NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Biotechnology: Principles & Processes | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: In the below represented plasmid an alien piece of DNA is inserted at EcoRI site. Which of the following strategies will be chosen to select the recombinant colonies? (NEET 2025)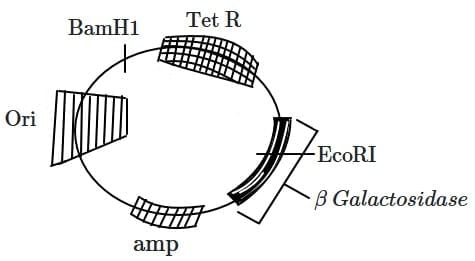 (a) White color colonies will be selected.
(a) White color colonies will be selected.
(b) Blue color colonies grown on ampicillin plates can be selected.
(c) Using ampicillin & tetracyclin containing medium plate.
(d) Blue color colonies will be selected.
Ans: (a)
White color colonies will be selected:
- In blue-white screening, the lacZ gene in the plasmid is disrupted when a foreign DNA fragment is inserted at the EcoRI site.
- The disruption prevents the production of β-galactosidase, an enzyme responsible for converting X-gal (an artificial substrate) into a blue-colored product.
- As a result, colonies with recombinant plasmids appear white, while non-recombinant colonies (where lacZ is intact) appear blue. Selecting white colonies ensures that recombinant plasmids containing the alien DNA are identified.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
- Using ampicillin & tetracycline containing medium plate: While antibiotic selection (e.g., ampicillin resistance) is often used to ensure the presence of plasmids in transformed bacteria, this method does not distinguish between recombinant and non-recombinant plasmids. It only selects bacteria that contain the plasmid.
- Blue color colonies will be selected: Blue colonies indicate non-recombinant plasmids where the lacZ gene is intact and functional. These colonies do not contain the inserted alien DNA and are not the desired recombinants.
- Blue color colonies grown on ampicillin plates can be selected: Blue colonies represent non-recombinant plasmids. Additionally, while ampicillin selects for plasmid-containing bacteria, it does not distinguish between recombinant and non-recombinant colonies.
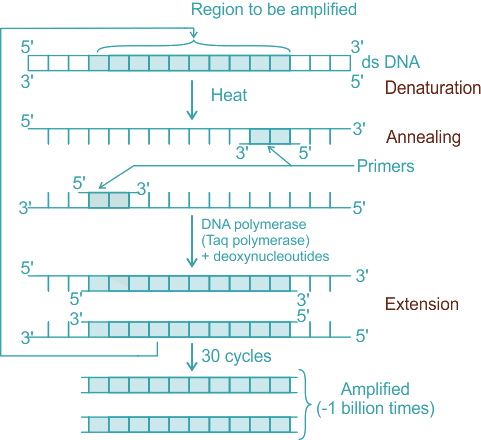
Q2: Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplifies DNA following the equation. (NEET 2025)
(a) 2n+1
(b) 2N2
(c) N2
(d) 2n
Ans: (d)
- The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a widely used molecular biology technique for amplifying specific DNA sequences exponentially.
- It involves repeated cycles of denaturation, annealing, and extension to double the amount of DNA with each cycle.
- The amplification follows the equation 2n, where n is the number of cycles performed. Each cycle doubles the amount of DNA present, leading to exponential growth.
Key Points about PCR:
- Denaturation: This is the first step of PCR. The reaction mixture is heated to around 94-98°C for 20-30 seconds, causing the double-stranded DNA to melt and separate into two single strands.
- Primer Annealing: The temperature is lowered to 50-65°C for 20-40 seconds to allow the primers to bind (anneal) to their complementary sequences on the single-stranded DNA template.
- Extension: The temperature is raised to around 72°C, the optimal temperature for Taq polymerase. This enzyme synthesizes a new DNA strand by adding nucleotides to the primer in a sequence-specific manner.
- Each cycle doubles the amount of DNA, leading to exponential amplification according to the formula 2ⁿ.
- PCR is used in various applications, including genetic testing, forensic analysis, and detecting pathogens.
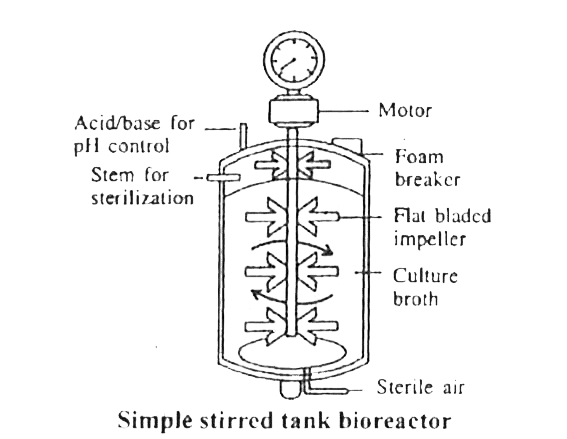
Q3: Identify the part of a bio-reactor which is used as a foam braker from the given figure. (NEET 2025)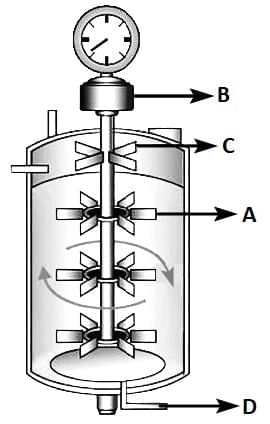 (a) D
(a) D
(b) C
(c) A
(d) B
Ans: (b)
- A bioreactor is a vessel or device in which biological reactions and processes are carried out under controlled conditions to produce biological products.
- A bioreactor provides the optimal conditions for achieving the desired product by providing optimum growth conditions (temperature, pH, substrate, salts, vitamins, oxygen).
- Foaming is a common issue in bioreactors, particularly in processes where gas sparging is employed. Foam formation can hinder the efficient operation of the bioreactor and may affect the quality of the product.
- Foam breaker: The foam breaker (identified as 'C' in the figure) is designed to disrupt and dissipate foam generated during the bioreactor operation. It ensures smooth processing by preventing foam overflow and maintaining the integrity of the biological processes.
- Foam breakers can be mechanical devices, such as rotating blades, or chemical agents that reduce surface tension and eliminate foam.
Q4: The blue and white selectable markers have been developed which differentiate recombinant colonies from non-recombinant colonies on the basis of their ability to produce colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate. (NEET 2025)
Given below are two statements about this method:
Statement I: The blue coloured colonies have DNA insert in the plasmid and they are identified as recombinant colonies.
Statement II: The colonies without blue colour have DNA insert in the plasmid and are identified as recombinant colonies.
(a) Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Ans: (b)
Statement I: "The blue-colored colonies have DNA insert in the plasmid and they are identified as recombinant colonies."
- This statement is incorrect because the blue-colored colonies represent non-recombinant colonies.
- These colonies have an intact lacZ gene, which produces β-galactosidase, resulting in the cleavage of X-gal and the formation of blue color.
- No DNA insert is present in these colonies, and thus they are not recombinant.
Statement II: "The colonies without blue color have DNA insert in the plasmid and are identified as recombinant colonies."
- This statement is correct because the absence of blue color (white colonies) indicates the disruption of the lacZ gene by the insertion of foreign DNA.
