Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Carbon And Its Compounds, Solutions- 1 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
(Page No:220)
Question 1:
Name the element whose one of the allotropic forms is buck minster fullerene.
Solution : Carbon is the element whose one of the allotropic forms is buck minster fullerence
Question 2:
What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the formation of a large number of carbon compounds ?
Solution : Catenation and tetravalency are two properties of carbon which lead to the formation of large number of carbon compounds.
Question 3:
State whether the following statement is true or false :
Diamond and graphite are the covalent compounds of calcium element
Solution : This statement is false because diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon element
(Page No:221)
Question 4:
Name the scientist who disproved the ‘vital force theory’ for the formation of organic compounds.
Solution : Friedrich Wholer disproved the ‘vital force theory” for the formation of organic compounds.
Question 5:
Name the element whose allotropic form is graphite.
Solution : Diamond and graphite are allotropic form of carbon.
Question 6:
In addition to some propane and ethane, LPG cylinders contain mainly two isomers of another alkane. Name the two isomers and write their condensed structural formulae.
Solution : The two other isomers of alkane found in LPG cylinders are N-butane and iso-butane.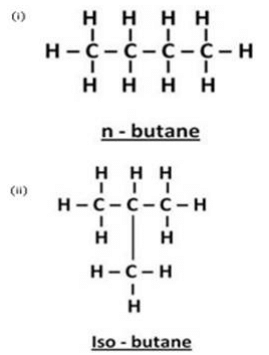
Question 7:
Buckminsterfullerene is a spherical molecule in which 60 carbon atoms are arranged in interlocking hexagonal and pentagonal rings of carbon atoms.
How many hexagons of carbon atoms are present in one molecule of buckminsterfullerene ?
How many pentagons of carbon atoms are present in one molecule of buckminsterfullerene ?
Solution :
(a) One C60 molecule contains 20 hexagons of carbon atoms.
(b) One C60 molecule contains 12 pentagons of carbon atoms.
Question 8:
Name the black substance of pencil. Will the current flow through the electrical circuit when we use the sharpened ends of the pencil to complete the circuit ?
Solution : Graphite is the black substance of pencil. When we use the sharpened ends of the pencil to complete the circuit, the current will flow through the electric circuit because graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Question 9:
How does graphite act as a lubricant?
Solution : In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded with 3 other carbon atoms to form hexagonal rings which join together by weak Vander Waal forces to form layers. Due to the weak force, these layers can slide over each other and therefore, graphite can be used as a lubricant.
Question 10:
Name the hardest natural substance known.
Solution : Diamond is the hardest natural substance known.
Question 11:
Which of the following molecule is called buckminsterfullerene ?
C90 C60 C70 C20
Solution : C60 is called buckministerfullerence.
Question 12:
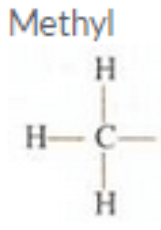
Give the name and structural formula of an alkyl group.
Solution : Methyl
Structural formulae:
Question 13:
Write the electron-dot structures for : (i) ethane, (ii) ethene, and (iii) ethyne.
Solution :
(i) The electron-dot structure for ethane is: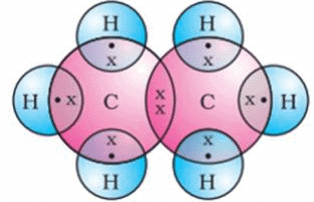
(ii) The electron-dot structure for ethene is: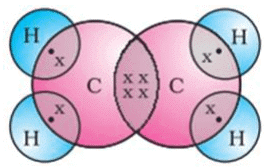
(iii) The electron-dot structure for ethyne is: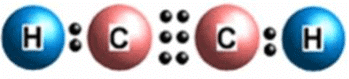
Question 14:
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound : C2H6
Solution : The IUPAC name of C2H6 is ethane.
Question 15:
Write the structural formula of propene.
Solution : The structural formulae of propene is: (C3H6)
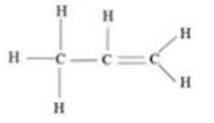 Question 16:
Question 16:
Write the structural formula of propyne.
