NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Biotechnology & Its Applications | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Which of the following genetically engineered organisms was used by Eli Lilly to prepare human insulin? (NEET 2025)
(a) Virus
(b) Phage
(c) Bacterium
(d) Yeast
Ans: (c)
- Human insulin, which is used to treat diabetes, is now commonly produced using genetic engineering techniques. This process involves inserting the human insulin gene into a suitable organism, which then produces insulin identical to that produced in the human body.
- Eli Lilly, a pharmaceutical company, was one of the pioneers in using genetically engineered organisms to manufacture human insulin. This marked a revolutionary advancement in biotechnology and medicine.
- The genetically engineered organism used for this purpose by Eli Lilly was the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli).
- E. coli, a common bacterium, was genetically modified to produce human insulin. Scientists introduced the human insulin gene into E. coli cells using recombinant DNA technology.
- The modified bacteria then synthesized insulin, which was harvested, purified, and used for medical purposes.
- This method replaced the earlier practice of extracting insulin from the pancreases of pigs or cows, which had limitations such as allergic reactions and a limited supply.
- Using bacteria like E. coli for insulin production is cost-effective, scalable, and ensures the production of insulin that is identical to human insulin.
Other Options:
- Yeast (Incorrect): While yeast cells, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, are also used in genetic engineering, they were not the organism initially used by Eli Lilly for insulin production. Yeast is sometimes used in modern biotechnology for producing proteins, but E. coli was the first organism used for this purpose in insulin production.
- Virus (Incorrect): Viruses are used in genetic engineering for purposes such as gene therapy or as vectors to deliver genetic material into cells. However, viruses are not suitable for producing large quantities of insulin due to their biology and replication mechanisms.
- Phage (Incorrect): Phages, or bacteriophages, are viruses that infect bacteria. They are often used in genetic research and as tools in biotechnology. They were not used by Eli Lilly for insulin production.
Q2: Silencing of specific mRNA is possible via RNAi because of - (NEET 2025)
(a) Complementary tRNA
(b) Non-complementary ssRNA
(c) Complementary dsRNA
(d) Inhibitory ssRNA
Ans: (c)
- Several nematodes parasitize a wide variety of plants and animals including human beings. A nematode Meloidegyne incognitia infects the roots of tobacco plants and causes a great reduction in yield.
- A novel strategy was adopted to prevent this infestation which was based on the process of RNA interference (RNAi).
- RNAi takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defense.
- This method involves the silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation of the mRNA (silencing).
- The source of this complementary RNA could be from an infection by viruses having RNA genomes or mobile genetic elements (transposons) that replicate via an RNA intermediate.
2024
Q1: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)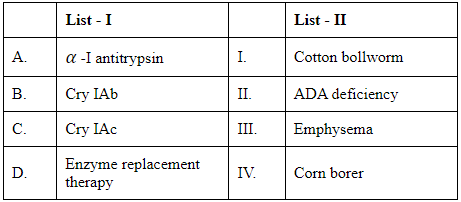
Choose the correct answer form the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(b) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
Ans: (c)
To provide the correct answer, let's evaluate each option by matching the items from List I with their corresponding descriptions from List II:
α-I antitrypsin - This is a protease inhibitor and its deficiency leads to emphysema due to the degradation of the lung tissue. Therefore, α-I antitrypsin corresponds to Emphysema (III).
Cry IAb - Part of a family of proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis used as a biological pesticide. Cry IAb is notably effective against certain types of Lepidoptera, including the European Corn Borer (IV).
Cry IAc - This is also a protein from Bacillus thuringiensis and is notably effective against Cotton Bollworm (I).
Enzyme replacement therapy - Typically used for treating deficiencies in certain enzymes; one prevalent example is Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency, which leads to immune deficiencies (II).
Let's match these back to the original options provided:
A-III (α -I antitrypsin matches with Emphysema)
B-IV (Cry IAb matches with Corn Borer)
C-I (Cry IAc matches with Cotton Bollworm)
D-II (Enzyme replacement therapy matches with ADA deficiency)
Based on these matches, the correct option would be: Option C: A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Q2: Which of the following statements is incorrect? (NEET 2024)
(a) A bio-reactor provides optimal growth conditions for achieving the desired product
(b) Most commonly used bio-reactors are of stirring type
(c) Bio-reactors are used to produce small scale bacterial cultures
(d) Bio-reactors have an agitator system, an oxygen delivery system and foam control system
Ans: (c)
The incorrect statement among the provided options is: Option C.