- The lack of β-galactosidase activity results in no cleavage of X-gal, and thus no blue color is produced.
- These colonies are recombinant as they contain the inserted DNA fragment in the plasmid.
Q5: Which of the following enzyme(s) are NOT essential for gene cloning? (NEET 2025)
A. Restriction enzymes
B. DNA ligase
C. DNA mutase
D. DNA recombinase
E. DNA polymerase
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D and E only
(b) B and C only
(c) C and D only
(d) A and B only
Ans: (c)
- Gene cloning is a method used to create identical copies of a specific gene or DNA segment. It involves isolating a desired gene, inserting it into a vector, and introducing it into a host organism to amplify and express the gene.
- Enzymes play a crucial role in the various steps of gene cloning. However, not all enzymes are essential for the process.
- The most commonly used enzymes in gene cloning are restriction enzymes, DNA ligase, and DNA polymerase.
- Restriction enzymes: These are essential enzymes for gene cloning. They recognize specific DNA sequences and cut the DNA at or near these sites, producing fragments that can be inserted into vectors.
- DNA ligase: This enzyme is critical for gene cloning. It joins the DNA fragments (e.g., the insert DNA and the vector) by forming phosphodiester bonds, making a stable recombinant DNA molecule.
- DNA polymerase: DNA polymerase is sometimes used in gene cloning for amplifying DNA through techniques like PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) or for filling in DNA overhangs after restriction digestion.
- DNA mutase: This enzyme is not essential for gene cloning. DNA mutase is involved in introducing mutations into DNA, which is not a requirement for cloning
- DNA recombinase: While recombinases facilitate site-specific recombination and have applications in advanced genetic engineering (e.g., CRISPR or recombineering), they are not essential for basic gene cloning processes.
Q6: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2025)
Statement I: The DNA fragments extracted from gel electrophoresis can be used in construction of recombinant DNA.
Statement II: Smaller size DNA fragments are observed near anode while larger fragments are found near the wells in an agarose gel.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct
(c) Both statement I and statement II are correct
(d) Both statement I and statement II are incorrect
Ans: (c)
- Statement I: The DNA fragments extracted from gel electrophoresis can be used in construction of recombinant DNA: This statement is correct. DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis can be extracted and purified for use in creating recombinant DNA, as they provide the necessary fragments for ligation into vectors.
- Statement II: Smaller size DNA fragments are observed near anode while larger fragments are found near the wells in an agarose gel: This statement is correct. In gel electrophoresis, smaller DNA fragments migrate further away from the wells towards the anode, whereas larger fragments travel a shorter distance and thus remain closer to the wells. DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules they can be separated by forcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix.
2024
Q1: Hind II always cuts DNA molecules at a particular point called recognition sequence and it consists of: (NEET 2024)
(a) 8 bp
(b) 6 bp
(c) 4 bp
(d) 10 bp
Ans: (b)
The correct answer is option (b).
The first restriction endonuclease - Hind II, whose functioning depends on a specific DNA nucleotide sequence was isolated. It was found that Hind II always cut DNA molecules at a particular point by recognising sequence of six base pairs.
Option (a), (c) and (d) are incorrect because they have either more than 6 or less than 6bp.
Q2: What is the fate of a piece of DNA carrying only gene of interest which is transferred into an alien organism?
A. The piece of DNA would be able to multiply itself independently in the progeny cells of the organism.
B. It may get integrated into the genome of the recipient.
C. It may multiply and be inherited along with the host DNA.
D. The alien piece of DNA is not an integral part of chromosome.
E. It shows ability to replicate.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: (NEET 2024)
(a) A and B only
(b) D and E only
(c) B and C only
(d) A and E only
Ans: (c)
When a piece of DNA carrying a gene of interest is transferred into an alien organism, its fate depends on several factors, including the mechanisms it has for replication, integration, and inheritance. Here is an analysis of each statement provided:
A. The piece of DNA would be able to multiply itself independently in the progeny cells of the organism.
This is incorrect unless the DNA contains an origin of replication that is compatible with the host cell's replication machinery.
B. It may get integrated into the genome of the recipient.
This is a likely scenario if the DNA has sequences that facilitate recombination with the host genome or if the host has natural mechanisms of DNA integration such as those observed in bacteria with transformation capabilities, or other eukaryotic organisms with similar processes.
C. It may multiply and be inherited along with the host DNA.
This statement can be true if the introduced DNA is replicated along with the host DNA, possibly through integration into the host genome or existence in the form of an episome that replicates independently yet synchronously with the host DNA.
D. The alien piece of DNA is not an integral part of chromosome.
This statement is generally accurate before integration. The introduced DNA, before integration, exists extrachromosomally and thus is not part of any chromosome, unless mechanisms are present for its integration into the host genome.
E. It shows ability to replicate.
This statement depends on specific sequences in the DNA, such as the origin of replication compatible with the host cell's machinery, mentioned in statement A. Without these, it will not replicate independently.
Given these explanations, the most accurate answer that describes the fate of the DNA in the recipient organism is: Option C: B and C only
'B' is correct as the DNA may integrate into the host genome, and 'C' is correct as the DNA might also multiply if replicated in sync with the host organism's DNA, particularly if it integrates or exists as an episome compatible with the host's cellular machinery.
Q3: The following diagram showing restriction sites in E. coli cloning vector pBR322. Find the role of ‘X’ and ‘Y’ genes : (NEET 2024)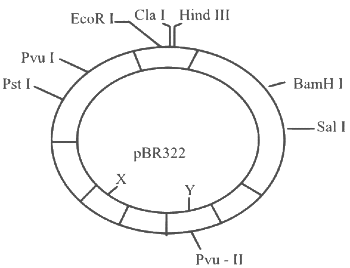
(a) The gene ‘X’ is responsible for resistance to antibiotics and ‘Y’ for protein involved in the replication of Plasmid.
(b) The gene ‘X’ is responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA and ‘Y’ for protein involved in the replication of Plasmid.
(c) The gene ‘X’ is for protein involved in replication of Plasmid and ‘Y’ for resistance to antibiotics.
(d) Gene ’X’ is responsible for recognitions sites and ‘Y’ is responsible for antibiotic resistance.
Ans: (b)
Correct answer is option (2), because
'X' in the given diagram is ori while 'Y' is rop.
'X' which is ori is responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA and 'Y' which is rop codes for protein involved in the replication of plasmid.
Options (1), (3) and (4) are incorrect as 'X' and 'Y' are not related to these functions.
Q4: The "Ti plasmid" of Agrobacterium tumefaciens stands for (NEET 2024)
(a) Tumour inhibiting plasmid
(b) Tumor independent plasmid
(c) Tumor inducing plasmid
(d) Temperature independent plasmid
Ans: (c)
The correct answer is Option C: Tumor inducing plasmid.
The "Ti plasmid" is a type of plasmid (a small DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently) found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. This bacterium is known for its ability to transfer a segment of its DNA to a plant, integrating this DNA into the plant's genome, causing the plant to develop tumors, known as crown gall disease.
