped as a semi-circle of diameter d = 20 cm rotates with a constant angular velocity ω = 100 rad/s in a uniform magnetic field of induction B = 5.0 mT, with 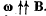 The rotation axis passes through the end A of the wire and is perpendicular to the diameter AC. Find the value of a line integral
The rotation axis passes through the end A of the wire and is perpendicular to the diameter AC. Find the value of a line integral 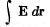 along the wire from point A to point C. Generalize the obtained result.
along the wire from point A to point C. Generalize the obtained result.
Solution. 291. By definition,
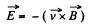
So, 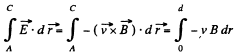
But, v = ωr, where r is the perpendicular distance of the point from A.
Hence, 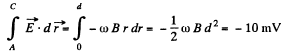
This result can be generalized to a wire AC of arbitary planar shape. We have
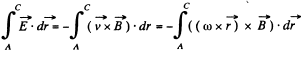
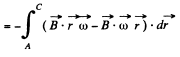
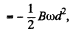

d being AC and  measured from A.
measured from A.
Q. 292. A wire loop enclosing a semi-circle of radius a is located on the boundary of a uniform magnetic field of induction B (Fig. 3.80). At the moment t = 0 the loop is set into rotation with a constant angular acceleration p about an axis 0 coinciding with a line of vector B on the boundary. Find the emf induced in the loop as a function of time t. Draw the approximate plot of this function. The arrow in the figure shows the emf direction taken to be positive.
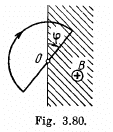
Solution. 292. Flux at any moment of time,
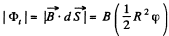
where φ is the sector angle, enclosed by the field.
Now, magnitude of induced e.m.f. is given by,
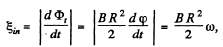
where ω is the angular v elocity o f the disc. But as it starts rotating from rest at t = 0 with an angular acceleration p its angular velocity ω (f) = βt. So,
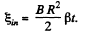
According to Lenz law the first half cycle current in the loop is in anticlockwise sense, and in subsequent half cycle it is in clockwise sense.
Thus in general, 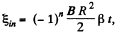 where n in number of half revolutions.
where n in number of half revolutions.
The plot 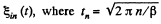 is shown in the answer sheet.
is shown in the answer sheet.
Q. 293. A long straight wire carrying a current I and a II-shaped conductor with sliding connector are located in the same plane as shown in Fig. 3.81. The connector of length l and resistance R slides to the right with a constant velocity v. Find the current induced in the loop as a function of separation r between the connector and the straight wire. The resistance of the H-shaped conductor and the selfinductance of the loop are assumed to be negligible.
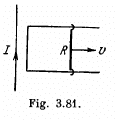
Solution. 293. Field, due to the current carrying wire in the region, right to it, is directed into the plane of the paper and its magnitude is given by,
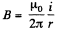 where r is the perpendicular distance from the wire.
where r is the perpendicular distance from the wire.
As B is same along the length of the rod thus motional e.m.f.
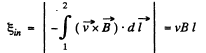
and it is directed in the sense of 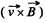
So, current (induced) in the loop,
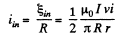
Q. 294. A square frame with side a and a long straight wire carrying a current I are located in the same plane as shown in Fig. 3.82. The frame translates to the right with a constant velocity v. Find the emf induced in the frame as a function of distance x.
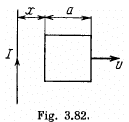
Solution. 294. Field, due to the current carrying wire, at a perpendicular distance x from it is given by,
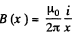
Motional e.m.f is given by 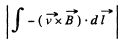
There will be no induced e.m.f. in the segments (2) and (4)
as, 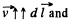 magnitude of e.m.f. induced in 1 and 3, will be
magnitude of e.m.f. induced in 1 and 3, will be
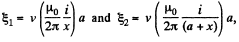
respectively, and their sense will be in the direction of 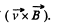
So, e.m .f., induced in the network 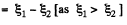
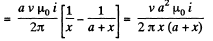
Q. 295. A metal rod of mass m can rotate about a horizontal axis O, sliding along a circular conductor of radius a (Fig. 3.83). The arrangement is located in a uniform magnetic field of induction B directed perpendicular to the ring plane. The axis and the ring are connected to an emf source to form a circuit of resistance R. Neglecting the friction, circuit inductance, and ring resistance, find the law according to which the source emf must vary to make the rod rotate with a constant angular velocity ω.
Solution. 295. As the rod rotates, an emf.
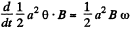
is induced in it The net current in the conductor is then
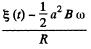
A magnetic force will then act on the conductor of magnitude BI per unit length. Its direction will be normal to B and the rod and its torque will be
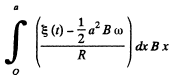
Obviously both magnetic and mechanical torque acting on the C.M. of the rod must be equal but opposite in sense. Then
for equilibrium at constant ω
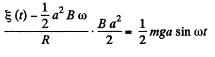
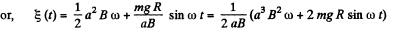
(The answer given in the book is incorrect dimensionally.)
Q. 296. A copper connector of mass m slides down two smooth copper bars, set at an angle a to the horizontal, due to gravity (Fig. 3.84). At the top the bars are interconnected through a resistance R. The separation between the bars is equal to l. The system is located in a uniform magnetic field of induction B, perpendicular to the plane in which the connector slides. The resistances of the bars, the connector and the sliding contacts, as well as the self-inductance of the loop, are assumed to be negligible. Find the steady-state velocity of the connector.
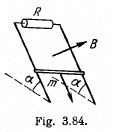
Solution. 296. From Lenz’s law, the current through the connector is directed form A to B. Here 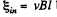 between A and B
between A and B
where v is the velocity of the rod at any moment.
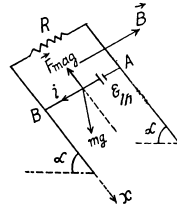
For the rod, from Fx = mwx
or, 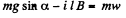
For steady state, acceleration of the rod must be equal to zero.
Hence, 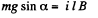 (1)
(1)
But, 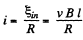
From (1) and (2) 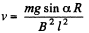
Q. 297. The system differs from the one examined in the foregoing problem (Fig. 3.84) by a capacitor of capacitance C replacing the resistance R. Find the acceleration of the connector.

Solution. 297. From Lenz’s 1 aw, the current through the copper bar is directed from 1 to 2 or in other words, the induced crrrent in the circuit is in clockwise sense.
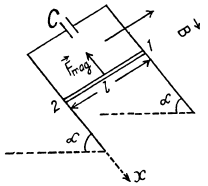
Potential difference across the capacitor plates,
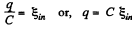
Hence, the induced current in the loop,
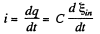
But the variation of magnetic flux through the loop is caused by the movement of the bar. So, the induced e.m.f. 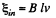
and, 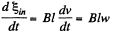
Hence, 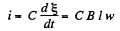
Now, the forces acting on the bars are the weight and the Ampere’s force, where
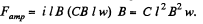
From Newton’s second law, for the rod, Fx = mwx
or, 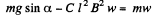
Hence
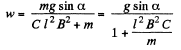
Q. 298. A wire shaped as a semi-circle of radius a rotates about an axis OO' with an angular velocity ω in a uniform magnetic field of induction B (Fig. 3.85). The rotation axis is perpendicular to the field direction. The total resistance of the circuit is equal to R. Neglecting the magnetic field of the induced current, find the mean amount of thermal power being generated in the loop during a rotation period.
Solution. 298. Flux of 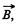 at an arbitrary moment of time t :
at an arbitrary moment of time t :
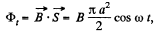
From Faraday’s law, induced e.m.f., 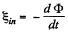
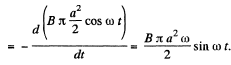
and induced current, 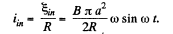
N ow thermal power, generated in the circuit, at the moment t = t :
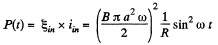
and mean thermal power generated,
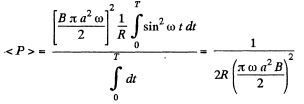
Note : The claculation of 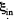 which can also be checked by using motional emf is correct even though the conductor is not a closed semicircle , for the flux linked to the rectangular part containing the resistance R is not changing. The answer given in the book is off by a factor 1/4.
which can also be checked by using motional emf is correct even though the conductor is not a closed semicircle , for the flux linked to the rectangular part containing the resistance R is not changing. The answer given in the book is off by a factor 1/4.
