Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: The Human Eyes And The Colorful World, Solutions- 1 | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Page No:269
Question 1: What kind of lens is present in the human eye ?
Solution : Convex lens
Question 2: Name two parts of the eye which refract light rays (or bend light rays)
Solution : Two parts which refract light rays are cornea and eye-lens.
Question 3: Name the part of the eye :
(a) which controls the amount of light entering the eye.
(b) on which the image is formed.
(c) which changes the focal length of eye-lens.
Solution : (a) Iris
(b) Retina
(c) Ciliary muscles
Question 4: What is the name of :
(a) the curved, transparent front surface of the eye ?
(b) the light-sensitive layer in the eye ?
Solution : (a) Cornea
(b) Retina
Question 5: Where is the image formed in a human eye ?
Solution : At retina
Question 6: What is the function of the lens in the human eye ?
Solution : Eye lens changes its shape and thickness to focus light on to the retina.
Question 7: What job does the pupil of the eye do ?
Solution : Pupil expands or contracts according to the intensity of light around the eye.
Question 8: Flow does the eye adjust to take account of an increase in brightness ?
Solution : The pupil of our eye contracts.
Question 9: Name that part of the eye which is equivalent to the photographic film in a camera.
Solution : Retina
Question 10: Name the part of the retina which is insensitive to light.
Solution : Blind spot
Question 11: Which part of the eye contains cells which are sensitive to light ?
Solution : Retina
Question 12: Name two types of cells in the retina of an eye which respond to light.
Solution : Rods and cones
Page No:270
Question 13: Out of rods and cones in the retina of your eye :
(a) which detect colour ?
(b) which work in dim light ?
Solution : (a) Cones
(b) Rods
Question 14: State whether the following statement is true or false :
The image formed on our retina is upside-down
Solution : True
Question 15: What is the principal function of the eye-lens ?
Solution : The principal function of the eye-lens is to focus light on to the retina.
Question 16: Where does the greatest degree of refraction of light occur in the eye ?
Solution : At cornea
Question 17: What changes the shape of lens in the eye ?
Solution : Ciliary muscles
Question 18: What do the ciliary muscles do when you are focusing on a nearby object ?
Solution : The ciliary muscles make the eyes lens thicker (more converging).
Question 19: What is the least distance of distinct vision for a normal human eye ?
Solution : The least distance of the distinct vision for a normal human eye is about 25cm.
Question 20: What is the :
(a) far point of a normal human eye ?
(b) near point of a normal human eye ?
Solution : (a) The far point of a normal human eye is at infinity.
(b) The near point of a normal human eye is at 25cm from the eye.
Question 21: What is the range of vision of a normal human eye ?
Solution : Range of vision of a normal human eyes is from infinity to about 25cm.
Question 22: Name the part of our eyes which helps us to focus near and distant objects in quick succession.
Solution : Ciliary muscles
Question 23: Define the term “power of accommodation” of human eye
Solution : The ability of an eye to focus the distant objects as well as the nearby objects on the retina by changing the focal length of its lens is called the power of accommodation.
Question 24: Give the scientific names of the following parts of the eye :
(a) carries signals from an eye to the brain.
(b) muscles which change the shape of the eye-lens.
(c) a hole in the middle of the iris.
(d) a clear window at the front of the eye.
(e) changes shape to focus a picture on the retina.
Solution : (a) Optic nerve
(b) Ciliary muscles
(c) Pupil
(d) Cornea
(e) Eye lens
Question 25: Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) Most of the refraction of light rays entering the eye occurs at the outer surface of the………….
(b) The part of eye sensitive to light is…………….
(c) The part of eye which alters the size of the pupil is………….
(d) When light is dim, the pupil becomes…………
(e) The iris controls the amount of…………… entering the eye.
(f) The ciliary muscles control the shape of the…………..
(g) To bring light from a distant object to a focus on the retina of the eye, the convex eye-lens needs to be made……
(h) To bring light from a near object to a focus on the retina of the eye, the convex eye-lens needs to be made……
Solution :
(a) cornea
(b) retina
(c) iris
(d) large
(e) light
(f) eye-lens
(g) thinner
(h) thicker
Question 26: Why is a normal eye not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm ?
Solution : The normal eye is not able to see clearly the objects placed closer than 25 cm because all the power of accomodation of the eye is exhausted at a distance of 25 cm. The maximum accomodation of the eye is reached when the object is placed at 25 cm fro the eye. After this the ciliary muscles cannot make the eye-lens more thick.
Question 27: What changes take place in the shape of eye-lens :
(a) when the eye is focused on a near object ?
(b) when the eye is focused on a distant object ?
Solution : (a) Eye-lens becomes thicker.
(b) Eye-lens become thinner.
Question 28: The eyes of a person are focused
- on a nearby object, and
- on a distant object, turn by turn. In which case :
(a) the focal length of eye-lens will be the maximum ?
(b) the converging power of eye-lens will be the maximum ?
Solution :
(a) When the eye is focused on a distant object.
(b) When the eye is focused on a nearby object.
Question 29: What change is made in the eye to enable it to focus on objects situated at different distances ? Illustrate your answer with the help of diagrams.
Solution : To focus on distant objects, the ciliary muscles of the eye get fully relaxed and pull the suspensory ligaments attached to the eye-lens tightly. This, in turn, stretches the eye-lens and the eye-lens becomes thin.
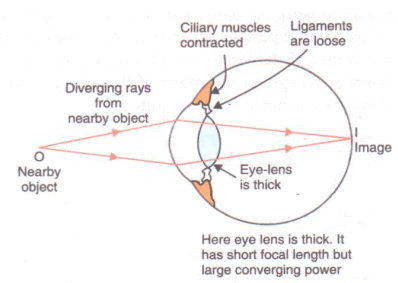
An eye focused on a nearby object
To focus on nearby objects, the ciliary muscles of the eyes contract and make the suspensory ligaments loose. The ligaments then stop pulling the eye-lens. The eye-lens bulges under its own elasticity and becomes thick.
Question 30: How is the amount of light entering the eye controlled ?
Solution : The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the iris. It automatically adjusts the size of the pupil according to the intensity of light received by the eye. If the amount of light received by the eye is large, then the iris contracts the pupil and reduces the amount of light entering the eye. If the amount of light received by the eye is small, then the iris expands the pupil so that more light may enter the eye.
Question 31: What happens to the eye when you enter a darkened cinema hall from bright sunshine ?
Solution : When we enter a darkened cinema hall from bright sunshine, at first we cannot see anything clearly. After a short time our vision improves. This is because in bright sunshine the pupil of our eye is small and when we just enter the darkened room very little light enters our eye due to which we cannot see properly. After a while, when the pupil of our eye expands, more light enters our eye and we can see clearly.
Question 32: Why does it take some time to see objects in a dim room when you enter the room from bright sunshine outside ?
Solution : It takes some time to see objects in a dim room when we enter the room from bright sunshine outside because it takes some time to the small pupil of our eye to become large so that more light enters our eye and we can see clearly.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: The Human Eyes And The Colorful World, Solutions- 1 - Science Class 10
| 1. How do the human eyes perceive different colors? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the human eye in perceiving the colorful world? |  |
| 3. How does light play a role in the perception of colors by the human eye? |  |
| 4. Can the human eye perceive all the colors in the electromagnetic spectrum? |  |
| 5. How do colors affect human emotions and psychology? |  |





