Solution : The structural formulae of propane is: (C3H4)
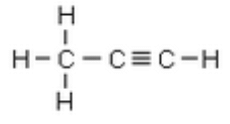 Question 17:
Question 17:
Write the structural formula of butane.
Solution : The structural formula of butane is: (C4H10)
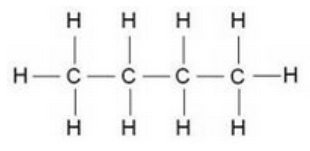
Question 18:
What do you call the compounds having the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements of atoms ?
Solution : Organic compounds with identical molecular formula but different structures are called isomers.
Question 19:
Write the names of any two isomers represented by the molecular formula C5H12.
Solution : Isopentane and neopentane are two isomers represented by the molecular formula C5H12.
Question 20:
Write down (i) structural formula, and (ii) electron-dot formula, of any one isomer of hexane (C6H14), other than n-hexane.
Solution :
(i) Isomer of hexane (C6H14 ) is 2-methylpentane.
Structural formula of 2-methylpentane (Isomer of hexane)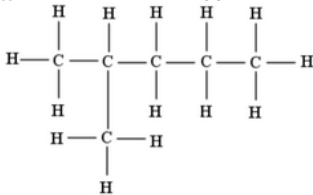
(ii) Electron-dot formula:
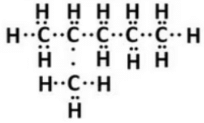
Question 21:
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) The form of carbon which is known as black lead is……………………..
(b) The form of carbon which is used as a lubricant at high temperature is……………………………
(c) Compounds of carbon with hydrogen alone are called…………………..
(d) CnH2n is the general formula of………………..
(e) Hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n-2 are called……………………..
(f) Ethene and ethyne are examples of…………….. hydrocarbons.
(g) Ethyne has…….. carbon-hydrogen single bonds.
(h) Carbon compounds have usually……………….. melting points and boiling points because they are……………… in nature.
(i) The property of carbon atoms to form long chains in compounds is called…………………………
(j) The general formula CnH2n for cycloalkanes is the same as that of……………………..
(k) The IUPAC name of ethylene is……………….
(l) The IUPAC name of acetylene is……………..
Solution :
(a) Graphite
(b) Graphite
(c) Hydrocarbons
(d) Alkene
(e) Alkynes
(f) Unsaturated
(g) Two
(h) Low; covalent
(i) Catenation
(j) Alkenes
(k) Ethene
(l) Ethyne
Question 22:
(a) What is the atomic number of carbon. Write its electronic configuration.
(b) What type of chemical bonds are formed by carbon ? Why ?
(c) Name the three allotropic forms of carbon.
Solution :
(a) The atomic number of electronic carbon is 6. Its configuration is 2, 4. Therefore, it contains 4 electrons in its outermost shell and it needs to gain or loss 4 electrons to attain stable noble gas configuration
(b) Carbon forms four covalent bonds to attain the novel gas configuration by sharing its valence electrons.
(c) Graphite, diamond and buckminsterfullerene are three allotropic forms of carbon.
Question 23:
(a) What is the general name of all the compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen ?
(b) Why does carbon form compounds mainly by covalent bonding ?
Solution :
(a) The general name of all the compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen is hydrocarbons.
(b) Carbon forms compounds mainly by forming covalent bonds because it can attain the novel gas configuration by sharing its valence electrons.
Question 24:
(a) What is meant by catenation ? Name two elements which exhibit the property of catenation.
(b) Write the names and structural formulae of all the possible isomers of hexane.
Solution :
(a) Carbon atoms have the unique ability to form bonds with other carbon atoms to form to large molecules. This property is called catenation. Carbon and silicon elements exhibit the property of catenation.
(b) Isomers of hexane:
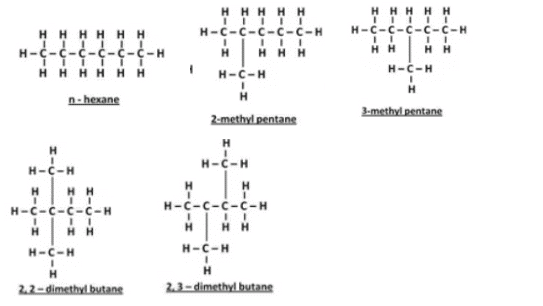
Question 25:
(a) What is buckminsterfullerene ? How is it related to diamond and graphite ?