Q. 299. A small coil is introduced between the poles of an electromagnet so that its axis coincides with the magnetic field direction. The cross-sectional area of the coil is equal to S = 3.0 mm2, the number of turns is N = 60. When the coil turns through 180° about its diameter, a ballistic galvanometer connected to the coil indicates a charge q = 4.5 μC flowing through it. Find the magnetic induction magnitude between the poles provided the total resistance of the electric circuit equals R = 40 Ω.
Solution. 299. The flux through the coil changes sign. Initially it is BS per turn.
Finally it is - BS per turn. Now if flux is 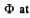 an intermediate state then the current at that moment will be
an intermediate state then the current at that moment will be
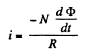
So charge that flows during a sudden turning of the coil is
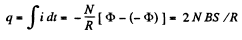
Hence, 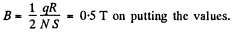
Q. 300. A square wire frame with side a and a straight conductor carrying a constant current I are located in the same plane (Fig. 3.86). The inductance and the resistance of the frame are equal to L and R respectively. The frame was turned through 180° about the axis OO' separated from the current-carrying conductor by a distance b. Find the electric charge having flown through the frame.
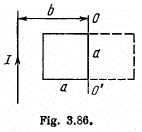
Solution. 300. According to Ohm’s law and Faraday’s law of induction, the current i0 appearing in the frame, during its rotation, is determined by the formula, 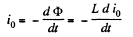
Hence, the required amount of electricity (charge) is,
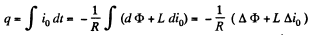
Since the frame has been stopped after rotation, the current in it vanishes, and hence Δ i0 = 0. It remains for us to find the increment of the flux 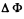 through the frame
through the frame 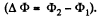
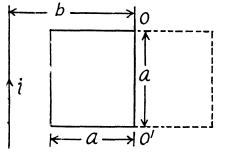
Let us choose the normal  the plane of the frame, for instance, so that in the final position,
the plane of the frame, for instance, so that in the final position,  directed behind the plane of the figure (along
directed behind the plane of the figure (along 
Then it can be easily seen that in the final position, 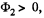 while in the initial position,
while in the initial position, 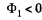 (th e normal is op posite to
(th e normal is op posite to 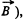 and
and 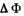 turns out to be simply equal to the fulx through the surface bounded b y the final and initial positions of the frame :
turns out to be simply equal to the fulx through the surface bounded b y the final and initial positions of the frame :
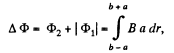
where B is a function of r, whose form can be easily found with the help of the theorem of circulation. Finally omitting the minus sign, we obtain,
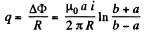
Q. 301. A long straight wire carries a current I0. At distances a and b from it there are two other wires, parallel to the former one, which are interconnected by a resistance R (Fig. 3.87). A connector slides without friction along the wires with a constant velocity v. Assuming the resistances of the wires, the connector, the sliding contacts, and the self-inductance of the freme to be negligible, find:
(a) the magnitude and the direction of the current induced in the connector;
(b) the force required to maintain the connector's velocity constant.
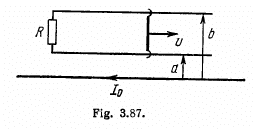
Solution. 301. As 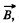 due to the straight current carrying wire, varies along the rod (connector) and enters linerarly so, to make the calculations simple
due to the straight current carrying wire, varies along the rod (connector) and enters linerarly so, to make the calculations simple 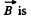 made constant by taking its average value in the range [a, b].
made constant by taking its average value in the range [a, b].
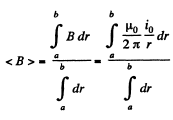
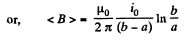
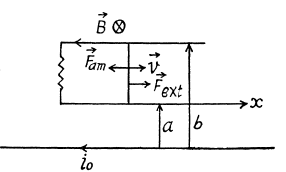
(a) The flux of 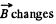 through the loop due to the movement of the connector. According to Lenz’s law, the current in the loop will be anticlockwise. The magnitude of motional e.m.f.
through the loop due to the movement of the connector. According to Lenz’s law, the current in the loop will be anticlockwise. The magnitude of motional e.m.f.
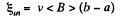
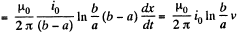
So, induced current
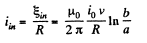
(b) The force required to maintain the constant velocity of the connector must be the magnitude equal to that of Ampere’s acting on the connector, but in opposite direction.
So, 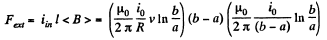
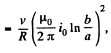 and will be directed as shown in the (Fig.)
and will be directed as shown in the (Fig.)
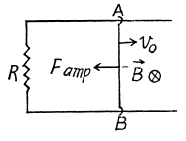
Q. 302. A conducting rod AB of mass m slides without friction over two long conducting rails separated by a distance l (Fig. 3.88). At the left end the rails are interconnected by a resistance R. The system is located in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the loop. At the moment t = 0 the rod AB starts moving to the right with an initial velocity vo. Neglecting the resistances of the rails and the rod AB, as well as the self-inductance, find:
(a) the distance covered by the rod until it comes to a standstill;
(b) the amount of heat generated in the resistance R during this process.
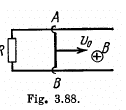
Solution. 302. (a) The flux through the loop changes due to the movement of the rod AB. Recording to Lenz’s law current should be anticlockwise in sense as we have assumed 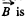 directed into the plane o f the loop. The motion e.m .f
directed into the plane o f the loop. The motion e.m .f 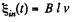
and, induced current 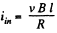
From Newton’s law in projection form fx = mwx
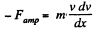
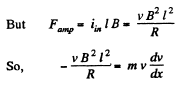
or, 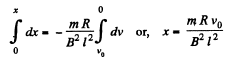
(b) From equation of energy conservation; Ef - Ei + Heat liberated = A cell + Aext


Q. 303. A connector AB can slide without friction along a Hshaped conductor located in a horizontal plane (Fig. 3.89). The connector has a length l, mass m, and resistance R. The whole system is located in a uniform magnetic field of induction B directed vertically. At the moment t = 0 a constant horizontal force F starts acting on the connector shifting it translationwise to the right. Find how the velocity of the connector varies with time t. The inductance of the loop and the resistance of the II-shaped conductor are assumed to be negligible.
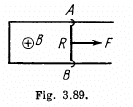
Solution. 303. With the help of the calculation, done in the previous problem, Ampere’s force on the connector,
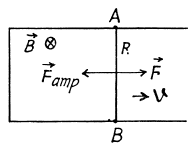

Now from Newton’s second law,
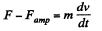
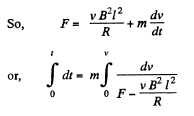
or, 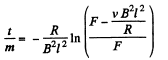
Thus 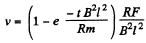
Q. 304. Fig. 3.90 illustrates plane figures made of thin conductors which are located in a uniform magnetic field directed away from a reader beyond the plane of the drawing. The magnetic induction starts diminishing. Find how the currents induced in these loops are directed.
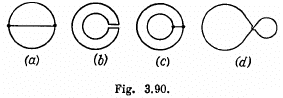
Solution. 304. According to Lenz, the sense of induced e.m.f. is such that it opposes the cause of change of flux. In our problem, magnetic field is directed away from the reader and is diminishing.
So, in figure (a), in the round conductor, it is clockwise and there is no current in the connector
In figure (b) in the outside conductor, clockwise.
In figure (c) in both the conductor, clockwise; and there is no current in the connector to obey the charge conservation.
In figure (d) in the left side of the figure, clockwise.