Bio-reactors, also known as fermenters, are primarily utilized for scaling up microbial processes to industrial scales. They are designed to support the growth of a high density of cells and microbes under controlled conditions to produce large volumes of biochemical products such as enzymes, pharmaceuticals, and other biologically active compounds. While bio-reactors can technically be used for small-scale laboratory experiments, their main application and design focus is on large-scale production.
Other Options:
Option A: This statement is correct. Bio-reactors are specifically designed to provide optimal conditions such as temperature, pH, oxygen supply, and nutrients for the growth of microorganisms or cells, which helps in achieving a higher yield of the desired product.
Option B: This statement is also true. The most common type of bio-reactors used in industrial processes are of the stirred type, which have mechanical agitators to evenly distribute nutrients and maintain uniform conditions within the tank.
Option D: True, bio-reactors often include several essential systems: an agitator system for mixing, an oxygen delivery system to provide sufficient respiration for aerobic organisms, and a foam control system to prevent the formation of excessive foam, which could interfere with the operation of the reactor.
Thus, the incorrect statement about the typical scale and focus of bio-reactor use is Option C.
Q3: Which of the following are fused in somatic hybridization involving two varieties of plants? (NEET 2024)
(a) Callus
(b) Somatic embryos
(c) Protoplasts
(d) Pollens
Ans: (c)
In somatic hybridization, the fusion of protoplasts from different plant varieties or species is a key technique. Protoplasts are plant cells that have had their cell walls enzymatically removed, exposing the cell membrane. This condition allows for the direct fusion of cellular contents including the nucleus and cytoplasm from different cells, facilitating recombination and the formation of a hybrid cell. The process of fusion typically involves techniques such as electrofusion or chemical treatments to encourage the protoplasts to merge.
Looking at the options provided:
- Option A: Callus – This is not correct. A callus is a mass of unorganized plant cells that are generally not involved in fusion during somatic hybridization but are rather a product of the culture of somatic cells.
- Option B: Somatic embryos – These are not the direct subjects of fusion in somatic hybridization. Somatic embryos can develop from hybrid cells, but they themselves are not fused; they are derived from somatic cells under appropriate conditions.
- Option C: Protoplasts – This is correct. Protoplasts are indeed what are fused in somatic hybridization to combine the genetic material from two different plants or varieties.
- Option D: Pollens – These do not fuse in somatic hybridization. Pollen fusion is more relevant to sexual reproduction and breeding, not somatic cell procedures.
Therefore, the correct answer is Option C: Protoplasts.
Q4: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I : Bt toxins are insect group specific and coded by a gene cry IAc.
Statement II : Bt toxin exists as inactive protoxin in B. thuringiensis. However, after ingestion by the insect the inactive protoxin gets converted into active form due to acidic pH of the insect gut.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: (c)
Statement I: Bt toxins are indeed insect group-specific and are coded by the cry gene family, including the cry IAc gene. This is true.
Statement II: While the Bt toxin is produced as an inactive protoxin, it is not the acidic pH of the insect gut but the alkaline pH that activates the protoxin into its toxic form. Therefore, Statement II is false.
Q5: The capacity to generate a whole plant from any cell of the plant is called: (NEET 2024)
(a) Totipotency
(b) Micropropagation
(c) Differentiation
(d) Somatic hybridization
Ans: (a)
Totipotency is defined as the capacity to generate a whole plant from any cell of the plant.
Q6: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: Two DNA sequences were prepared corresponding to A and B chains of human insulin and were introduced in the plasmids of Agrobacterium to produce the insulin chain.
Statement II: Chain A and B were produced separately, extracted, and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
Ans: (d)
Statement I: This statement is false because although Agrobacterium is often used in plant genetic engineering, it is not typically used to produce human insulin. Instead, Escherichia coli (E. coli) or yeast are commonly used to produce the insulin chains (A and B) by introducing the corresponding DNA sequences for each chain. Agrobacterium is more commonly used for plant transformation, not for human insulin production.
