Subjective Type Questions: Miscellaneous (Sets, Relations, Statistics & Mathematical | JEE Advanced | 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE PDF Download
Q.1. An investigator interviewed 100 students to determine their preferences for the three drinks : milk (M), coffee (C) and tea (T). He reported the following : 10 students had all the three drinks M, C and T; 20 had M and C; 30 had C and T; 25 had M and T; 12 had M only; 5 had C only; and 8 had T only.
Using a Venn diagram find how many did not take any of the three drinks. (1978)
Ans. Sol. We have
n (U) = 100, where U stands for universal set
n (M ∩ C ∩ T) = 10; n (M ∩ C) = 20;.
n (C ∩ T) = 30; n (M ∩ T) = 25;
n (M only) = 12; n (only C) = 5;
n (only T) = 8
Filling all the entries we obtain the Venn diagram as shown :
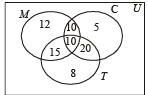
∴ n (M ∩ C ∪ T) = 12 + 10 + 5 + 15 + 10 + 20 + 8 = 80
∴ n (M ∪ C ∪ T)' = 100 – 80 = 20
Q.2. (a) Construct a triangle with base 9 cm and altitude 4 cm, the ratio of the other two sides being 2 : 1.
(b) Construct a triangle in which the sum of the three sides is 15 cm with base angles 60° and 45°. Justify your steps.
(1979)
Ans. Sol. (a) To construct a Δ with base = 9 cm, altitude = 4 cm and ratio of the other two sides as 2 : 1.
Steps of Construction : 1. Draw BC = 9 cm
2. Divide BC internally at P and externally at Q in the ratio 2 : 1.
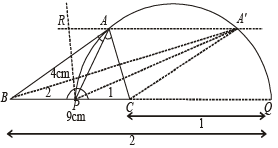
3. Draw a semicircle on PQ.
4. Draw a line || BQ at a distance of 4 cm from intersecting semicircle at A and A'.
5. ABC and A'BC are the required Δ's.
(b) To construct a Δ with perimeter = 15 cm, base angles 60° and 45°.
Steps of Construction :
1. Draw PQ = 15 cm
2. At P draw ∠RPQ = 60° and 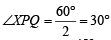
and at Q draw ∠SQP = 45° and ∠YQP =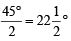
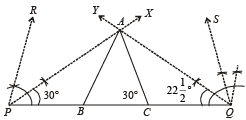
3. PX and QY meet each other at A.
4. Through A draw AB || PR and AC || QS.
5. ABC is the required Δ.
Justification: Q AB || PR and PA transversal
∴∠PAB = ∠RPA = 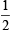 x 60° = 30°
x 60° = 30°
∠APB = ∠BAP = 30° ⇒ AB = PB
Similarly AC = CQ
∴ AB + BC + CA = PB + BC + CQ = 15 cm
Also ∠ABC = ∠RPB = 60° and ∠ACB = ∠SQS = 45°
Q.3. A tent is made in the form of a frustrum A of a right circular cone surmounted by another right circular cone B. The diameter of the ends of the frustrum A are 8 m and 4 m, its height is 3 m and the height of the cone B is 2 m. Find the area of the canvas required. (1979)
Ans. Sol. Slant height of frustum 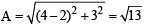
∴ Curved surface area of frustum =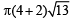
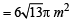
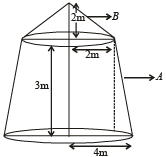
Also slant height of cone 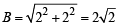
∴ Curved surface area of cone = 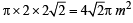
∴ Area of canvas required = 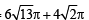
Q.4. In calculating the mean and variance of 10 readings, a student wrongly used the figure 52 for the correct figure of 25. He obtained the mean and variance as 45.0 and 16.0 respectively. Determine the correct mean and variance. (1979)
Ans. Sol. Let the remaining 9 readings be x1, x2, x3 ..... x9 and tenth is taken by the student as 52.
∴ Incorrect mean 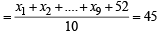
⇒ x1 + x2 + ....+ x9 = 450 – 52 = 398
∴ Correct mean 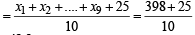
⇒ Correct mean = 42.3
Incorrect variance 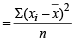
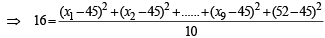
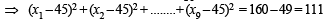
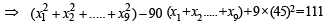
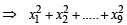
= 111 + 90 × 398 – 9 × (45)2 = 17706 ...(2)
Correct variance 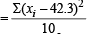
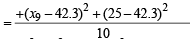
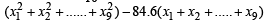
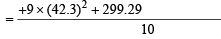
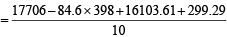
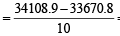
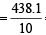 = 43.81
= 43.81
Q.5. The diameter PQ of a semicircle is 6 cm. Construct a square ABCD with points A, B on the circumference, and the side CD on the diameter PQ. Describe briefly the method of con struction. (1980)
Ans. Sol. The rough figure is as shown, let 2x be the side of square.
In ΔOBC r2 = x2 + 4x2
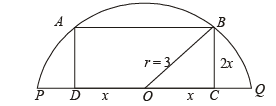
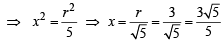
Now on number line we locate M such that OM = 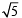
Divide OM in five equal parts and take a point C on it such that OC : CM = 3 : 2. So, that 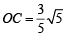
Now, draw a line segment PQ = 6 cm whose mid-point is O.