Q. 305. A plane loop shown in Fig. 3.91 is shaped as two squares with sides a = 20 cm and b = 10 cm and is introduced into a uniform magnetic field at right angles to the loop's plane. The magnetic induction varies with time as B = B0 sin ωt, where B0 = 10 mT and ω = 100 s-1 . Find the amplitude of the current induced in the loop if its resis- tance per unit length is equal to p = 50 mΩ/m. The inductance of the loop is to be neglected.
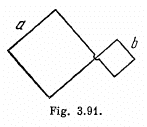
Solution. 305. The loops are connected in such a way that if the current is clockwise in one, it is anticlockwise in the other. Hence the e.m.f. in loop b opposes the e.m.f. in loop a.
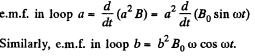
Hence, net e.m.f. in the circuit 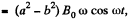 as both the e.m.f’s are in opposite sense, and resistance of the circuit = 4 (a + b) p
as both the e.m.f’s are in opposite sense, and resistance of the circuit = 4 (a + b) p
Therefore, the amplitude of the current 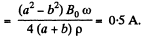
Q. 306. A plane spiral with a great num- ber N of turns wound tightly to one another is located in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the spiral's plane. The outside radius of the spiral's turns is equal to a. The magnetic induction varies with time as B = B0 sin ωt, where B0 and ω are constants. Find the amplitude of emf induced in the spiral
Solution. 306. The flat shape is made up of concentric loops, having different radii, varying from 0 to a.
Let us consider an elementary loop of radius r, then e.m.f. induced due to this loop 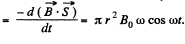
and the total induced e.m.f.,
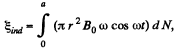 (1)
(1)
where π r2 ω cos ωt is the contribution of one turn of radius r and dN is the number of turns in the interval [r, r + dr].
So, 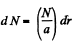 (2)
(2)
From (1) and (2), 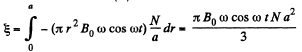
Maximum value of e.m.f. amplitude 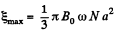
Q. 307. A H-shaped conductor is located in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the conductor and varying with time at the rate 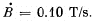 A conducting connector starts moving with an acceleration w = 10 cm/s2 along the parallel bars of the conductor. The length of the connector is equal to l = 20 cm. Find the emf induced in the loop t = 2.0 s after the beginning of the motion, if at the moment t = 0 the loop area and the magnetic induction are equal to zero. The inductance of the loop is to be neglected.
A conducting connector starts moving with an acceleration w = 10 cm/s2 along the parallel bars of the conductor. The length of the connector is equal to l = 20 cm. Find the emf induced in the loop t = 2.0 s after the beginning of the motion, if at the moment t = 0 the loop area and the magnetic induction are equal to zero. The inductance of the loop is to be neglected.
Solution. 307. The flux through the loop changes due to the variation in 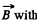 time and also due to the movement of the connector.
time and also due to the movement of the connector.
So , 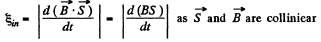
But, B, after t sec. of beginning of motion - Bt, and S becomes 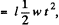 as connector starts moving from rest with a constant acceleration w.
as connector starts moving from rest with a constant acceleration w.
So, 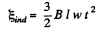
Q. 308. In a long straight solenoid with cross-sectional radius a and number of turns per unit length n a current varies with a constant velocity 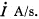 . Find the magnitude of the eddy current field strength as a function of the distance r from the solenoid axis. Draw the approximate plot of this function.
. Find the magnitude of the eddy current field strength as a function of the distance r from the solenoid axis. Draw the approximate plot of this function.
Solution. 308. 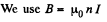
Then, from the law of electromagnetic induction
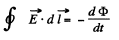
So, for r < a
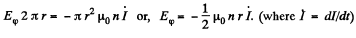
For r>a
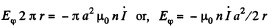
The meaning of minus sign can be deduced from Lenz's law.
Q. 309. A long straight solenoid of cross-sectional diameter d = 5 cm and with n = 20 turns per one cm of its length has a round turn of copper wire of cross-sectional area S = 1.0 mm2 tightly put on its winding. Find the current flowing in the turn if the current in the solenoid winding is increased with a constant velocity 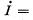 100 A/s. The inductance of the turn is to be neglected.
100 A/s. The inductance of the turn is to be neglected.
Solution. 309. The e.m.f. induced in the turn is 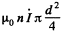
The resistance is 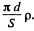
So, the current is 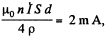 where p is the resistivity of copper.
where p is the resistivity of copper.
Q. 310. A long solenoid of cross-sectional radius a has a thin insulated wire ring tightly put on its winding; one half of the ring has the resistance η times that of the other half. The magnetic induction produced by the solenoid varies with time as B = bt, where b is a constant. Find the magnitude of the electric field strength in the ring.
Solution. 310. The changing magnetic field will induce an e.m.f. in the ring, which is obviously equal, in the two parts by symmetry (the e.m.f. induced by electromagnetic induction does not depend on resistance). The current, that will flow due to this, will be different in the two parts. This will cause an acceleration of charge, leading to the setting up of an electric field E which has opposite sign in the two parts. Thus,
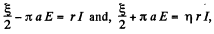
where 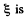 the total induced e.m.f. From this,
the total induced e.m.f. From this,
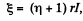
and 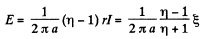
But by Faraday's law 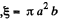
so, 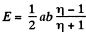
Q. 311. A thin non-conducting ring of mass m carrying a charge q can freely rotate about its axis. At the initial moment the ring was at rest and no magnetic field was present. Then a practically uniform magnetic field was switched on, which was perpendicular to the plane of the ring and increased with time according to a certain law B (t). Find the angular velocity ω of the ring as a function of the induction B (t).
Solution. 311. Go to the rotating frame with an instantaneous angular velocity 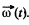 In this frame, a Coriolis force,
In this frame, a Coriolis force, 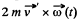
acts which must be balanced by the magnetic force, 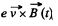
Thus,
(It is assumed that 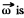 small and varies slowly, so ω2 and ω can be neglected.)
small and varies slowly, so ω2 and ω can be neglected.)
Q. 312. A thin wire ring of radius a and resistance r is located inside a long solenoid so that their axes coincide. The length of the solenoid is equal to l, its cross-sectional radius, to b. At a certain moment the solenoid was connected to a source of a constant voltage V. The total resistance of the circuit is equal to R. Assuming the inductance of the ring to be negligible, find the maximum value of the radial force acting per unit length of the ring.
Solution. 312. The solenoid has an inductance,
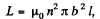
where n = number of turns of the solenoid per unit length. When the solenoid is connected to the source an e.m.f. is set up, which, because of the inductance and resistance, rises slowly, according to the equation
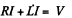
This has the well known solution,
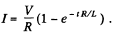
Corresponding to this current, an e.m.f. is induced in the ring. Its magnetic field 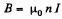 in the solenoid, produces a force per unit length,
in the solenoid, produces a force per unit length, 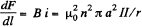
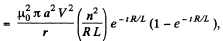
acting on each segment of the ring. This force is zero initially and zero for large t. Its maximum value is for some finite t. The maximum value of
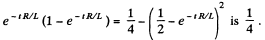
So 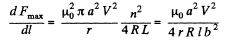
Q. 313. A magnetic flux through a stationary loop with a resistance R varies during the time interval 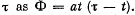 Find the amount of heat generated in the loop during that time. The inductance of the loop is to be neglected.
Find the amount of heat generated in the loop during that time. The inductance of the loop is to be neglected.
Solution. 313. The amount of heat generated in the loop during a small time interval dt,
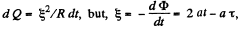
So, 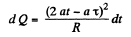
and hence, the amount of heat, generated in the loop during the time interval 0 to τ.
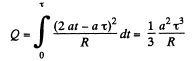
Q. 314. In the middle of a long solenoid there is a coaxial ring of square cross-section, made of conducting material with resistivity p. The thickness of the ring is equal to h, its inside and outside radii are equal to a and b respectively. Find the current induced in the ring if the magnetic induction produced by the solenoid varies with time as B = βt, where β is a constant. The inductance of the ring is to be neglected.
Solution. 314. Take an elementary ring of radius r and width dr. The e.m.f. induced in this elementary ring is πr2β.