Statement II: This statement is true. After producing insulin chains A and B separately (often using bacteria or yeast), the two chains are extracted and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin. These disulfide bonds are crucial for the correct folding and functional activity of insulin.
Thus, Statement I is false, but Statement II is true.
Q7: Important objective of biotechnology in agriculture is to: (NEET 2024)
(a) Produce pest-resistant varieties of plants.
(b) Increase nitrogen content in plants.
(c) Decrease the seed number.
(d) Increase the plant weight.
Ans: (a)
One of the primary objectives of biotechnology in agriculture is to develop genetically modified (GM) crops that are resistant to pests, diseases, or environmental stresses. This can help reduce the need for chemical pesticides, improve crop yields, and ensure food security.
The other options:
- Increase nitrogen content in plants: While this can be beneficial (for example, through nitrogen-fixing bacteria), it is not the primary goal of agricultural biotechnology.
- Decrease seed number: This is not a common goal of biotechnology in agriculture, as increasing seed production is often preferred to improve crop yield.
- Increase plant weight: While improving plant growth is important, pest resistance (as mentioned in option a) is a more prominent application of biotechnology.
Q8: Given below are two statements: One is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R). (NEET 2024)
Assertion (A): Some ethical standards are required to evaluate the morality of scientific human activities that might help or harm living organisms.
Reason (R): Genetic Engineering Approval Committee makes decisions regarding the validity of Genetically Modified (GM) research and the safety of introducing GM organisms for public services.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are True, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are True, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is True, but (R) is False.
(d) (A) is False, but (R) is True.
Ans: (b)
Assertion (A): Ethical standards are indeed required to evaluate the morality of scientific activities, especially in areas like genetic engineering, where the manipulation of genes in living organisms can have both beneficial and harmful effects. This is true because scientific advancements, especially in biotechnology, can raise significant ethical concerns related to their potential impacts on health, environment, and society.
Reason (R): The Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) is responsible for making decisions regarding the validity of genetically modified (GM) research and ensuring the safety of GM organisms before they are released into the environment or used for public services. This is also true as GEAC plays a critical role in overseeing the ethical and safety aspects of GM technology in India.
Although both statements are true, (R) does not directly explain (A). The requirement for ethical standards (A) is broader and pertains to evaluating the morality of various scientific activities, whereas (R) specifically talks about the function of the GEAC, which is more focused on regulatory aspects of GM organisms. Hence, (R) is not the correct explanation for (A).
Q9: Bt toxin protein that can kill many insects, doesn't kill the Bacillus because: (NEET 2024)
(a) Bt toxin requires acidic pH for activation.
(b) Bacillus has a protective mechanism against it.
(c) In Bacillus, it is present in an inactive state, and once insects ingest it, it is converted to an active form.
(d) The protoxin requires a protein conjugate for its activation.
Ans: (c)
Bt toxin (from Bacillus thuringiensis) is produced as a protoxin in an inactive form. When insects ingest it, the toxin is activated in their alkaline gut environment, where it is converted into its active form. This active toxin then binds to receptors in the insect’s gut, causing damage and ultimately killing the insect.
Bacillus thuringiensis itself is not harmed by the toxin because it is stored in an inactive form within the bacterial cells. The toxin does not activate inside the bacterium, and Bacillus has mechanisms that prevent the activated toxin from affecting itself. Therefore, the reason it doesn't harm the Bacillus is because the toxin is in an inactive form until ingested by an insect.
The other options are not entirely correct in this context:
- Option A: The acidic pH helps activate the toxin, but this is not the primary reason why it doesn't affect the bacterium.
- Option B: While Bacillus may have protective mechanisms, the key factor is the inactive form of the toxin inside the bacterium.
- Option C: The protoxin itself does not require a protein conjugate for activation; it is activated by the insect's digestive environment.
Q10: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: The Indian Government has set up GEAC, which will make decisions regarding the validity of GM research.
Statement II: Biopiracy is the term used to refer to the use of bio-resources by native people.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False.