The term "Ti plasmid" stands for "Tumor inducing plasmid" because of its role in this process. When Agrobacterium tumefaciens infects a plant, the Ti plasmid transfers a portion of its DNA-known as T-DNA (transfer DNA)-into a random site in the plant's genome. The expression of genes in the T-DNA leads to the overproduction of certain growth hormones (auxins and cytokinins), which results in the formation of tumors on the plant.
Thus, Option C "Tumor inducing plasmid" most accurately describes the Ti plasmid's function of inducing tumor formation in infected plants. Options A, B, and D do not correctly describe the properties or functions of the Ti plasmid.
Q5: Which of the following statements is incorrect? (NEET 2024)
(a) Most commonly used bio-reactors are of stirring type.
(b) Bio-reactors are used to produce small scale bacterial cultures.
(c) Bio-reactors have an agitator system, an oxygen delivery system, and foam control system.
(d) A bio-reactor provides optimal growth conditions for achieving the desired product.
Ans: (b)
Bio-reactors are typically used for large-scale production, not small-scale bacterial cultures. They provide a controlled environment to cultivate microorganisms, plant cells, or animal cells for producing various products like antibiotics, enzymes, biofuels, and more.
The other statements are correct:
- Statement 1: Most commonly used bio-reactors are of the stirring type, known as stirred-tank bio-reactors.
- Statement 3: Bio-reactors are equipped with systems like an agitator system, oxygen delivery system, and foam control system to maintain optimal conditions for microbial growth.
- Statement 4: A bio-reactor indeed provides optimal growth conditions to achieve the desired product, such as maintaining temperature, pH, and nutrient levels.
Q6: Which of the following is not a selectable marker of cloning vectors? (NEET 2024)
(a) Ampicillin
(b) Metformin
(c) Chloramphenicol
(d) Tetracycline
Ans: (b)
Selectable markers are genes introduced into cloning vectors to enable the identification of successfully transformed cells. These markers usually provide resistance to specific antibiotics, allowing only the transformed cells to grow in the presence of the antibiotic.
- Ampicillin, Chloramphenicol, and Tetracycline are all common selectable markers used in cloning vectors because they confer resistance to these antibiotics.
- Metformin, however, is a drug used primarily for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and is not used as a selectable marker in cloning vectors.
Q7: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: Restriction Endonuclease finds its specific recognition sequence and binds to the DNA.
Statement II: Restriction Endonuclease cuts each of the two strands of the double helix at specific points in their sugar phosphate backbones.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are True
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are False
(c) Statement I is True but Statement II is False
(d) Statement I is False but Statement II is True
Ans: (a)
Statement I: Restriction Endonuclease recognizes specific sequences of nucleotides in the DNA, known as the recognition sequence, and binds to them. This statement is true.
Statement II: After binding to the recognition sequence, Restriction Endonuclease cuts both strands of the DNA double helix at specific points in their sugar-phosphate backbone. This is also true, as these enzymes typically create staggered or blunt ends by cleaving the DNA at these specific sites.
Thus, both statements are correct.
Q8: In a chromosome, there is a specific DNA sequence, responsible for initiating replication. It is called as: (NEET 2024)
(a) recognition sequence
(b) cloning site
(c) restriction site
(d) ori site
Ans: (d)
The ori site (origin of replication) is the specific DNA sequence responsible for initiating DNA replication in a chromosome. It is the site where the process of DNA replication begins, allowing the DNA to be copied for cell division. The ori site is crucial for the proper replication of the chromosome in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
The other options:
- Recognition sequence: This refers to a specific sequence recognized by enzymes like restriction endonucleases but is not involved in replication initiation.
- Cloning site: This refers to a specific site in vectors where foreign DNA can be inserted, not related to DNA replication initiation.
- Restriction site: This refers to a specific sequence recognized and cut by restriction enzymes but is not involved in replication initiation.
Q9: Identify the incorrect statement related to electrophoresis: (NEET 2024)
(a) Separated DNA fragments can be directly seen under UV radiation
(b) Separated DNA can be extracted from gel piece.
(c) Fragments of DNA move toward anode.
(d) Sieving effect of agarose gel helps in separation of DNA fragments.
Ans: (a)
Incorrect Statement: Separated DNA fragments cannot be directly seen under UV radiation. After electrophoresis, DNA fragments are typically stained with a dye such as ethidium bromide, which intercalates with the DNA and fluoresces under UV light. Without staining, DNA fragments cannot be directly observed under UV light.
The other statements are correct:
- Statement 2: Separated DNA can indeed be extracted from the gel after electrophoresis using a process called gel extraction.
- Statement 3: DNA is negatively charged, and during electrophoresis, it moves toward the positive electrode (anode).
- Statement 4: The sieving effect of agarose gel helps separate DNA fragments based on their size, with smaller fragments moving faster through the gel than larger ones.
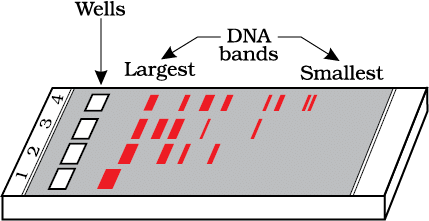
Q10: Select the restriction endonuclease enzymes whose restriction sites are present for the tetracycline resistance (tetR) gene in the pBR322 cloning vector: (NEET 2024)
(a) Bam HI and Sal I
(b) Sal I and Pst I
(c) Pst I and Pvu I
(d) Pvu I and Bam HI
Ans: (a)
The pBR322 cloning vector contains restriction sites for several restriction endonucleases. The tetracycline resistance (tetR) gene is part of the pBR322 vector and has specific restriction enzyme sites.
The Bam HI and Sal I restriction enzymes have their restriction sites within or near the tetR gene in pBR322. These enzymes can be used to cut the plasmid at specific sites, making it possible to insert foreign DNA or manipulate the plasmid.
The other options do not match the specific restriction sites within the tetracycline resistance gene in pBR322.
Q11: Recombinant DNA molecule can be created normally by cutting the vector DNA and source DNA respectively with:
(NEET 2024)
(a) Hind II, Hind II
(b) Hind II, Alu I
(c) Hind II, EcoR I
(d) Hind II, Bam HI
Ans: (a)
To create a recombinant DNA molecule, the vector DNA and source DNA must be cut with the same restriction enzyme to ensure compatible sticky ends that can be ligated together. In this case, Hind II is used to cut both the vector DNA and the source DNA, producing compatible ends for ligation.
The other options involve different restriction enzymes that would produce incompatible ends or not the correct cutting pattern for creating recombinant DNA with compatible ends.
Q12: Which of the following are correct about EcoRI? (NEET 2024)
A. Cut the DNA with blunt end
B. Cut the DNA with sticky end
C. Recognises a specific palindromic sequence.
D. Cut the DNA between the base G and A where it encounters the DNA sequence 'GAATTC'
E. Exonuclease
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, E only
(b) A, D, E only
(c) A, C, D only
(d) B, C, D only
Ans: (d)
B. Cut the DNA with sticky end: EcoRI is a restriction enzyme that produces sticky (cohesive) ends by cutting between the G and A in the sequence GAATTC.
C. Recognises a specific palindromic sequence: EcoRI recognizes the palindromic sequence GAATTC, where the sequence reads the same in both directions.