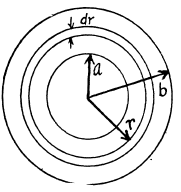
Now the conductance of this ring is.
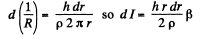
Integrating we get the total current,
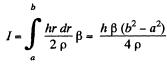
Q. 315. How many metres of a thin wire are required to manufacture a solenoid of length l0 = 100 cm and inductance L = 1.0 mH if the solenoid's cross-sectional diameter is considerably less than its length?
Solution. 315. Given 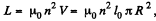 where R is the radius o f the solenoid.
where R is the radius o f the solenoid.
Thus, 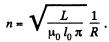
So, length of the wire required is,
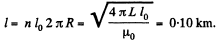
Q. 316. Find the inductance of a solenoid of length l whose winding is made of copper wire of mass m. The winding resistance is equal to R. The solenoid diameter is considerably less than its length.
Solution. 316. From the previous problem, we know that,
l' = length of the wire needed 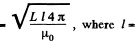 length of solenoid here.
length of solenoid here.
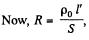 (where S = area of crossection of the wire. Also m = p S l')
(where S = area of crossection of the wire. Also m = p S l')
Thus, 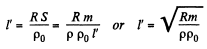
where p0 = resistivity of copper and p = its density.
Equating, 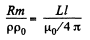
or, 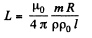
Q. 317. A coil of inductance L = 300 mH and resistance R = 140 mΩ is connected to a constant voltage source. How soon will the coil current reach η = 50% of the steady-state value?
Solution. 317. The current at time t is given by,
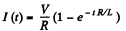
The steady state value is, 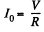
and 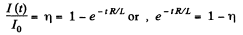
or, 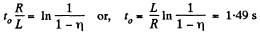
Q. 318. Calculate the time constant τ of a straight solenoid of length l = 1.0 m having a single-layer winding of copper wire whose total mass is equal to m = 1.0 kg. The cross-sectional diameter of the solenoid is assumed to be considerably less than its length.
Note. The time constant ti is the ratio LIR, where L is inductance and R is active resistance.
Solution. 318. The time constant τ is given by
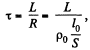
where, p0 = resistivity, l0 = length of the winding wire, S = cross section of the wire. But
But 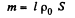
So eliminating
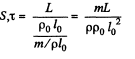
From problem Q.315 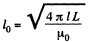
(note the interchange of l and l0 because of difference in notation here.)
Thus,
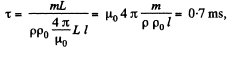
Q. 319. Find the inductance of a unit length of a cable consisting of two thin-walled coaxial metallic cylinders if the radius of the outside cylinder η = 3.6 times that of the inside one. The permeability of a medium between the cylinders is assumed to be equal to unity.
Solution. 319. Between the cables, where a< r<b , the magnetic field 
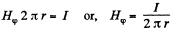
So 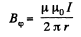
The associated flux per unit length is 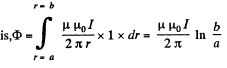
Hence, the inductance per unit length 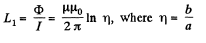
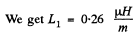
Q. 320. Calculate the inductance of a doughnut solenoid whose inside radius is equal to b and cross-section has the form of a square with side a. The solenoid winding consists of N turns. The space inside the solenoid is filled up with uniform paramagnetic having permeability μ.
Solution. 320. Within the solenoid, 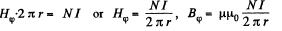
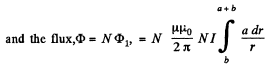
Finally, 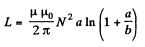
Q. 321. Calculate the inductance of a unit length of a double tape line (Fig. 3.92) if the tapes are separated by a distance h which is considerably less than their width b, namely, b/h = 50.
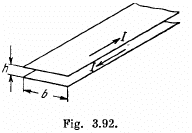
Solution. 321. Neglecting end effects the magnetic field B, between the plates, which is mainly parallel to the plates, is 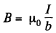
(For a derivation see Q.229 b)
Thus, the associated flux per unit length of the plates is,
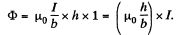
So, L1 = inductance per unit length 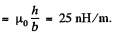
Q. 322. Find the inductance of a unit length of a double line if the radius of each wire is II times less than the distance between the axes of the wires. The field inside the wires is to be neglected, the permeability is assumed to be equal to unity throughout, and η ≫ 1
Solution. 322. For a single current carrying wire 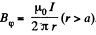 For the double line cable, with current, flowing in opposite directions, in the two conductors,
For the double line cable, with current, flowing in opposite directions, in the two conductors,
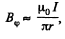 between the cables, by superposition. The associated flux is,
between the cables, by superposition. The associated flux is,
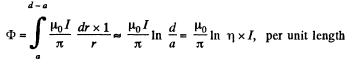
Hence, 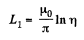
is the inductance per unit length
Q. 323. A superconducting round ring of radius a and inductance L was located in a uniform magnetic field of induction B. The ring plane was parallel to the vector B, and the current in the ring was equal to zero. Then the ring was turned through 90° so that its plane became perpendicular to the field. Find:
(a) the current induced in the ring after the turn;
(b) the work performed during the turn.
Solution. 323. In a superconductor there is no resistance, Hence,
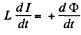
So integrating, 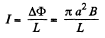
because 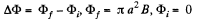
Also , the work done is 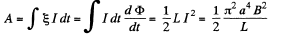
Q. 324. A current I0 = 1.9 A flows in a long closed solenoid. The wire it is wound of is in a superconducting state. Find the current flowing in the solenoid when the length of the solenoid is increased by η = 5%.
Solution. 324. In a solenoid, the inductance 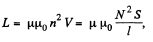
where S = area of cross section of the solenoid, l = its length, 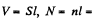 total number of turns.
total number of turns.
When the length of the solenoid is increased, for example, by pulling it, its inductance will decrease. If the current remains unchanged, the flux, linked to the solenoid, will also decrease. An induced e.m.f. will then come into play, which by Lenz’s law will try to oppose the decrease of flux, for example, by increasing the current. In the superconducting state the flux will not change and so,

Hence, 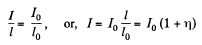
Q. 325. A ring of radius a = 50 mm made of thin wire of radius b = 1.0 mm was located in a uniform magnetic field with induction B = 0.50 mT so that the ring plane was perpendicular to the vector B. Then the ring was cooled down to a superconducting state, and the magnetic field was switched off. Find the ring current after that. Note that the inductance of a thin ring along which the surface current flows is equal to 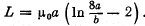
Solution. 325. The flux linked to the ring can not change on transition to the superconduction state, for reasons, similar to that given above. Thus a current / must be induced in the ring, where,
Q. 326. A closed circuit consists of a source of constant  a choke coil of inductance L connected in series. The active resistance of the whole circuit is equal to R. At the moment t = 0 the choke coil inductance was decreased abruptly η times. Find the current in the circuit as a function of time t.
a choke coil of inductance L connected in series. The active resistance of the whole circuit is equal to R. At the moment t = 0 the choke coil inductance was decreased abruptly η times. Find the current in the circuit as a function of time t.
Instruction. During a stepwise change of inductance the total magnetic flux (flux linkage) remains constant.
Solution. 326. We write the equation of the circuit as,
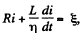
for t > 0. The current at t - 0 just after inductance is changed, is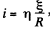 so that the flux through the inductance is unchanged.
so that the flux through the inductance is unchanged.
We look for a solution of the above equation in the form
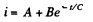
Substituting 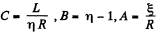
Thus, 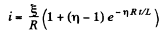
Q. 327. Find the time dependence of the current flowing through the inductance L of the circuit shown in Fig. 3.93 after the switch Sw is shorted at the moment t = 0.
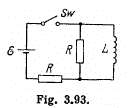
Solution. 327.
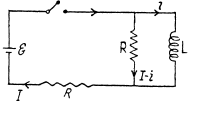
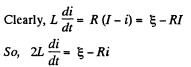
This equation has the solution (as in Q.312)
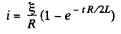
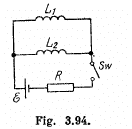
Q. 328. In the circuit shown in Fig. 3.94 an 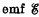 , a resistance R, and coil inductances L1 and L2 are known. The internal resistance of the source and the coil resistances are negligible. Find the steadystate currents in the coils after the switch Sw was shorted.