(b) Statement I is False but Statement II is True.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are True.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
Ans: (a)
Statement I: True. The Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) is indeed set up by the Indian government to make decisions regarding the validity of genetically modified (GM) research and the safety of introducing GM organisms. GEAC is responsible for regulating genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in India, ensuring that they are safe for use in the environment and for public consumption.
Statement II: False. Biopiracy refers to the unauthorized use or patenting of biological resources, often by companies or individuals from developed countries, without proper compensation or recognition of the indigenous communities who have traditionally used these resources. It is not the term used for the use of bio-resources by native people themselves. Instead, biopiracy often involves the exploitation of traditional knowledge or natural resources without proper consent or benefit-sharing with local communities.
Thus, Statement I is True, but Statement II is False.
Q11: Following are the steps involved in the action of toxin in Bt Cotton: (NEET 2024)
A. The inactive toxin is converted into an active form due to the alkaline pH of the gut of the insect.
B. Bacillus thuringiensis produces crystals with toxic insecticidal proteins.
C. The alkaline pH solubilizes the crystals.
D. The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut cells, creates pores, and causes the death of the insect.
E. The toxin proteins exist as inactive protoxins in bacteria.
Choose the correct sequence of steps from the options given below:
(a) E → C → B → A → D
(b) B → C → A → E → D
(c) A → E → B → D → C
(d) B → E → C → A → D
Ans: (d)
- B: Bacillus thuringiensis produces crystals containing toxic insecticidal proteins. These proteins are produced by the bacterium as a defense mechanism.
- E: The toxin proteins exist as inactive protoxins in the bacteria. These protoxins are stored as crystalline proteins and are inactive in their native state.
- C: The alkaline pH in the insect’s gut solubilizes the crystals, which then allows the protoxin to be released.
- A: The inactive toxin is converted into its active form due to the alkaline pH of the insect’s gut. This conversion activates the toxin.
- D: The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut cells, creating pores in the cells, leading to the death of the insect by disrupting the digestive system.
Thus, the correct sequence of steps is B → E → C → A → D.
Q12: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)
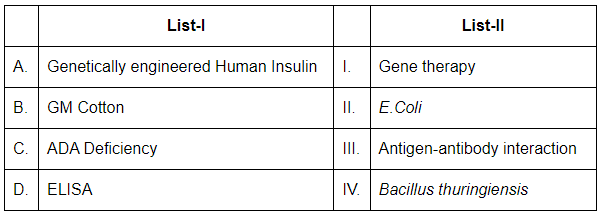
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(b) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(c) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
Ans: (d)
- A. Genetically engineered Human Insulin: Genetically engineered human insulin is produced using E. coli (II) through recombinant DNA technology. The gene for human insulin is inserted into E. coli, which then produces the insulin protein.
- B. GM Cotton: Genetically modified cotton is engineered using Bacillus thuringiensis (IV). The bacterium's Bt toxin gene is inserted into cotton plants to make them resistant to insect pests like bollworms.
- C. ADA Deficiency: ADA deficiency (Adenosine Deaminase deficiency) is treated through Gene therapy (I). Gene therapy involves inserting a normal copy of the ADA gene into the patient's cells to correct the genetic defect.
- D. ELISA: ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) is a technique used to detect antigen-antibody interaction (III). It is commonly used in diagnostic applications to detect the presence of specific antigens or antibodies in a sample.
Thus, the correct matching is A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III.
Q13: The Bt toxin in genetically engineered Bt cotton kills the pest by: (NEET 2024)
(a) Creating pores in the midgut
(b) Damaging the respiratory system
(c) Degenerating the nervous system
(d) Altering the pH of body fluids
Ans: (a)
The Bt toxin in genetically engineered Bt cotton kills pests, such as the cotton bollworm, by binding to the midgut cells of the insect. Once inside the gut, the toxin is activated by the alkaline pH and binds to receptors on the midgut cells, creating pores in the cell membranes. This disrupts the integrity of the gut cells, leading to the leakage of ions and eventually the death of the insect due to gut paralysis and nutrient absorption failure. This method of action is specific to insects, making Bt cotton effective in pest control without harming other organisms.
Q14: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: RNA interference takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defense.
Statement II: RNAi involves the silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary single-stranded RNA molecule that binds and prevents translation of mRNA.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False.