D. Cut the DNA between the base G and A where it encounters the DNA sequence 'GAATTC': This is the specific action of EcoRI, cutting the DNA between the G and A of the GAATTC sequence.
A. Cut the DNA with blunt end: EcoRI cuts the DNA with sticky ends, not blunt ends.
E. Exonuclease: EcoRI is not an exonuclease. It is a restriction endonuclease, which cuts DNA at specific sequences, rather than progressively trimming nucleotides from the ends.
Q13: Following are the steps involved in the process of PCR: (NEET 2024)
A. Annealing
B. Amplification (~1 billion times)
C. Denaturation
D. Treatment with Taq polymerase and deoxynucleotides
E. Extension
Choose the correct sequence of steps of PCR from the options given below:
(a) C → A → D → E → B
(b) A → B → E → D → C
(c) A → C → E → D → B
(d) D → B → E → C → A
Ans: (a)
The correct sequence of steps in the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) process is as follows:
C. Denaturation: The DNA sample is heated to around 94-98°C to separate the two strands of the DNA template.
A. Annealing: The temperature is lowered to 50-65°C to allow the primers to bind to the complementary sequences on the single-stranded DNA templates.
D. Treatment with Taq polymerase and deoxynucleotides: The Taq polymerase enzyme, along with free nucleotides (dNTPs), is added for the extension process.
E. Extension: The Taq polymerase synthesizes a new strand of DNA starting from the primers at around 75-80°C.
B. Amplification (~1 billion times): The process is repeated through many cycles (usually 20-40), resulting in exponential amplification of the target DNA sequence.
Thus, the correct sequence is C → A → D → E → B.
2023
Q1: Which of the following is not a cloning vector? (NEET 2023)
(a) BAC
(b) YAC
(c) pBR322
(d) Probe
Ans: (d)
Option (d) is correct answer because a single stranded DNA or RNA tagged with a radioactive molecule is called a probe and it helps in the detection of mutated gene.
Option (b), (c) and (a) are not correct because YAC, BAC, pBR322 are vectors.
Q2: Upon exposure to UV radiation, DNA stained with ethidium bromide will show: (NEET 2023)
(a) Bright orange colour
(b) Bright red colour
(c) Bright blue colour
(d) Bright yellow colour
Ans: (a)
Ethidium bromide is a fluorescent dye commonly used in molecular biology to visualize nucleic acids, especially DNA, under UV light. When exposed to UV light, ethidium bromide intercalates between the base pairs of DNA, emitting a bright orange fluorescence. This property makes it extremely useful for detecting DNA bands in agarose gel electrophoresis. The fluorescence is specific to DNA and is not emitted by other molecules, which is why it is widely used in DNA analysis.
Q3: During the purification process for recombinant DNA technology, addition of chilled ethanol precipitates out: (NEET 2023)
(a) Polysaccharides
(b) RNA
(c) DNA
(d) Histones
Ans: (c)
In recombinant DNA technology, ethanol precipitation is used to purify DNA from a solution. DNA is soluble in water but is precipitated out when chilled ethanol is added. This is because ethanol reduces the solubility of DNA, causing the DNA molecules to clump together and form a visible precipitate. This process is essential for isolating DNA after various stages such as restriction digestion or PCR amplification. The addition of salt, such as sodium acetate, helps in neutralizing the charge of the DNA, making it more likely to precipitate out when ethanol is added.
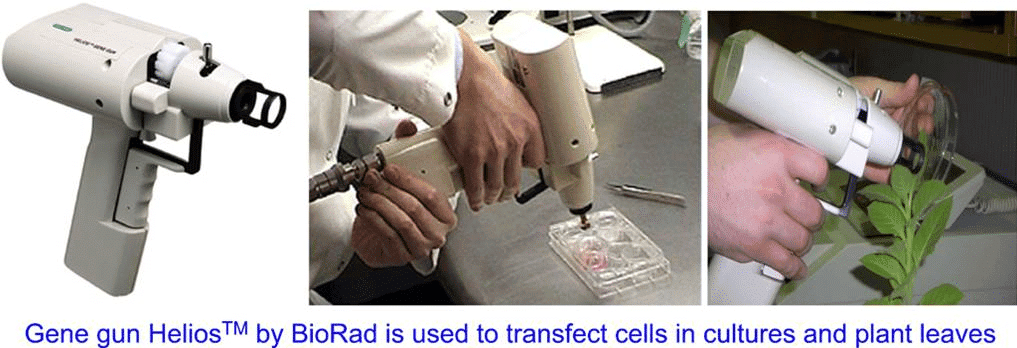
Q4: In gene gun method used to introduce alien DNA into host cells, microparticles of ___________ metal are used. (NEET 2023)
(a) Silver
(b) Copper
(c) Zinc
(d) Tungsten or gold
Ans: (d)
The gene gun, also known as the biolistic method, is a technique used to deliver foreign DNA into cells. In this method, tungsten or gold microparticles are coated with the DNA of interest and then fired into plant or animal cells under high pressure. The heavy metal particles penetrate the cell membrane, carrying the DNA with them. This method is particularly useful in plant biotechnology, as it does not require the use of plant-specific transformation methods like Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. The use of tungsten or gold ensures that the particles are dense and can effectively carry the DNA into cells.
Q5: Main steps in the formation of Recombinant DNA are given below. Arrange these steps in a correct sequence. (NEET 2023)
A. Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host cell.
B. Cutting of DNA at specific location by restriction enzyme.
C. Isolation of desired DNA fragment.
D. Amplification of gene of interest using PCR.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, D, A, C
(b) B, C, D, A
(c) C, A, B, D
(d) C, B, D, A
Ans: (b)
The correct sequence of steps in recombinant DNA technology is as follows:
- B (Cutting of DNA): First, the DNA of interest and the vector are cut using restriction enzymes to generate sticky ends.
- C (Isolation of desired DNA fragment): The fragment of interest is then isolated from the rest of the DNA.
- D (Amplification of gene of interest using PCR): The desired DNA fragment is often amplified using PCR to produce enough copies for cloning.
- A (Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host cell): Finally, the recombinant DNA is inserted into the host cell for expression or further manipulation. This process is crucial in genetic engineering and cloning.
Q6: Thermostable DNA polymerase used in PCR was isolated from: (NEET 2023)
(a) Thermus aquaticus
(b) Escherichia coli
(c) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
(d) Bacillus thuringiensis
Ans: (a)
Taq polymerase, a thermostable DNA polymerase, was originally isolated from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus, which thrives in the high-temperature environment of hot springs. The enzyme is capable of withstanding the high temperatures used in the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), which involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling. This property makes Taq polymerase ideal for PCR, as it does not denature at high temperatures, unlike most other enzymes. It efficiently synthesizes new DNA strands during the extension step of PCR, enabling rapid amplification of DNA sequences.
Q7: Ligation of foreign DNA at which of the following site will result in loss of tetracycline resistance of pBR322? (NEET 2023)
(a) PsT I
(b) Pvu I
(c) EcoR I
(d) BamH I
Ans: (d)
In the pBR322 plasmid, the tetracycline resistance (tetR) gene is located in a region that contains a BamH I restriction site. If foreign DNA is inserted into the BamH I site of the tetracycline resistance gene, it disrupts the gene's function, leading to the loss of tetracycline resistance. This is a key feature in recombinant DNA technology because plasmids are often designed so that when foreign DNA is inserted into a specific site, it can deactivate a reporter gene like tetR. This allows researchers to easily identify transformed cells by their ability to resist or not resist tetracycline.