(b) Why is diamond used for making cutting tools (like glass cutters) but graphite is not ?
(c) Why is graphite used for making dry cell electrodes but diamond is not ?
Solution :
(a) Buckminsterfullerene is an allotrope of carbon that was discovered in 1985 containing clusters of 60 carbon atoms joined together to form spherical molecules. When it is burnt, it forms carbon dioxide leaving nothing behind which means it is only made up of carbon and this is how it is related to diamond and graphite.
(b) Diamond is used for making cutting tools because of its hardness but graphite is not used as it is soft.
(c) Graphite is a good conductor of electricity while diamond is not and that’s why graphite is used for making dry cell electrodes but diamond is not.
(Page No:222)
Question 26:
(a) Give the general formula of an : (i) alkane (ii) alkene (in) alkyne.
(b) Classify the following compounds as alkanes, alkenes and alkynes :
C2H4, C3H4, C4H8, C5H12, C5H8, C3H8, C6H6
Solution :
(a) (i) CnH2n+2
(ii) CnH2n
(iii) CnH2n-2
(b) Alkanes:
C5H12
C3H8
Alkenes:
C2H4
C4H8
Alkynes:
C3H4
C5H8
Question 27:
(a) Friedrich Wohler converted an inorganic compound into an organic compound in the laboratory.
(i) Give the name and formula of inorganic compound.
(ii) Write the name and formula of organic compound formed.
(b) Give the molecular formula of butane and mention the names of its two isomers. Name one fuel which contains both these isomers.
Solution :
(a) (i) Friedrich Wohler disproved the vital force theory by preparing urea from inorganic compound called ammonium cyanate (NH4 CNO).
(ii) Formed organic compound is urea CO(NH2)2
(b) Molecular formula of butane is C4H10 . The isomers of butane are n-butane and 2- methylpropane. LPG (a fuel) contains both these isomers.
Question 28:
(a) Give IUPAC names and formulae of an organic compound containing single bonds and the other
containing a triple bond.
(b) Which of the following is the molecular formula of benzene ?
C6H6, C6H10, C6H12, C6H14
(c) Which of the two has a branched chain : isobutane or normal butane ?
Solution :
(a) The IUPAC name of an organic compound which has single bonds is ethane. The molecular formula of propane is C2H6 .
The IUPAC name of an organic compound which has triple bond is ethyne. The molecular formula of ethyne is C2H2 .
(b) The molecular formula of benzene is C6H6.
(c) Isobutane has branches chain
Question 29:
Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of catenation of the two elements. Give reasons.
Solution : Carbon forms very strong bonds with other elements and makes the carbon compound very stable whereas silicon forms compound with hydrogen which have chains of upto seven or eight atoms, but these compounds are very reactive because of weak bonds.
Question 30:
(a) How can diamonds be made artificially ? How do synthetic diamonds differ from natural ones ?
(b) Give any two differences between the properties of diamond and graphite. What causes these differences ?
Solution :
(a) Diamonds can be synthesised by subjecting pure carbon to very high pressure and temperature. These synthetic diamonds are small but are otherwise indistinguishable from natural diamonds.
(b) (i) Diamond is a bad conductor of electricity whereas graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
(ii) Diamond is a hard substance whereas graphite is soft.
The difference in the physical properties of diamond and graphite arises because of the arrangements of carbon atoms different in both diamond and graphite.
Question 31:
(a) Why does the element carbon from a large number of carbon compounds ?
(b) Write down the structures and names of two isomers of butane (C4H10)
Solution :
(a) The element carbon forms a large number of carbon compounds because carbon atoms can getlinked to each other by covalent bonds to form long chains.
(b) Isomer of butane (C4H10):
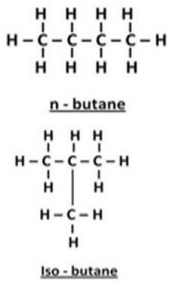
Question 32:
(a) Give the name and structural formula of one member each of the following :
(i) alkane (ii) alkene (iii) alkyne (iv) cycloalkane
(b) Give the common name of (i) ethyne, and (ii) ethene.