(b) Statement I is False but Statement II is True.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are True.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are False.
Ans: (b)
Statement I: RNA interference (RNAi) is not found in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defense. While RNAi is a well-known and widespread defense mechanism in many eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, it is not necessarily present in all eukaryotic organisms. Some organisms may lack the RNAi pathway or have a less pronounced RNAi mechanism. Therefore, Statement I is False.
Statement II: RNAi indeed involves the silencing of a specific mRNA. This is achieved through a complementary single-stranded RNA molecule (such as small interfering RNA or microRNA) that binds to the target mRNA and prevents its translation or induces its degradation. This process effectively silences the expression of specific genes. Therefore, Statement II is True.
2023
Q1: During the purification process for recombinant DNA technology, addition of chilled ethanol precipitates out
(a) DNA
(b) Histones
(c) Polysaccharides
(d) RNA (NEET 2023)
Ans: (a)
- Option (A) is the correct answer as, during isolation of the genetic material, purified DNA ultimately precipitates out after the addition of chilled ethanol.
- Option (B) is not the answer as, proteins can be removed by treatment with proteases.
- Option (D) is not the answer as RNA can be removed by treatment with ribonuclease.
Q2: In gene gun method used to introduce alien DNA into host cells, microparticles of ________ metal are used.
(a) Zinc
(b) Tungsten or gold
(c) Silver
(d) Copper (NEET 2023)
Ans: (b)
Option (B) is the correct answer because in gene gun method, microparticles of tungsten or gold are used. Gold or tungsten are inert in nature so they do not alter the chemical composition of cells.
Q3: Main steps in the formation of Recombinant DNA are given below. Arrange these steps in a correct sequence.
A. Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host cell
B. Cutting of DNA at specific location by restriction enzyme
C. Isolation of desired DNA fragment
D. Amplification of gene of interest using PCR
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) C, A, B, D
(b) C, B, D, A
(c) B, D, A, C
(d) B, C, D, A (NEET 2023)
Ans: (d)
The correct answer is option (D) because recombinant DNA technology involves several steps in specific sequence such as isolation of DNA, fragmentation of DNA by restriction endonucleases, isolation of desired DNA fragment, ligation of the DNA fragment into a vector, transferring the recombinant DNA into the host, culturing the host cells in a medium at large scale and extraction of the desired product.
Q4: Which one of the following techniques does not serve the purpose of early diagnosis of a disease for its early treatment?
(a) Enzyme Linked Immuno-Sorbent Assay (ELISA) technique
(b) Recombinant DNA Technology
(c) Serum and Urine analysis
(d) Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technique (NEET 2023)
Ans: (c)
-Serum and Urine Analysis: This technique involves testing bodily fluids to detect abnormalities or diseases. While it can provide valuable information, it is generally not the primary method for early diagnosis of many diseases.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is a molecular technique used to amplify DNA. It is highly sensitive and specific, making it an excellent tool for the early diagnosis of infectious diseases and genetic disorders.
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): ELISA is a widely used laboratory test to detect and quantify proteins, antibodies, and hormones. It is effective for early diagnosis of various diseases, including infections and autoimmune disorders.
- Recombinant DNA Technology: This technique involves manipulating DNA to study genes and produce proteins. It can be used for early diagnosis, particularly in genetic testing and identifying pathogens.
Thus, Serum and Urine analysis does not serve the primary purpose of early disease diagnosis as effectively as the other listed techniques.
Q5: Select the incorrect statement regarding the chemical structure of insulin: (NEET 2023)
(a) Mature insulin molecule consists of three polypeptide chains - A, B, and C.
(b) Insulin is synthesized as a prohormone which contains an extra stretch of C-peptide.
(c) C-peptide is not present in the mature insulin molecule.
(d) Polypeptide chains A and B are linked by disulfide bridges.
Ans: (a)
- The mature insulin molecule consists of two polypeptide chains (A and B), not three. The C-peptide is a part of the proinsulin form and is removed during the conversion to mature insulin.
- Statement (b): Insulin is synthesized as a prohormone, known as proinsulin, which indeed contains an extra stretch called the C-peptide.
- Statement (c): C-peptide is not present in the mature insulin molecule. Once proinsulin is processed, the C-peptide is cleaved off, and only the A and B chains remain, linked by disulfide bridges.