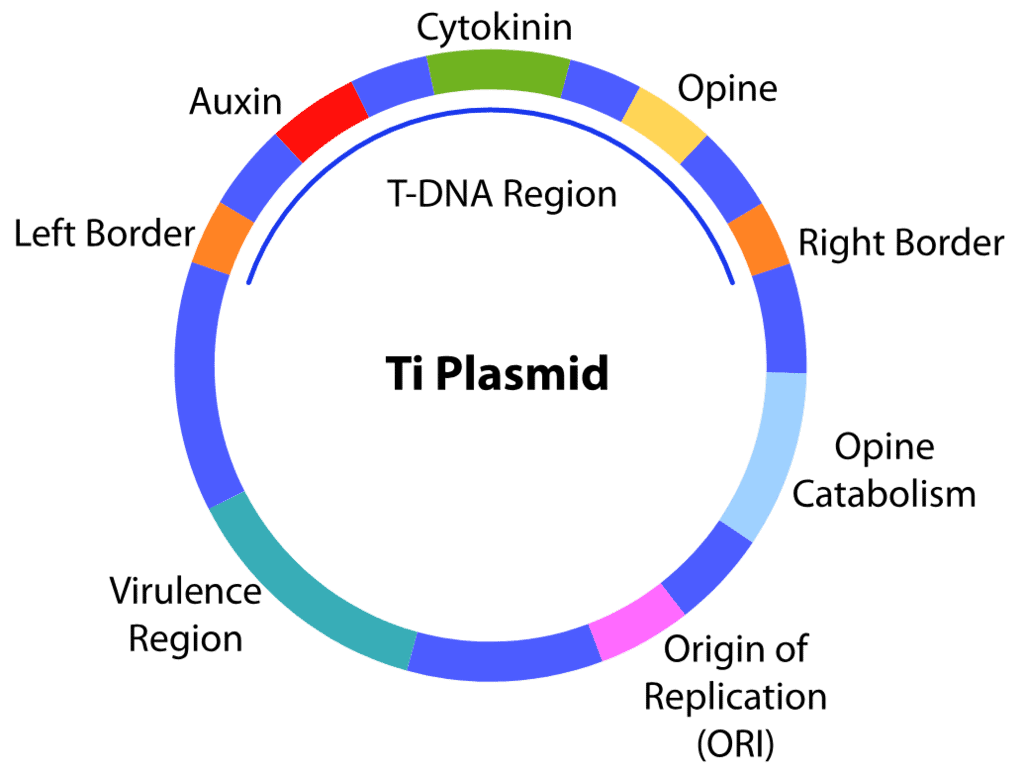
Q8: Which of the following statement is incorrect about Agrobacterium tumefaciens? (NEET 2023)
(a) It is used to deliver gene of interest in both prokaryotic as well as eukaryotic host cells.
(b) 'Ti' plasmid from Agrobacterium tumefaciens used for gene transfer is not pathogenic to plant cells.
(c) It transforms normal plant cells into tumor cells.
(d) It delivers 'T-DNA' into plant cell.
Ans: (a)
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is primarily used to transfer genes into eukaryotic plant cells, not prokaryotic cells. It uses a plasmid known as the Ti plasmid to insert a segment of DNA (T-DNA) into the plant genome. This process is a natural form of horizontal gene transfer that has been harnessed in genetic engineering for plant transformation. Agrobacterium is not used for gene transfer in prokaryotic cells, as they do not possess the machinery to process the T-DNA in the same way eukaryotic plant cells do. The other statements about Agrobacterium tumefaciens are correct, such as its ability to deliver T-DNA into plant cells and its role in transforming plant cells into tumor cells.
Q9: Which of the following can act as molecular scissors? (NEET 2023)
(a) Restriction enzymes
(b) DNA ligase
(c) RNA polymerase
(d) DNA polymerase
Ans: (a)
Restriction enzymes, also known as restriction endonucleases, act as "molecular scissors" because they can cut DNA at specific sequences. These enzymes recognize particular sequences of nucleotides in the DNA and make cuts, typically resulting in sticky or blunt ends, depending on the enzyme. This property is widely used in molecular biology for DNA manipulation, such as in cloning, genetic engineering, and DNA analysis.
- DNA ligase is an enzyme that joins two DNA fragments together by forming phosphodiester bonds, not cutting DNA.
- RNA polymerase is responsible for synthesizing RNA from a DNA template in transcription, not for cutting DNA.
- DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA from a template strand during replication or PCR, but it does not act as molecular scissors.
2022
Q1: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). (NEET 2022)
Assertion (A): Polymerase chain reaction is used in DNA amplification
Reason (R): The ampicillin resistant gene is used as a selectable marker to check transformation
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(b) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
(c) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
(d) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Ans: (a)
- Both the statements are correct but the given reason is not the correct explanation. Polymerase chain reaction is used in DNA amplification.
- Ampicillin resistance gene is a selectable marker that helps to check transformation by selection of transformants.
Q2: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022)
Statement I: Restriction endonucleases recognise specific sequence to cut DNA known as palindromic nucleotide sequence.
Statement II: Restriction endonucleases cut the DNA strand a little away from the centre of the palindromic site.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(b) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(c) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Ans: (d)
Option (d) is the correct answer because both the statements I and II are correct. Each restriction endonuclease recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequences in the DNA. It will bind to the DNA and cut each of the two strands of double helix at specific points. Restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindrome site; but between the same two bases on the opposite strands. So both the statements I and II are correct.
Q3: Which of the following is not a desirable feature of a cloning vector? (NEET 2022)
(a) Presence of a marker gene
(b) Presence of single restriction enzyme site
(c) Presence of two or more recognition sites
(d) Presence of origin of replication
Ans: (c)
Option (c) is the correct answer which is not the desirable feature of a cloning vector. Cloning vectors are the carriers of the desired gene in the host cell. The features desirable in a cloning vector are :-
- Presence of origin of replication
- Presence of marker genes
- Presence of very few, preferably single recognition site for the commonly used restriction enzymes
Q4: Which one of the following statement is not true regarding gel electrophoresis technique? (NEET 2022)
(a) The process of extraction of separated DNA strands from gel is called elution.
(b) The separated DNA fragments are stained by using ethidium bromide.
(c) The presence of chromogenic substrate gives blue coloured DNA bands on the gel.
(d) Bright orange coloured bands of DNA can be observed in the gel when exposed to UV light.
Ans: (c)
Option (c) is the incorrect statement, as bright coloured bands of DNA can be observed in the gel when EtBr (Ethidium bromide) treated DNA is exposed to UV light.
Q5: Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : When a particular restriction enzyme cuts strand of DNA, overhanging stretches or sticky ends are formed.
Reason (R) : Some restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of palindromic site.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(c) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(d) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (b)
Option (b) is the correct answer because when restriction enzymes cut the strand of DNA a little away from the centre of the palindrome sites, but between the same two bases on the opposite strands, then single stranded portions are left at the ends. These overhanging stretches on each strand are called sticky ends.