, a resistance R, and coil inductances L1 and L2 are known. The internal resistance of the source and the coil resistances are negligible. Find the steadystate currents in the coils after the switch Sw was shorted.
Solution. 328. The equations are,
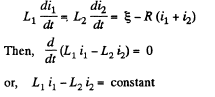
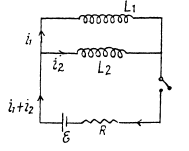
But initially at 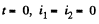 so constant must be zero and at all times,
so constant must be zero and at all times,
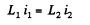
In the final steady atate, current must obviously be 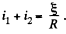 Thus in steady state,
Thus in steady state,
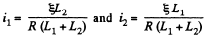
Q. 329. Calculate the mutual inductance of a long straight wire and a rectangular frame with sides a and b. The frame and the wire lie in the same plane, with the side b being closest to the wire, separated by a distance l from it and oriented parallel to it.
Solution. 329. Here 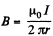 at a distance r from the wire. The flux through the frame is obtained as,
at a distance r from the wire. The flux through the frame is obtained as,
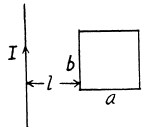
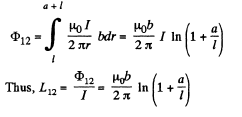
Q. 330. Determine the mutual inductance of a doughnut coil and an infinite straight wire passing along its axis. The coil has a rectangular cross-section, its inside radius is equal to a and the outside one, to b. The length of the doughnut's cross-sectional side parallel to the wire is equal to h. The coil has N turns. The system is located in a uniform magnetic with permeability μ.
Solution. 330.
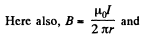
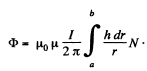
Thus, 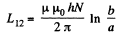
Q. 331. Two thin concentric wires shaped as circles with radii a and b lie in the same plane. Allowing for a ≪ b, find:
(a) their mutual inductance;
(b) the magnetic flux through the surface enclosed by the outside wire, when the inside wire carries a current I.
Solution. 331. The direct calculation of the  is a rather complicated problem, since the configuration of the field itself is complicated. However, the application of the reciprocity theorem simplifies the solution of the problem. Indeed, let the same current i flow through loop 2. Then the magnetic flux created by this current through loop 1 can be easily found.
is a rather complicated problem, since the configuration of the field itself is complicated. However, the application of the reciprocity theorem simplifies the solution of the problem. Indeed, let the same current i flow through loop 2. Then the magnetic flux created by this current through loop 1 can be easily found.
Magnetic induction at the centre of the loop, 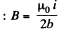
So, flux throug loop 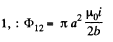
and from reciprocity theorem,
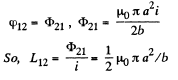
Q. 332. A small cylindrical magnet M (Fig. 3.95) is placed in the centre of a thin coil of radius a consisting of N turns. The coil is connected to a ballistic galvanometer. The active resistance of the whole circuit is equal to R. Find the magnetic moment of the magnet if its removal from the coil results in a charge q flowing through the galvanometer.
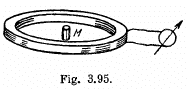
Solution. 332. Let 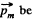 be the magnetic moment of the magnet Af. Then the magnetic field due to this magnet is,
be the magnetic moment of the magnet Af. Then the magnetic field due to this magnet is,
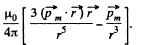
The flux associated with this, when the magnet is along the axis at a distance x from the centre, is
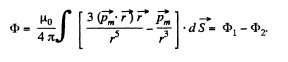
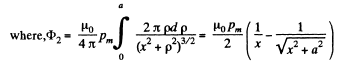
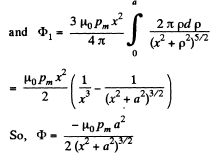
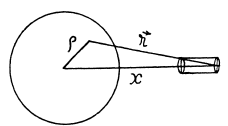
When the flux changes, an e.m.f. 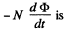 induced and a current
induced and a current 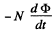 flows. The total charge q, flowing, as the magnet is removed to infinity from x = 0 is,
flows. The total charge q, flowing, as the magnet is removed to infinity from x = 0 is,
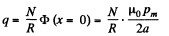
or, 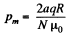
Q. 333. Find the approximate formula expressing the mutual inductance of two thin coaxial loops of the same radius a if their centres are separated by a distance l, with l ≫ a.
Solution. 333. If a current l flows in one of the coils, the magnetic field at the centre of the other coil is,
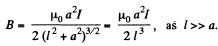
The flux associated with the second coil is then approximately 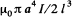
Hence, 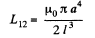
Q. 334. There are two stationary loops with mutual inductance L12. The current in one of the loops starts to be varied as I1 = αt, where α is a constant, t is time. Find the time dependence I2 (t) of the current in the other loop whose inductance is L2 and resistance R.
Solution. 334. When the current in one of the loop is 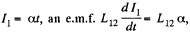 is induced in the other loop. Then if the current in the other loop is I2 we must have,
is induced in the other loop. Then if the current in the other loop is I2 we must have,
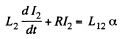
This familiar equation has the solution,
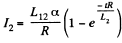 which is the required current
which is the required current
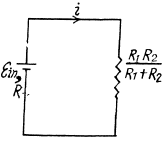
Q. 335. A coil of inductance L = 2.0 µH and resistance R = 1.0 Ω is connected to a source of constant 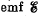 = 3.0 V (Fig. 3.96). A resistance R0 = 2.0 Ω is connected in parallel with the coil. Find the amount of heat generated in the coil after the switch Sw is disconnected. The internal resistance of the source is negligible.
= 3.0 V (Fig. 3.96). A resistance R0 = 2.0 Ω is connected in parallel with the coil. Find the amount of heat generated in the coil after the switch Sw is disconnected. The internal resistance of the source is negligible.
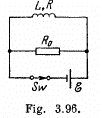
Solution. 335. Initially, after a steady current is set up, the current is flowing as shown.
In steady condition 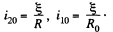
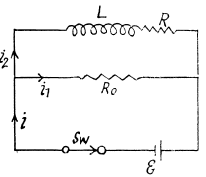
When the switch is disconnected, the current through R0 changes from i10 to the right, to i20 to the left. (The current in the inductance cannot change suddenly.). We then have the equation,
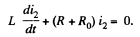
This equation has the solution 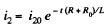
The heat dissipated in the coil is,
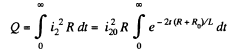
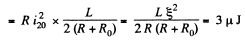
Q. 336. An iron tore supports N = 500 turns. Find the magnetic field energy if a current I = 2.0 A produces a magnetic flux across the tore's cross-section equal to 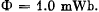
Solution. 336. To find the magnetic field energy we recall that the flux varies linearly with current Thus, when the flux 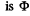 for current i, we can write
for current i, we can write 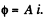 The total energy inclosed in the field, when the current is /, is
The total energy inclosed in the field, when the current is /, is
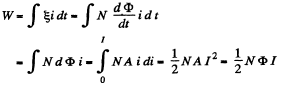
The characteristic factor 1/2 appears in this way.
Q. 337. An iron core shaped as a doughnut with round cross-section of radius a = 3.0 cm carries a winding of N = 1000 turns through which a current I = 1.0 A flows. The mean radius of the doughnut is b = 32 cm. Using the plot in Fig. 3.76, find the magnetic energy stored up in the core. A field strength H is supposed to be the same throughout the cross-section and equal to its magnitude in the centre of the cross-section.
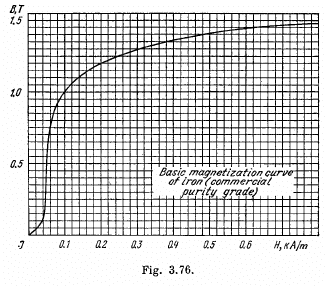
Solution. 337. We apply circulation theorem
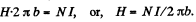
Thus the total energy,
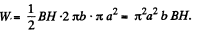
Given N , l , b we know H , and can find out B from the B - H curve. Then W can be calculated.