- Statement (d): Polypeptide chains A and B are linked by disulfide bridges, which is true for the structure of mature insulin. These disulfide bridges stabilize the insulin molecule.
Thus, Statement (a) is incorrect because insulin consists of two chains (A and B), not three.
Q6: Match List - I with List - II (NEET 2023)
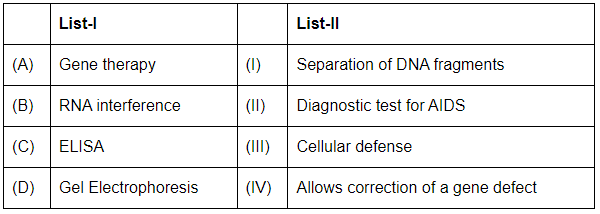
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A)IV (B)I (C)II (D)III
(b) (A)IV (B)II (C)III (D)I
(c) (A)IV (B)III (C)II (D)I
(d) (A)IV (B)III (C)I (D)II
Ans: (c)
(A) Gene therapy: Gene therapy involves the correction of a gene defect by introducing or altering a gene within a patient's cells, so it matches with (IV) Allows correction of a gene defect.
(B) RNA interference: RNA interference (RNAi) is a cellular defense mechanism where RNA molecules inhibit gene expression or translation, so it corresponds with (III) Cellular defense.
(C) ELISA: ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) is widely used as a diagnostic test for AIDS by detecting HIV antibodies or antigens, so it matches with (II) Diagnostic test for AIDS.
(D) Gel Electrophoresis: Gel electrophoresis is a technique used for separating DNA fragments based on size and charge, so it corresponds with (I) Separation of DNA fragments.
Thus, the correct matching is (A)IV, (B)III, (C)II, (D)I.
2022
Q1: Milk of transgenic ‘Cow Rosie’ was nutritionally more balanced product for human babies than natural cow milk because it contained:
(a) Human enzyme Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)
(b) Human protein α-1-antitrypsin
(c) Human alpha-lactalbumin
(d) Human insulin-like growth factor (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
- Option (c) is the correct answer because the first transgenic cow Rosie produced human protein-enriched milk. The milk contained the human alpha-lactalbumin and was nutritionally a more balanced product for human babies than natural cow milk.
- Option (a) is not the correct answer because ADA deficiency in humans can be cured by gene therapy.
- Option (b) is not the correct answer because transgenic sheep produced human α-1-antitrypsin that is used to treat emphysema.
- Option (d) is not the correct answer because insulin-like growth factor was not present in Rosie’s milk.
Q2: In gene therapy of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency, the patient requires a periodic infusion of genetically engineered lymphocytes because: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Gene isolated from marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into cells at embryonic stages
(b) Lymphocytes from patient's blood are grown in culture, outside the body.
(c) Genetically engineered lymphocytes are not immortal cells.
(d) Retroviral vector is introduced into these lymphocytes.
Ans: (c)
- Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) is an enzyme required for the proper functioning of the immune system.
- ADA deficiency is caused due to deletion of the gene for the enzyme adenosine deaminase.
- ADA deficiency can be treated through gene therapy.
- In gene therapy, the lymphocytes from the patient are grown outside the body and a functional ADA cDNA is introduced (using a retroviral vector) into the lymphocytes.
- The genetically engineered lymphocytes are then introduced back into the patient.
- These genetically engineered lymphocytes are immortal hence, the patient has to be infused with such lymphocytes regularly.
So, the correct answer is option c.
Q3: Statements related to human Insulin are given below. (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Which statements is/are correct about genetically engineered Insulin?
(a) Pro-hormone insulin contain extra stretch of C-peptide
(b) A-peptide and B-peptide chains of insulin were produced separately in E.coli, extracted and combined by creating disulphide bond between them.
(c) Insulin used for treating Diabetes was extracted from Cattles and Pigs.
(d) Pro-hormone Insulin needs to be processed for converting into a mature and functional hormone.