Q6: Separation of DNA fragments is done by a technique known as (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Gel electrophoresis
(b) Polymerase Chain Reaction
(c) Recombinant technology
(d) Southern blotting
Ans: (a)
- Option (a) is the correct answer because separation of DNA fragments which is carried out after restriction enzyme digestion, is done by a technique known as gel electrophoresis.
- Option (b) is not the correct answer because polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used for amplification of gene of interest.
- Option (c) is not the correct answer because recombinant DNA technology comprises altering genetic material outside an organism to obtain enhanced and desired characteristics in living organisms or as their products.
- Option (d) is not the answer because Southern blotting is a method used for detection of specific DNA sequences in samples.
Q7: The enzyme (a) is needed for isolating genetic material from plant cells and enzyme (b) for isolating genetic material from fungus. Choose the correct pair of options from the following :
(a) (a) Cellulase (b) Lipase
(b) (a) Cellulase (b) Protease
(c) (a) Cellulase (b) Chitinase
(d) (a) Chitinase (b) Lipase (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
- Option (3) is the correct answer because cellulase is used to isolate genetic material from plant cells and chitinase is used to isolate genetic material from fungal cells.
- Option (2) is incorrect because protease is used for digestion of proteins.
- Option (1) and (4) are incorrect because lipase is used for the breakdown of lipids.
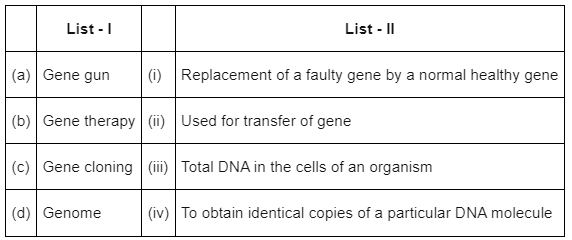
Q8: Match List-I with List-II : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
(b) (a) - (ii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (iii)
(c) (a) - (i), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (iv)
(d) (a) - (iv), (b) - (i), (c) - (iii), (d) - (ii)
Ans: (b)
Option (2) is the correct answer because
- Gene gun or biolistics is a direct gene transfer method suitable for plant cell.
- Gene therapy involves replacement of a faulty gene by a normal healthy gene.
- Gene cloning is done to make identical copies of a particular DNA molecule.
- Genome is the total DNA in the cells of an organism.
Q9: Pathogenic bacteria gain resistance to antibiotics due to changes in their : (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Nucleoid
(b) Cosmids
(c) Plasmids
(d) Nucleus
Ans: (c)
Plasmid is small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA. The plasmid DNA confers certain unique phenotypic characters to the bacteria such as resistance to antibiotics.
Q10: Which of the following methods is not commonly used for introducing foreign DNA into the plant cell?
(a) Bacteriophages
(b) Agrobacterium mediated transformation
(c) Gene gun
(d) ‘Disarmed pathogen’ vectors (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (a)
- Option (a) is the correct answer because bacteriophages act as a cloning vector for bacterial cells, not the plant cells.
- Options (b), (c) and (d) are not the correct answers because Agrobacterium, gene gun and disarmed pathogens as vectors are used for introducing foreign DNA into the plant cells.
Q11:Refer to the following statements for agarose-gel electrophoresis: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Agarose is a natural polymer obtained from sea-weed.
(b) The separation of DNA molecules in agarose-gel electrophoresis depends on the size of DNA.
(c) The DNA migrates from negatively-charged electrode to the positively-charged electrode
(d) The DNA migrates from positively-charged electrode to the negatively-charged electrode.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
(a) (b), (c) and (d) only
(b) (a) and (b) only
(c) (a), (b) and (c) only
(d) (a), (b) and (d) only
Ans: (c)
- Option (c) is the correct answer as the most commonly used matrix in gel electrophoresis is agarose which is a natural polymer extracted from sea weeds.
- In agarose gel electrophoresis, the DNA fragments separate (resolve) according to their size through sieving effect provided by the agarose gel.
- Since, DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules, they migrate towards the anode (positively-charged electrode) under an electric field through a medium/martix.
2021
Q1: During the purification process for recombinant DNA technology, addition of chilled ethanol precipitates out: (NEET 2021)
(a) Histones
(b) Polysaccharides
(c) RNA
(d) DNA
Ans: (d)
- Various enzymes like protease, RNase, etc. are added to break down substances like proteins, RNA, etc. Once all these substances are broken down, DNA is left which is precipitated out by adding chilled ethanol.
- Ethanol has a lower dielectric constant than water, making it to promote ionic bond formation the Na+ (from the salt) and the PO−3 (from the DNA backbone), further, causing the DNA to precipitate.
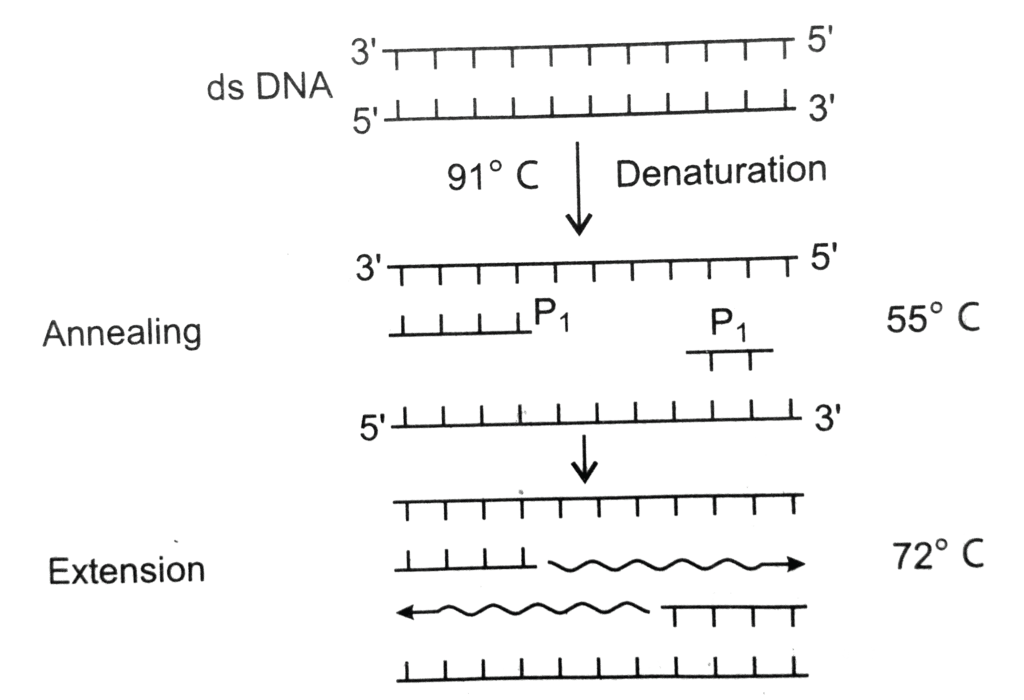
Q2: Which of the following is a correct sequence of steps in a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)? (NEET 2021)
(a) Extension, Denaturation, Annealing
(b) Annealing, Denaturation, Extension
(c) Denaturation, Annealing, Extension
(d) Denaturation, Extension, Annealing
Ans: (c)
- PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction. It is a technique in which multiple copies of gene of interest is synthesised using two sets of primers and the enzyme DNA polymerase. The correct sequence of steps in a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) are
- Denaturation In which the double-stranded template DNA is heated at 95°C to separate it into two single strands.