Q. 338. A thin ring made of a magnetic has a mean diameter d = 30 cm and supports a winding of N = 800 turns. The crosssectional area of the ring is equal to S = 5.0 cm2. The ring has a cross-cut of width b = 2.0 mm. When the winding carries a certain current, the permeability of the magnetic equals μ = 1400. Neglecting the dissipation of magnetic flux at the gap edges, find:
(a) the ratio of magnetic energies in the gap and in the magnetic;
(b) the inductance of the system; do it in two ways: using the flux and using the energy of the field.
Solution. 338. From 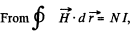
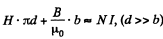
Also, 
Since B is continuous across the gap, B is given by,
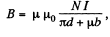 both in the magnetic and the gap.
both in the magnetic and the gap.
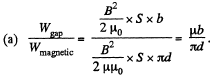
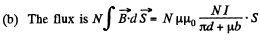
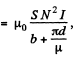
So, 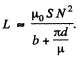
Energy wise; total energy
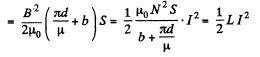
The L, found in the one way, agrees with that, found in the other way. Note that, in calculating the flux, we do not consider the field in the gap, since it is not linked to the winding. But the total energy includes that of the gap.
Q. 339. A long cylinder of radius a carrying a uniform surface charge rotates about its axis with an angular velocity ω. Find the magnetic field energy per unit length of the cylinder if the linear charge density equals λ, and μ, = 1.
Solution. 339. When the cylinder with a linear charge density λ rotates with a circular frequency co, a surface current density (charge / length x time) of 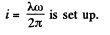
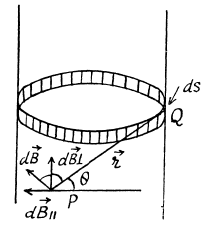
The direction of the surface current is normal to the plane of paper at Q and the contribution of this current to the magnetic field at P is 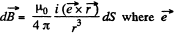 is the direction of the current. In magnitude,
is the direction of the current. In magnitude, 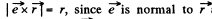 and the direction of
and the direction of 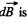 shown.
shown.
It’s component, 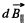 cancels out by cylindrical symmetry. The component that survives is,
cancels out by cylindrical symmetry. The component that survives is,
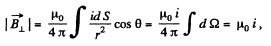
where we have used 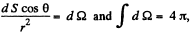 the total solid angle around any point.
the total solid angle around any point.
The magnetic field vanishes outside the cylinder by similar argument.
The total energy per unit length of the cylinder is,
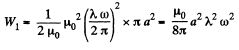
Q. 340. At what magnitude of the electric field strength in vacuum the volume energy density of this field is the same as that of the magnetic field with induction B = 1.0 T (also in vacuum).
Solution. 340. 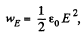 for the electric field,
for the electric field,
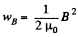 for the magnetic field.
for the magnetic field.
Thus, 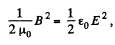
when 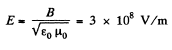
Q. 341. A thin uniformly charged ring of radius a = 10 cm rotates about its axis with an angular velocity ω = 100 rad/s. Find the ratio of volume energy densities of magnetic and electric fields on the axis of the ring at a point removed from its centre by a distance l = a.
Solution. 341. The electric field at P is,
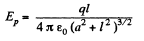
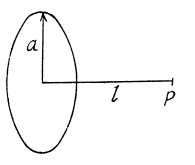
To get the magnetic field, note that the rotating ring constitutes a current i - q ω/2 π, and the corresponding magnetic field at P is,
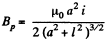
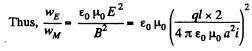
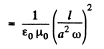
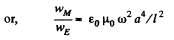
Q. 342. Using the expression for volume density of magnetic energy, demonstrate that the amount of work contributed to magnetization of a unit volume of para- or diamagnetic, is equal to A = — JB/2.
Solution. 342. The total eneigy of the magnetic field is,
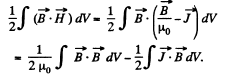
The second term can be interpreted as the energy of magnetization, and has the density
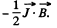
Q. 343. Two identical coils, each of inductance L, are interconnected (a) in series, (b) in parallel. Assuming the mutual inductance of the coils to be negligible, find the inductance of the system in both cases.
Solution. 343. (a) In series, the current I flows through both coils, and the total e.m.f. induced, when the current changes is,
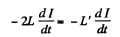
or, L' = 2L
(b) In parallel, the current flowing through either coil is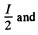 the e.m.f. induced is
the e.m.f. induced is
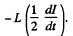
Equating this to 
Q. 344. Two solenoids of equal length and almost equal crosssectional area are fully inserted into one another. Find their mutual inductance if their inductances are equal to L1 and L2.
Solution. 344. We use 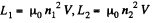
So, 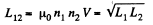
Q. 345. Demonstrate that the magnetic energy of interaction of two current-carrying loops located in vacuum can be represented as 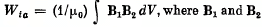 are the magnetic inductions within a volume element dV, produced individually by the currents of the first and the second loop respectively.
are the magnetic inductions within a volume element dV, produced individually by the currents of the first and the second loop respectively.
Solution. 345. The interaction energy is
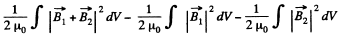
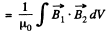
Here, if 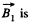 the magnetic field produced by the first of the current carrying loops, and
the magnetic field produced by the first of the current carrying loops, and 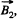 that of the second one, then the magnetic field due to both the loops will be
that of the second one, then the magnetic field due to both the loops will be 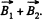
Q. 346. Find the interaction energy of two loops carrying currents I1 and I2 if both loops are shaped as circles of radii a and b, with a ≪ b. The loops' centres are located at the same point and their planes form an angle θ between them.
Solution. 346. We can think of the smaller coil as constituting a magnet of dipole moment,
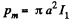
Its direction is normal to the loop and makes an angle θ with the direction of the magnetic field, due to the bigger loop. This magnetic Geld is,
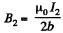
The interaction energy has the magnitude,
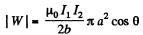
Its sign depends on the sense of the currents.
Q. 347. The space between two concentric metallic spheres is filled up with a uniform poorly conducting medium of resistivity p and permittivity ε. At the moment t = 0 the inside sphere obtains a certain charge. Find:
(a) the relation between the vectors of displacement current density and conduction current density at an arbitrary point of the medium at the same moment of time;
(b) the displacement current across an arbitrary closed surface wholly located in the medium and enclosing the internal sphere, if at the given moment of time the charge of that sphere is equal to q.
Solution. 347. (a) There is a radial outward conduction current Let Q be the instantaneous charge on the inner sphere, then,
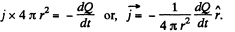
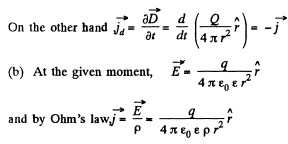
Then, 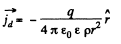
and 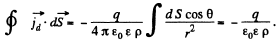
The surface integral must be - ve because 
Q. 348. A parallel-plate capacitor is formed by two discs with a uniform poorly conducting medium between them. The capacitor was initially charged and then disconnected from a voltage source. Neglecting the edge effects, show that there is no magnetic field between capacitor plates.
Solution. 348. Here also we see that neglecting edge effects, 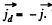 Thus Maxwell’s equations reduce to ,div
Thus Maxwell’s equations reduce to ,div 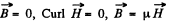
A general solution of this equation is 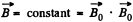 can be thought of as an extraneous extraneous magnetic field. If it is zero,
can be thought of as an extraneous extraneous magnetic field. If it is zero, 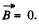
Q. 349. A parallel-plate air condenser whose each plate has an area S = 100 cm2 is connected in series to an ac circuit. Find the electric field strength amplitude in the capacitor if the sinusoidal current amplitude in lead wires is equal to Im. = 1.0 mA and the current frequency equals ω = 1.6-107 s-1.