(e) Some patients develop allergic reactions to the foreign insulin.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
(a) (a), (b) and (d) only
(b) (b) only
(c) (c) and (d) only
(d) (c), (d) and (e) only
Ans: (b)
- Option (b) is the correct answer as genetically engineered insulin has A-peptide and B-peptide chains of insulin which are produced separately in E.coli, then they are extracted and combined by creating disulphide bond between them.
- Statement (a) is incorrect as genetically engineered insulin does not have an extra stretch of C-peptide. Statement (c) is incorrect as insulin obtained from cattles and pigs is not genetically engineered insulin. Statement (d) is incorrect because conversion of pro-insulin to insulin is not required during production of insulin by genetic engineering as A-peptide and B-peptide chains are produced separately. Statement (e) is incorrect as allergic reactions to insulin are mostly seen when the insulin is obtained from animals.
2021
Q1: When gene targeting involving gene amplification is attempted in an individual's tissue to treat disease, it is known as:
(a) Molecular diagnosis
(b) Safety testing
(c) Biopiracy
(d) Gene therapy (NEET 2021)
Ans: (d)
The correct option is (d)
- Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child/embryo.
- Biopiracy is the term used to refer to the use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organisations without proper authorisation from the countries and people concerned without compensatory payment.
- Molecular diagnosis refers to the act or process of determining the nature and cause of a disease.
Q2: With regard to insulin choose correct options. (2021)
(a) C-peptide is not present in mature insulin.
(b) The insulin produced by rDNA technology has C-peptide.
(c) The pro-insulin has C-peptide.
(d) A-peptide and B-peptide of insulin are interconnected by disulphide bridges.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (a), (c) and (d) only
(b) (a) and (d) Only
(c) (b) and (d) only
(d) (b) and (c) only
Ans: (a)
- Insulin is synthesized as a pro-hormone which contains A-chain, B-chain and an extra stretch called the C-peptide.
- C-peptide is not present in mature insulin called humulin.
- Chains A and B are connected by interchain disulphide bridges.
2020
Q1: Match the following columns and select the correct option. (NEET 2020)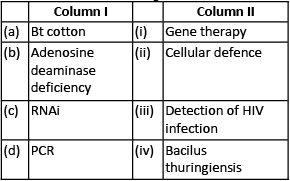
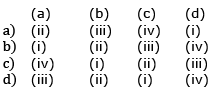
Ans: (c)
Bt cotton the specific Bt toxin gene was isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis. The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4-year old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency. RNAi (RNA interference) takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defense. PCR is now routinely used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients
Q2: Which of the following statements is not correct? (NEET 2020)
(a) The functional insulin has A and B chains linked together by hydrogen bonds.
(b) Genetically engineered insulin is produced in E-Coli.
(c) In man insulin is synthesised as a proinsulin.
(d) The proinsulin has an extra peptide called C-peptide.
Ans: (a)
Functional insulin has A and B chains linked together by disulphide bridges.
2018
Q1: In India, the organisation responsible for assessing the safety of introducing genetically modified organisms for public use is (NEET 2018)
(a) Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
(b) Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR)
(c) Research Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM)
(d) Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)
Ans: (d)
Indian government has set up organisation such as GEAC (Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee) which makes decisions regarding the validity of GM research and safety of introducing GM organisms for public services.
Q2: Use of bioresources by multinational companies and organisations without authorisation from the concerned country and its people is called (NEET 2018)
(a) Bio-infringement
(b) Biopiracy
(c) Biodegradation
(d) Bioexploitation
Ans: (b)
Biopiracy refers to the use of bio-resources by multinational companies and other organizations without proper authorization from the countries and people concerned.
Q3: A ‘new’ variety of rice was patented by a foreign company, though such varieties have been present in India for a long time, This is related to (NEET 2018)
(a) Co-667
(b) Sharbati Sonora
(c) Lerma Rojo
(d) Basmati
Ans: (d)
In 1997, an American company got patent rights on Basmati rice through the US Patent and Trademark Office. This allowed the company to sell a ‘new’ variety of Basmati.
2016
Q1: Which kind of therapy was given in 1990 to a four-year-old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency? (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Gene therapy
(b) Chemotherapy
(c) Immunotherapy
(d) Radiation therapy
Ans: (a)
Gene therapy is a technique of genetic engineering which involves replacement of a faulty/disease causing gene by a normal healthy functional gene. The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4-year old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency. This enzyme is very important for the immune system to function. The deficiency of this enzyme can lead to severe combined immune deficiency (SCID).