- Annealing In which the temperature is lowered to 50°C which enables the DNA primers to attach to the template DNA.
- Extension/Extending In which the temperature is raised and the new strand of DNA is made by the taq polymerase enzyme.
- These three stages are repeated 20-40 times, doubling the number of DNA copies each time.
Q3: Plasmid pBR322 has a PstI restriction enzyme site within gene ampR that confers ampicillin resistance. If this enzyme is used for inserting a gene for β-galactosidase production and the recombinant plasmid is inserted in an E.coli strain, (NEET 2021)
(a) it will lead to the lysis of host cells.
(b) it will be able to produce a novel protein with dual abilities.
(c) it will not be able to confer ampicillin resistance to the host cell.
(d) the transformed cells will have the ability to resist ampicillin as well as produce β-galactoside.
Ans: (c)
- pBR322 is a commonly used cloning vector. When the gene for β-galactoside is inserted in the ampicillin resistance gene by using Pst I, the recombinant E.coli will lose ampicillin resistance due to insertional inactivation of the antibiotic resistance gene.
- The host (recombinant) cell will produce β-galactoside which is not a novel protein nor does it have dual ability.
- The transformed cells cannot resist ampicillin as they have lost ampicillin resistance.
- A recombinant E. coli is produced and the host cell will not undergo lysis due to insertion of β-galactoside gene.
Q4: During the process of gene amplification using PCR, very high temperature is not maintained in the beginning, then which of the following step in PCR will be affected first? (NEET 2021)
(a) Denaturation
(b) Ligation
(c) Annealing
(d) Extension
Ans: (a)
Let us see the steps in PCR:
Denaturation
- In this process, the two strands of DNA are separated by heating them at a very high temperature (94 to 98 degrees).
- If high temperature is not maintained denaturation will not occur.
- The hydrogen bonds between two strands break and single strands are produced.
Annealing
- In this step, primers are used. The primers are allowed to interact with the single strands of DNA.
- There is a pairing between the primer and its complementary DNA strand (template DNA).
- A proper temperature (lower than the temperature used for denaturation) is provided for proper hybridization between the primer and the template DNA.
- The DNA polymerase enzyme binds to the primer-template hybrid and the synthesis of DNA begins.
Extension
- Enzyme Taq polymerase (obtained from bacteria Thermus aquaticus) is used here and the temperature maintained is 75 to 80 degrees.
- The enzymes add nucleotides in the 5’-3’ direction and synthesize the complementary DNA strand.
- This cycle can be repeated multiple times ( approximately 30 times) to obtain millions of copies of the DNA.
Q5: A specific recognition sequence identified by endonucleases to make cuts at specific positions within the DNA is: (NEET 2021)
(a) Palindromic Nucleotide sequences
(b) Poly(A) tail sequences
(c) Degenerate primer sequence
(d) Okazaki sequences
Ans: (a)
- Each restriction endonuclease recognizes a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA. Once it finds its specific recognition sequence it bind to DNA and cuts each of the two strands of DNA.
- During post transcriptional modification in eukaryotes, poly(A) tail (200-300 adenylate residues) are added at 3' end of hnRNA.
- During DNA replication Okazaki fragments are synthesized discontinuously and joined by DNA ligase.
- A PCR primer sequence is termed degenerate if some of its position have several possible bases.
2020
Q1: In-gel electrophoresis, separated DNA fragments can be visualized with the help of: (NEET 2020)
(a) acetocarmine in UV radiation
(b) ethidium bromide in infrared radiation
(c) acetocarmine in bright blue light
(d) ethidium bromide in UV radiation
Ans: (d)
The separated DNA fragments can be visualised only after staining the DNA with Ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation.
Q2: Identify the wrong statement with regard to restriction enzymes. (NEET 2020)
(a) They are useful in genetic engineering.
(b) Sticky ends can be joined by using DNA ligases.
(c) Each restriction enzyme functions by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence.
(d) They cut the strand of DNA at palindromic sites.
Ans: (c)
The incorrect statement is Option C: "Each restriction enzyme functions by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence." This statement is misleading because restriction enzymes do not function by inspecting the length of DNA sequences; instead, they recognize and cut DNA at specific nucleotide sequences, typically at palindromic sites. This specificity does not depend on the length of the DNA but on the sequence configuration that the enzyme recognizes.
Q3: The specific palindromic sequence which is recognized by EcoRI is: (NEET 2020)
(a) 5’- CTTAAG -3’, 3’GAATTC - 5’
(b) 5’- GGATCC - 3’, 3’- CCTAGG - 5’
(c) 5’- GAATTC - 3’, 3’ -CTTAAG - 5’
(d) 5’ - GGAACC - 3’, 3’ - CCTTGG - 5’
Ans: (c)
The specific palindromic sequence which is recognised by EcoRI is
5’ - GAATTC - 3’
3’ - CTTAAG - 5’
Q4: The sequence that controls the copy number of the linked DNA in the vector, is termed (NEET 2020)
(a) Palindromic sequence
(b) Recognition site
(c) Selectable marker
(d) Ori site
Ans: (d)
Ori sequence is responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA in the vector. Ori i.e. origin of replication is responsible for initiation of replication.
Q5: Choose the correct pair from the following (NEET 2020)
(a) Nucleases - Separate the two strands of DNA
(b) Exonucleases - Make cuts at specified positions within DNA
(c) Ligases - Join the two DNA molecules
(d) Polymerases - Break the DNA into fragments
Ans: (c)
Ligases join the two DNA molecules. DNA ligase is an enzyme which can connect two strands of DNAtogether by forming a bond between the phosphate group of one strand and the deoxyribose group on another. It is used in cells to join together the Okazaki fragments which are formed on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
2019
Q1: The following statements describe the characteristics of the enzyme restriction endonuclease. Identify the incorrect statement. (NEET 2019)
(a) The enzyme recognises a specific palindromic nucleotide sequence in the DNA.
(b) The enzyme cuts DNA molecule at an identified position within the DNA.
(c) The enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cuts only one of the two strands.
(d) The enzyme cuts the sugar-phosphate backbone at specific sites on each strand.
Ans: (c)
Enzyme binds DNA at specific sites and cut both the strands by breaking phosphodiester linkage.
Q 20: DNA precipitation out of a mixture of biomolecules can be achieved by treatment with (NEET 2019)
(a) Chilled chloroform
(b) Isopropanol
(c) Chilled ethanol
(d) Methanol at room temperature
Ans: (c)
Chilled ethanol is used for DNA precipitation out of a mixture of biomolecules. Process is called spooling.
2018
Q1: The correct order of steps in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is (NEET 2018)
(a) Extension, denaturation, annealing
(b) Annealing, extension, denaturation
(c) Denaturation, extension, annealing
(d) Denaturation, annealing, extension
Ans: (d)
Each cycle of PCR has three steps :
(1) Denaturation,
(2) Primer annealing,
(3) Extension of primers.