(c) Write the molecular formula and structure of benzene.
Solution :
(i) alkane: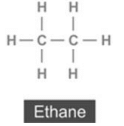
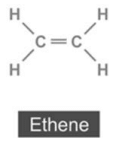
(ii) Alkene:
(iii) Alkyne: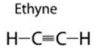
(iv) Cycloalkane: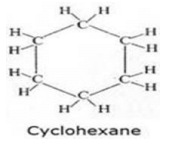
(b) (i) The common name of ethyne is acetylene.
(ii) The common name of ethane is ethylene.
(c) The molecular formula of benzene is C6H6.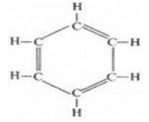
Question 33:
(a) What is the unique property of carbon atom ? How is this property helpful to us ?
(b) Explain why, diamond is hard while graphite is soft (though both are made of carbon atoms).
Solution :
(a) The unique property of carbon atoms is their ability to link with each other through covalent bonds. This property is useful for us as it can give rise to a large number of carbon compounds.
(b) In a diamond crystal, each carbon atom is bonded to 4 other carbon atoms through strong covalent bonds. These four atoms form four vertices of a regular tetrahedron which form a rigid structure and thus make it hard. The structure of graphite is very different from that of diamond. A graphite crystal consists of layers of carbon atoms or sheets of carbon atoms and these layers are held together by weak Van der Waals forces making it a soft substance.
Question 34:
(a) Giving their structures, state the number of single bonds, double bonds and triple bonds (if any) in the following compounds :
(i) ethyne (ii) ethene (iii) benzene
(b) Write the molecular formula and structure of cyclohexane. How many covalent bonds are there in a molecule of cyclohexane ?
Solution :
(a) (i) Ethyne:
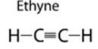
In ethyne, single bond is two and triple bond is one.
(ii) Ethane:
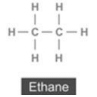
In ethane, single bond is seven and no triple bond.
(iii) Benzene:
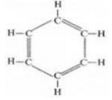
In benzene, single bond is nine and no triple bond
(b) Molecular formula of cyclohexane is C6H12. No of covalent bonds in cyclohexane molecule is 18.
Question 35:
(a) Write two points of difference in the structures of diamond and graphite.
(b) Explain why, graphite can be used as a lubricant but diamond cannot.
(c) Explain why, diamond can be used in rock drilling equipment but graphite cannot.
(d) State one use of diamond which depends on its ‘extraordinary brilliance’ and one use of graphite which depends on its being ‘black and quite soft’.
Solution : (a)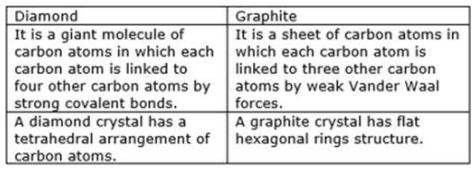 (b) In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded with 3 other carbon atoms to form hexagonal rings which join together by weak Vander Waal forces to form layers. Due to the weak force, these layers can slide over each other and therefore, graphite can be used as a lubricant. Whereas diamond being extremely hard cannot be used as a lubricant.
(b) In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded with 3 other carbon atoms to form hexagonal rings which join together by weak Vander Waal forces to form layers. Due to the weak force, these layers can slide over each other and therefore, graphite can be used as a lubricant. Whereas diamond being extremely hard cannot be used as a lubricant.
(c) In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to 4 other carbon atoms through strong covalent bonds. These four atoms form four vertices of a regular tetrahedron which form a rigid structure and thus make it hard. Hence, it is used in rock drilling equipments but graphite is soft and hence not used in rock drilling equipments.
(d) Diamonds are used in making jewellery because of its extraordinary brilliance while graphite is used for making pencils leads because of its black and soft nature.
Question 36:
(a) What is diamond ? Of what substance is diamond made ?
(b) Describe the structure of diamond. Draw a simple diagram to show the arrangement of carbon atoms in diamond.
(c) Explain why, diamond has a high melting point.
(d) State any two uses of diamond.