Solution. 349. Given I = Im sin ωt. We see that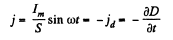
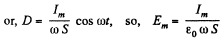 is the amplitude of the electric field and is 7V / cm
is the amplitude of the electric field and is 7V / cm
Q. 350. The space between the electrodes of a parallel-plate capacitor is filled with a uniform poorly conducting medium of conductivity σ and permittivity ε. The capacitor plates shaped as round discs are separated by a distance d. Neglecting the edge effects, find the magnetic field strength between the plates .at a distance r from their axis if an ac voltage V = Vm, cos cot is applied to the capacitor.
Solution. 350. The electric field between the plates can be written as,

This gives rise to a conduction current,
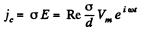
and a displacement current,
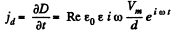
The total current is,
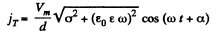
where, 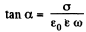 on taking the real part of the resultant.
on taking the real part of the resultant.
The corresponding magnetic field is obtained by using circulation theorem,
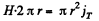
or, H = Hm cos (ωt + α), where,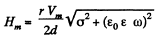
Q. 351. A long straight solenoid has n turns per unit length. An alternating current I = Im sin ωt flows through it. Find the displacement current density as a function of the distance r from the solenoid axis. The cross-sectional radius of the solenoid equals R.
Solution. 351. Inside the solenoid, there is a magnetic field,
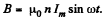
Since this varies in time there is an associated electric field. This is obtained by using,
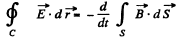
For 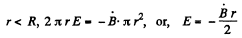
For 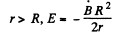
The associated displacement current density is,
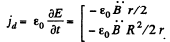
The answer, given in the book, is dimensionally incorrect without the factor ε0.
Q. 352. A point charge q moves with a non-relativistic velocity v = const. Find the displacement current density jd at a point located at a distance r from the charge on a straight line
(a) coinciding with the charge path;
(b) perpendicular to the path and passing through the charge.
Solution. 352. In the non-relativistic limit.
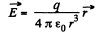
(a) On a straight line coinciding with the chaige path,
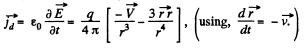
But in this case, 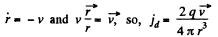
(b) In this 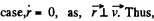
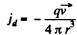
Q. 353. A thin wire ring of radius a carrying a charge q approaches the observation point P so that its centre moves rectilinearly with a constant velocity v. The plane of the ring remains perpendicular to the motion direction. At what distance xm, from the point P will the ring be located at the moment when the displacement current density at the point P becomes maximum? What is the magnitude of this maximum density?
Solution. 353. We have , 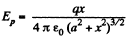
then 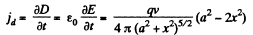
This is maximum, when x = xm = 0, and minimum at some other value. The maximum displacement current density is
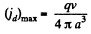
To check this we calculate 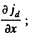
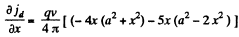
This vanishes for x = 0 and for 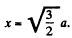 The latter is easily shown to be a smaller local minimum (negative maximum).
The latter is easily shown to be a smaller local minimum (negative maximum).
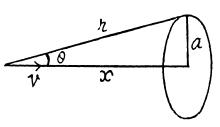
Q. 354. A point charge q moves with a non-relativistic velocity v = const. Applying the theorem for the circulation of the vector H around the dotted circle shown in Fig. 3.97, find H at the point A as a function of a radius vector r and velocity v of the charge.
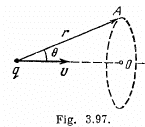
Solution. 354. We use Maxwell's equations in the form ,
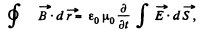
when the conduction current vanishes at the site.
We know that,
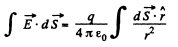
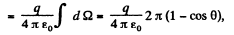
where, 2k (1 - cos θ) is the solid angle, formed by the disc like surface, at the charge.
Thus, 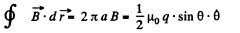
On the other hand 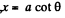
differentiating and using 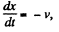
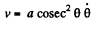
Thus, 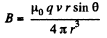
This can be written as, 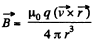
and 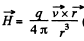 (The sense has to be checked independently.)
(The sense has to be checked independently.)
Q. 355. Using Maxwell's equations, show that
(a) a time-dependent magnetic field cannot exist without an electric field;
(b) a uniform electric field cannot exist in the presence of a timedependent magnetic field;
(c) inside an empty cavity a uniform electric (or magnetic) field can be time-dependent.
Solution. 355.
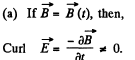
So, 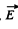 cannot vanish.
cannot vanish.
(b) Here also, curl 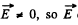 cannot be uniform.
cannot be uniform.
(c) Suppose for instance, 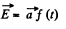
where 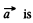 spatially and temporally fixed vector. Then
spatially and temporally fixed vector. Then 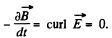 Generally speaking this contradicts the other equation curl
Generally speaking this contradicts the other equation curl 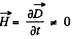 for in this case the left hand side is time independent but RHS. depends on time. The only exception is when f (r) is linear function. Then a uniform field
for in this case the left hand side is time independent but RHS. depends on time. The only exception is when f (r) is linear function. Then a uniform field 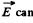 be time dependent.
be time dependent.
Q. 356. Demonstrate that the law of electric charge conservation, i.e. 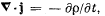 follows from Maxwell's equations.
follows from Maxwell's equations.
Solution. 356. From the equation Curl 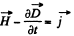
We get on taking divergence of both sides 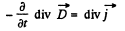
But div 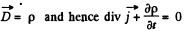
Q. 357. Demonstrate that Maxwell's equations 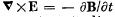 and
and 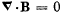 are compatible, i.e. the first one does not contradict the second one.
are compatible, i.e. the first one does not contradict the second one.
Solution. 357. From 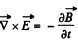
we get on taking diveigence
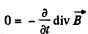
This is compatible with div 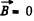
Q. 358. In a certain region of the inertial reference frame there is magnetic field with induction B rotating with angular velocity ω. Find 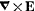 in this region as a function of vectors ω and B.
in this region as a function of vectors ω and B.
Solution. 358. A rotating magnetic field can be represented by,
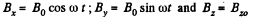
Then curl, 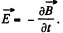
So, 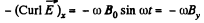
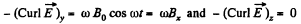
Hence, 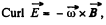
where, 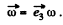
Q. 359. n the inertial reference frame K there is a uniform magnetic field with induction B. Find the electric field strength in the frame K' which moves relative to the frame K with a non-relativistic velocity v, with v⊥B. To solve this problem, consider the forces acting on an imaginary charge in both reference frames at the moment when the velocity of the charge in the frame K' is equal to zero.
Solution. 359. Consider a particle with charge ey moving with velocity 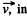 frame K. It experiences a force
frame K. It experiences a force 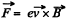
In the frame K', moving with velocity  to K, the particle is at rest. This means that there must be an electric field
to K, the particle is at rest. This means that there must be an electric field 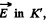 so that the particle experinces a force,
so that the particle experinces a force,
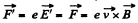
Thus, 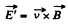
Q. 360. A large plate of non-ferromagnetic material moves with a constant velocity v = 90 cm/s in a uniform magnetic field with induction B = 50 mT as shown in Fig. 3.98. Find the surface density of electric charges appearing on the plate as a result of its motion.
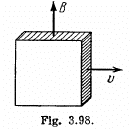
Solution. 360. Within the plate, there will appear a 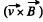 force, which will cause charges inside the plate to drift, until a countervailing electric field is set up. This electric field is related to By by E = eB, since v & B are mutually perpendicular, and E is perpendicular to both. The charge density ± σ, on the force of the plate, producing this electric field, is given by
force, which will cause charges inside the plate to drift, until a countervailing electric field is set up. This electric field is related to By by E = eB, since v & B are mutually perpendicular, and E is perpendicular to both. The charge density ± σ, on the force of the plate, producing this electric field, is given by
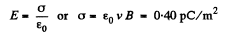
Q. 361. A long solid aluminum cylinder of radius a = 5.0 cm rotates about its axis in a uniform magnetic field with induction B = 10 mT. The angular velocity of rotation equals ω = 45 rad/s, with 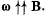 . Neglecting the magnetic field of appearing charges, find their space and surface densities.