2017
Q1: The DNA fragments separated on an agarose gel can be visualised after staining with (NEET 2017)
(a) Acetocarmine
(b) Aniline blue
(c) Ethidium bromide
(d) Bromophenol blue
Ans: (c)
Ethidium bromide (Et Br) is used to stain the DNA fragments and will appear as orange coloured bands when kept under UV light.
Q2: DNA fragments are (NEET 2017)
(a) Negatively charged
(b) Neutral
(c) Either positively or depending on their size
(d) Positively charged
Ans: (a)
DNA fragments are negatively charged because of presence of phosphate group.
Q3: What is the criterion for DNA fragments movement on agarose gel during gel electrophoresis? (NEET 2017)
(a) The smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
(b) Positively charged fragments move to the farther end.
(c) Negatively charged fragments do not move.
(d) The larger the fragment size, the farther it moves.
Ans: (a)
DNA fragments during gel electrophoresis, separate (resolve) according to their size due to sieving effect provided by agarose gel.
Q4: A gene whose expression helps to identify transformed cell is known as (NEET 2017)
(a) Vector
(b) Plasmid
(c) Structural gene
(d) Selectable marker
Ans: (d)
Selectable markers in recombinant DNA technology, helps in identification and elimination of non-transformants and selectively permits the growth of the transformants.
Q5: The process of separation mid purification of expressed protein before marketing is called (NEET 2017)
(a) Downstream processing
(b) Bioprocessing
(c) Postproduction processing
(d) Upstream processing
Ans: (a)
The various stages of processing that occur after the completion of fermentation or biosynthetic stage which include separation and purification of product called downstream processing.
2016
Q1: Stirred-tank bioreactors have been designed for (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Purification of product
(b) Addition of preservatives to the product
(c) Availability of oxygen throughout the process
(d) Ensuring anaerobic conditions in the culture vessel
Ans: (c)
A stirred-tank reactor is usually cylindrical or with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents. The stirrer facilitates, even mixing and oxygen availability throughout the bioreactor.
Q2: A foreign DNA and plasmid cut by the same restriction endonuclease can be joined to form a recombinant plasmid using (NEET 2016)
(a) EcoRl
(b) Taq polymerase
(c) Polymerase III
(d) Ligase
Ans: (d)
Ligase is a class of enzymes that catalyse the formation of covalent bonds using the energy released by the cleavage of ATP. Ligases arc important in the synthesis and repair of many biological molecules, including DNA ligase and used in genetic engineering to insert foreign DNA into cloning vectors.
Q3: Which of the following is not a component of downstream processing? (NEET 2016)
(a) Separation
(b) Purification
(c) Preservation
(d) Expression
Ans: (d)
After the formation of the product in bioreactor, it undergoes some processes before a finished product to be ready for marketing. Downstream processing includes separation and purification process. The product obtained is subjected to quality' control, testing and kept in suitable preservatives.
Q4: Which of the following restriction enzymes produces blunt ends? (NEET 2016)
(a) Sal I
(b) Eco RV
(c) Xho I
(d) Hind III
Ans: (b)
EcoRV is a type II restriction endonuclease isolated from certain strains of E.coli. It creates blunt ends. It recognises the palindromic sequence of 6 bases. Sal I, Xho I and Hind lll restriction enzymes produce sticky ends.
Q5: Which of the following is not a feature of the plasmids? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Transferable
(b) Single-stranded
(c) Independent replication
(d) Circular structure
Ans: b
Plasmid has an extra chromosomal, double stranded circular DNA.
Q6: Which of the following is a restriction endonuclease? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) DNase I
(b) RNasc
(c) Hind ll
(d) Protease
Ans: (c)
A restriction enzyme or restriction endonuclease is an enzyme that cuts DNA at or near specific recognition nucleotide sequences known as restriction sites. Hind II among these is a type of restriction endonuclease.
Q7: Which of the following is not required for any of the techniques of DNA fingerprinting available at present? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Restriction enzymes
(b) DNA-DNA hybridisation
(c) Polymerase chain reaction
(d) Zinc finger analysis
Ans: (d)
Any small, functional, freely folded domain in which coordination of one or more zinc ions is required to stabilise its structure is known as zinc finger. The z.inc finger domains are widely dispersed in eukaryotic genomes and are actively involved in sequence specific binding to DNA/RNA and contribute in protein-protein recognitions.
Q8: The Taq polymerase enzyme is obtained from (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Bacillus subtilis
(b) Pseudomonas putida
(c) Thermus aquaticus
(d) Thiobacillus ferroxidans
Ans: (c)
The Taq polymerase enzyme is obtained from Thermus aquaticus which lives in hot springs.
2015
Q1: The cutting of DNA at specific locations became possible with the discovery of (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015 )
(a) Probes
(b) Selectable markers
(c) Ligases
(d) Restriction enzymes
Ans: (d)
Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA at specific locations
Q2: The DNA molecule to which the gene of interest is integrated for cloning is called: (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015 )
(a) Vector
(b) Template
(c) Carrier
(d) Transformer
Ans: (a)
Vector is a DNA molecule that carries a foreign DNA segment and replicates inside a host cell. The vector DNA and foreign DNA carrying gene of interest are cut by the same restriction endonuclease enzyme to produce complementary sticky ends. With the help of DNA ligase enzyme, the complementary sticky ends of the two DNAs are joined to produce a recombinant DNA (rDNA), which is then introduced into the host cell.
2014
Q1: An analysis of chromosomal DNA using the Southern hybridization technique does not use: (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014 )
(a) Electrophoresis
(b) Blotting
(c) Autoradiography
(d) PCR
Ans: (d)
PCR is used only for amplification of DNA. It is not directly involved in Southern hybridisation technique.
Q2: Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are : (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014 )
(a) BAC and YAC
(b) T/A Cloning Vectors
(c) T− DNA
(d) Expression Vectors
Ans: (a)
Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) vectors are based on natural, extra-chromosomal plasmid of E. coli. BAC vector contains genes for replication and maintenance of the F-factor, a selectable marker and cloning site. These vectors can accommodate upto 300-350 kb of foreign DNA and are also being used in genome sequencing project. Yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) vectors are used to clone DNA fragments of more than 1Mb in size. Therefore, they have been exploited extensively in mapping the large genomes, e.g., in the Human Genome Project. These vectors contain the telomeric sequence, the centromere and the autonomously replicating sequence from yeast chromosomes.
Q 45: Which vector can clone only a small fragment of DNA? (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014 )
(a) Bacterial artificial chromosome
(b) Yeast artificial chromosome
(c) Plasmid
(d) Cosmid
Ans: (c)
Plasmids are small extranuclear circular DNAs that carry extrachromosomal genes in bacteria and some fungi. They replicate independently. The best-known vectors which are also available commercially are pBR322 and pUC-18.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Biotechnology: Principles & Processes - Biology Class 12
| 1. What are the basic principles of biotechnology? |  |
| 2. How are processes like cloning and gene editing carried out in biotechnology? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of biotechnology in today's world? |  |
| 4. How do scientists ensure the safety and ethical use of biotechnology? |  |
| 5. What are the future prospects of biotechnology in terms of advancements and applications? |  |






