Solution :
(a) Diamond is a well-known allotrope of carbon. It is a colourless transparent substance having extraordinary brilliance due to its high refractive index. It is made up carbon which is black.
(b) A diamond crystal is a giant molecule of carbon atoms in which each carbon atom is linked to four other carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds forming a rigid three-dimensional network structure, which is responsible for its hardness.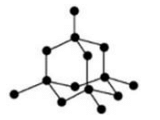 (c) In diamond crystal, each carbon atom is covalently bonded to other four carbon atoms to form three-dimensional network structure. This network is very strong and rigid. A lot of energy is required to break the network of strong covalent bonds in the diamond crystal. This makes the diamond’s melting point very high.
(c) In diamond crystal, each carbon atom is covalently bonded to other four carbon atoms to form three-dimensional network structure. This network is very strong and rigid. A lot of energy is required to break the network of strong covalent bonds in the diamond crystal. This makes the diamond’s melting point very high.
(d) Uses of diamond:
(i) It is used in knives for cutting marble, granite and glass.
(ii) It is used in making jewellery.
Question 37:
(a) What is graphite ? Of what substance is graphite made ?
(b) Describe the structure of graphite with the help of a labelled diagram.
(c) Why is graphite a good conductor of electricity but diamond is a non-conductor of electricity ?
(d) State any two uses of graphite.
Solution :
(a) Graphite is an allotrope of carbon. It is a greyish black opaque substance. Graphite is formed by carbon atoms.
(b) A graphite crystal consists of layers of carbon atoms or sheets of carbon atoms. In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds in the same plane giving a hexagonal array.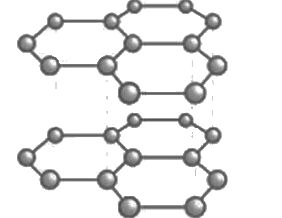 (c) Graphite is good conductor of electricity because of presence of free electron whereas diamond doesn’t have free electrons and is a non-conductor of electricity.
(c) Graphite is good conductor of electricity because of presence of free electron whereas diamond doesn’t have free electrons and is a non-conductor of electricity.
(d) Uses of graphite:
(i) It is used in making electrode in cells.
(ii) It is used as a powered lubricant for the parts of machinery.
Question 38:
(a) Explain the term ‘isomers’. Give one example of isomers.
(b) Write (i) structural formula, and (ii) electron-dot structure, of any one isomer of n-heptane (C7H16)
(c) Write IUPAC name of the compound having the formula n-C4H10.
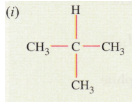
(d) Give the IUPAC names for the following :
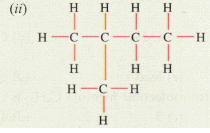
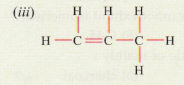
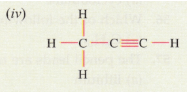
Solution :
(a) Isomers: Organic compounds with identical molecular formula but different structures are called isomers. Iso-pentane and neopentane are two isomers represented by the molecular formula C5H12 .
(b) Isomer of n-heptane: 2-methylhexane
(i) Structural formula of 2-methylhexane:
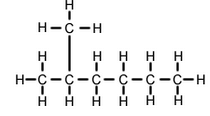 (ii) Electron-dot structure of 2-methylhexane:
(ii) Electron-dot structure of 2-methylhexane: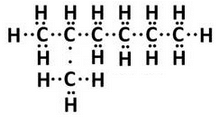
(c) The IUPAC name of of the compound having the formula n-C4H10 is butane.
n-C4H10
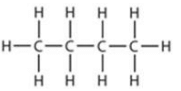
(d) (i) IUPAC name: 2-methylpropane
(ii) IUPAC name: 2-methylbutane
(iii) IUPAC name: Propene
(iv) IUPAC name: Propyne
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Carbon And Its Compounds, Solutions- 1 - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the key characteristics of carbon compounds? |  |
| 2. How does the bonding in carbon compounds affect their properties? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of carbon compounds? |  |
| 4. Why are carbon compounds important in everyday life? |  |
| 5. What role do carbon compounds play in environmental chemistry? |  |

