Q2: The two polypeptides of human insulin are linked together by (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Covalent bond
(b) Disulphide bridges
(c) Hydrogen bonds
(d) Phosphodiester bond
Ans: (b)
Insulin is a hormone consisting of 2 polypeptide chains. Each chain is composed of a specific sequence of amino acid residues connected by peptide bonds. In humans, chain A has 21 amino acids, and chain B has 30. Post translational modifications result in the connection of these two chains by disulfide bridges. Cysteine residues on A7 and B7, as well as A20 to B19 are covalently connected by disulfide bridges.
Q3: Which part of the tobacco plant is infected by Meloidogyne incognita? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Stem
(b) Root
(c) Flower
(d) Leaf
Ans: (b)
Meloidogyne incognita is a nematode (roundworm) in the family Heteroderidae. It is commonly called the “southern rootknot nematode” or the “cotton root-knot nematode”.
2015
Q1: Golden rice is a genetically modified crop plant where the incorporated gene is meant for biosynthesis of : (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015 )
(a) Vitamin C
(b) Omega 3
(c) Vitamin A
(d) Vitamin B
Ans: (c)
Golden rice (Oryza sativa) is a genetically modified crop. It biosynthesizes β - carotene which is the precursor of vitamin-A.
Q2: In Bt cotton, the Bt toxin present in plant tissue as pro-toxin is converted into active toxin due to: (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015 )
(a) Acidic pH of the insect gut
(b) Action of gut micro-organisms
(c) Presence of conversion factors in insect gut
(d) Alkaline pH of the insect gut
Ans: (d)
Bt toxin are solubilised in alkaline pH of the insect gut causing death.
Q3: The crops engineered for glyphosate are resistant/ tolerant to: (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015 )
(a) Bacteria
(b) Insects
(c) Herbicides
(d) Fungi
Ans: (c)
Today plants having the broad leaves are made resistant to a powerful biodegradable herbicide glyphosate. It is an active ingredient of Round Up ready plant. It disturbs the working of EPSP synthetase enzyme. If it is taken up by crop plants they will die. So, the bioengineers have transferred gene for synthesis of EPSP synthetase enzyme to crop plant.
Q4: Which body of the Government of India regulates GM research and safety of introducing GM organisms for public services ? (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Indian Council of Agricultural Research
(b) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee
(c) Research Committee on Genetic Manipulation
(d) Bio-safety committee
Ans: (b)
Genetic modification of organisms can have unpredictable results, when such organisms are introduced into the ecosystem. Therefore, the Indian Government has set up organizations such as GEAC (Genetic Engineering Approval Committee), which makes decisions regarding the validity of GM research and the safety of introducing GM-organisms for public services.
2014
Q1: The first human hormone produced by recombinant DNA technology is: (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014 )
(a) Insulin
(b) Estrogen
(c) Thyroxin
(d) Progesterone
Ans: (a)
Mammalian hormones were among the first products prepared in bacteria by r-DNA technology. Human insulin and human growth hormone are earliest examples.
Q2: To obtain virus−free healthy plants from a diseased one by tissue culture technique, which part/parts of the diseased plant will be taken ? (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014 )
(a) Epidermis only
(b) Palisade parenchyma
(c) Both apical and axillary meristems
(d) Apical meristem only
Ans: (c)
To obtain virus - free healthy plants from a diseased one by tissue culture technique, both apical and axillary meristems of the diseased plant will be taken. Plant tissue culture is used to maintain or grow plant cells, tissues or organs under sterile conditions on a nutrient culture medium of known composition. Plant tissue culture is widely used to produce clones of a plant in a method known as micro propagation.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Biotechnology & Its Applications - Biology Class 12
| 1. What are the applications of biotechnology in the field of medicine? |  |
| 2. How is biotechnology used in agriculture? |  |
| 3. What is the role of biotechnology in environmental conservation? |  |
| 4. How is biotechnology used in forensic science? |  |
| 5. What are the ethical considerations associated with biotechnology and its applications? |  |






