. Neglecting the magnetic field of appearing charges, find their space and surface densities.
Solution. 361. Choose 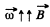 along the z-axis, and choose
along the z-axis, and choose 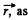 the cylindrical polar radius vector of a reference point (perpendicular distance from the axis). This point has the velocity,
the cylindrical polar radius vector of a reference point (perpendicular distance from the axis). This point has the velocity,
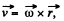
and experiences a 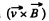 force, which m ust b e counterbalanced by an electric field,
force, which m ust b e counterbalanced by an electric field,
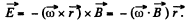
There must appear a space charge density,
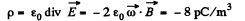
Since the cylinder, as a whole is electrically neutral, the surface of the cylinder must acquire a positive charge of surface density,
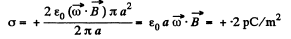
Q. 362. A non-relativistic point charge q moves with a constant velocity v. Using the field transformation formulas, find the magnetic induction B produced by this charge at the point whose position relative to the charge is determined by the radius vector r.
Solution. 362. In the reference frame K', moving with the particle,
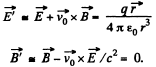
Here,  velocity of K', relative to the K frame, in which the particle has velocity
velocity of K', relative to the K frame, in which the particle has velocity 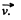
Clearly, 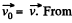 the second equation,
the second equation,
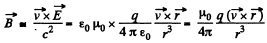
Q. 363. Using Eqs. (3.6h), demonstrate that if in the inertial reference frame K there is only electric or only magnetic field, in any other inertial frame K' both electric and magnetic fields will coexist simultaneously, with E' ⊥ B'
Solution. 363. Suppose, there is only electric field 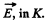 Then in K', considering nonrelativistic velocity
Then in K', considering nonrelativistic velocity 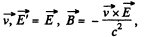
So, 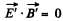
In the relativistic case,
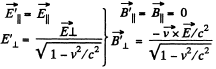
Now, 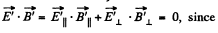
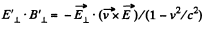
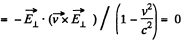
Q. 364. In an inertial reference frame K there is only magnetic field with induction B = b (yi — xj)/ (x2 + y2), where b is a constant, i and j are the unit vectors of the x and y axes. Find the electric field strength E' in the frame K' moving relative to the frame K with a constant non-relativistic velocity v = vk; k is the unit vector of the z axis. The z' axis is assumed to coincide with the z axis. What is the shape of the field E'
Solution. 364. 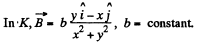
In 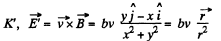
The electric field is radial 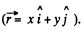
Q. 365. In an inertial reference frame K there is only electric field of strength E = a (xi + yj)/(x2 + y2), where a is a constant, i and j are the unit vectors of the x and y axes. Find the magnetic induction B' in the frame K' moving relative to the frame K with a constant non-relativistic velocity v = vk; k is the unit vector of the z axis. The z' axis is assumed to coincide with the z axis. What is the shape of the magnetic induction B'?
Solution. 365. 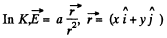
In 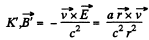
The magnetic lines are circular.
Q. 366. Demonstrate that the transformation formulas (3.6h) follow from the formulas (3.6i) at v0 ≪ c.
Solution. 366. In the non relativistic limit, we neglect v2/ c2 and write,
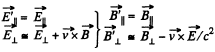
These two equations can be combined to give,
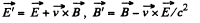
Q. 367. In an inertial reference frame K there is only a uniform electric field E = 8 kV/m in strength. Find the modulus and direction
(a) of the vector E', (b) of the vector B' in the inertial reference frame K' moving with a constant velocity v relative to the frame K at an angle α = 45° to the vector E. The velocity of the frame K' is equal to a β = 0.60 fraction of the velocity of light.
Solution. 367. Choose 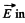 he direction of the z-axis,
he direction of the z-axis, 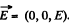 The frame K' is moving with velocity
The frame K' is moving with velocity 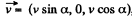 in the x - z plane. Then in the frame K',
in the x - z plane. Then in the frame K',
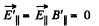
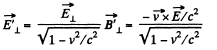
The vector along 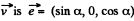 and the perpendicular vector in the x - z plane is
and the perpendicular vector in the x - z plane is
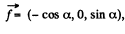
(a) Thus using 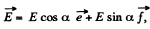
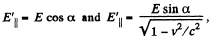
So 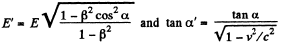
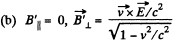
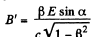
Q. 368. Solve a problem differing from the foregoing one by a magnetic field with induction B = 0.8 T replacing the electric field.
Solution. 368. Choose 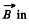 the z direction, and the velocity
the z direction, and the velocity 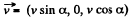 in the x - z plane, then in the K! frame,
in the x - z plane, then in the K! frame,
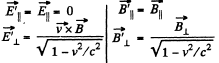
We find similarly, 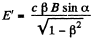
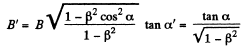
Q. 369. Electromagnetic field has two invariant quantities. Using the transformation formulas (3.6i), demonstrate that these quantities are
(a) EB; (b) E2 — c2B2.
Solution. 369. (a) We see that, 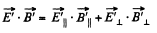
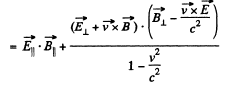
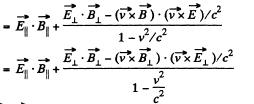
But, 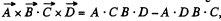
so, 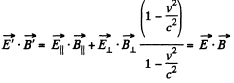
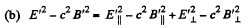
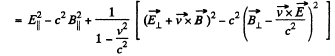
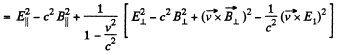
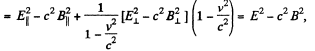
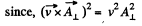
Q. 370. In an inertial reference frame K there are two uniform mutually perpendicular fields: an electric field of strength E = 40 kV/m and a magnetic field induction B = 0.20 mT. Find the electric strength E' (or the magnetic induction B') in the reference frame K' where only one field, electric or magnetic, is observed.
Instruction. Make use of the field invariants cited in the foregoing problem.
Solution. 370. In this case, 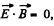 as the fields are mutually perpendicular. Also,
as the fields are mutually perpendicular. Also,
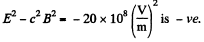
Thus, we can find a frame, in which E' = 0, and
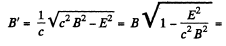
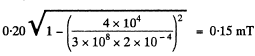
Q. 371. A point charge q moves uniformly and rectilinearly with a relativistic velocity equal to a β fraction of the velocity of light (β = v/c). Find the electric field strength E produced by the charge at the point whose radius vector relative to the charge is equal to r and forms an angle θ with its velocity vector.
Solution. 371. Suppose the charge qr moves in the positive direction of the x-axis of the frame K. Let us go over to the moving frame K', at whose origin the charge is at rest. We take the x and x' axes of the two frames to be coincident, and the y & y' axes, to be parallel.
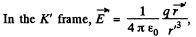
and this has the following components,
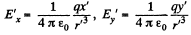
Now let us go back to the frame K. At the moment, when the origins of the two frames coincide, we take t * 0. Then,
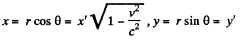
Also, 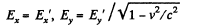
From these equations, 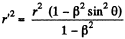
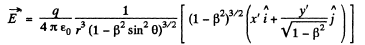
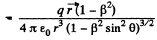
FAQs on Irodov Solutions: Electromagnetic Induction: Maxwell’s Equations - I. E. Irodov Solutions for Physics Class 11 & Class 12 - JEE
| 1. What are Maxwell's equations and how are they related to electromagnetic induction? |  |
| 2. How can Maxwell's equations be applied to solve problems related to electromagnetic induction? |  |
| 3. What are the key components of Maxwell's equations and how do they relate to electromagnetic induction? |  |
| 4. Can Maxwell's equations be used to analyze complex electromagnetic induction phenomena? |  |
| 5. What are some practical applications of Maxwell's equations in the context of electromagnetic induction? |  |
