From this cut a line segment 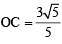 and
and 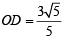 on opposite sides of O.
on opposite sides of O.
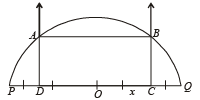
At C and B draw perpendiculars to PQ. With O as centre and OP as radius, draw a semicircle intersecting the perpendiculars draw at C & D at A and P respectively. Join AB. ABCD is the required square.
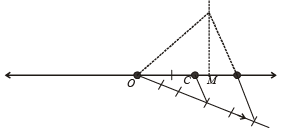
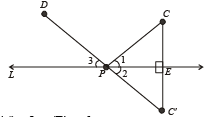
Q.6. C and D are any two points on the same side of a line L.
Show how to find a point P on the line L such that PC and PD are equally inclined to the line L. Justify your steps. (1980)
Ans. Sol. Here we are given two points C and D on the same side of line L. To find a point P on L such that PC and PD are equally inclined to L.
Steps of Construction : 1. From C draw CE ⊥ L and produce it to C ' such that EC ' = EC.
2. Join C ' D intersecting L at P. Also join CP.
3. By simple geometry ∠1 = ∠2 and ∠2 = ∠3 ⇒ ∠1 = ∠3
∴ PC and PD are the required lines inclined equally to L.
Q.7. (i) Set A has 3 elements, and set B has 6 elements. What can be the minimum number of elements in the set A ∪ B? (1980) (ii) P, Q, R are subsets of a set A. Is the following equality true ?
R × (Pc ∪ Qc)c = (R × P) ∩ (R × Q)? (1980)
(iii) For any two subset X and Y of a set A define X o Y = (Xc ∩ Y) ∪ (X ∩Yc) Then for any three subsets X, Y and Z of the set A, is the following equality true. (X o Y) o Z = X o (Y o Z)? (1980)
Ans. Sol. (i) n (A) = 3, n (B) = 6
We know that n (A ∪ B) ≥ max (n (A), n (B)) ⇒ n (A ∪ B) ≥ 6
∴ Min number of element that A ∪ B can have is 6.
(ii) Here R × (Pc ∪ Qc)c = R × (P ∩ Q) = (R × P) ∩ (R × Q)
∴ Given equality is true.
(iii) Yes
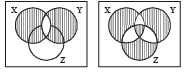
From (1) and (2) (X o Y) o Z = X o (Y o Z)
Q.8. Suppose A1, A2, ........ A30 are thirty sets each with five elements and B1, B2, ....... Bn are n sets each with three elements. Let 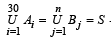 Assume that each element of S belongs to exactly ten of the Ai’ s and to exactly nine of the Bj’ s. Find n. (1981 - 2 Marks)
Assume that each element of S belongs to exactly ten of the Ai’ s and to exactly nine of the Bj’ s. Find n. (1981 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. We are given that 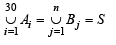 ....(1)
....(1)
Each A'is contain 5 elements, so 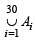 contains 5 × 30 = 150 elements (with repetition) out of which each element is repeated 10 times, (as given that each element of S belongs to 10 A'is)
contains 5 × 30 = 150 elements (with repetition) out of which each element is repeated 10 times, (as given that each element of S belongs to 10 A'is)
∴ Number of different elements in 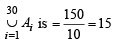
∴ From eqn (1) we can say S contains 15 elements...(2) Again each B'js contains 3 elements, so 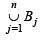 contains 3 × n = 3n elements (with repetition), out of which each element is repeated 9 times (as each element of S belongs to 9 B'js)
contains 3 × n = 3n elements (with repetition), out of which each element is repeated 9 times (as each element of S belongs to 9 B'js)
∴ No. of different elements in 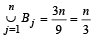
∴ From eqn (1) we can say S contain n/3 elements....(3) From (2) and (3) we get 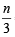 =15 ⇒ n = 45
=15 ⇒ n = 45
Q.9. The mean square deviations of a set of observations x1, x2, ....., xn about a points c is defined to be
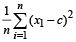 The mean suqare deviations about –1 and +1 of a set of observatons are 7 and 3 respectively. Find the standard deviation of this set of observations. (1981 - 2 Marks)
The mean suqare deviations about –1 and +1 of a set of observatons are 7 and 3 respectively. Find the standard deviation of this set of observations. (1981 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Given that : Mean square deviation for the observations x1, x2, .... xn, about a point. c is given by 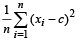 Also given that mean square deviations about – 1 and + 1 are 7 and 3 for a particular set of observations.
Also given that mean square deviations about – 1 and + 1 are 7 and 3 for a particular set of observations.
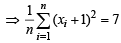 and
and 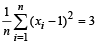
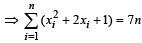 and
and 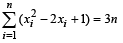
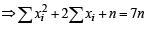 and NOTE THIS STEP
and NOTE THIS STEP
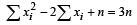
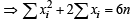 ...(1)
...(1)
and 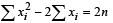 ...(2)
...(2)
Subtracting (2) from (1), we get
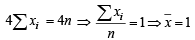
Now standard deviation for same set of observations
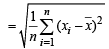
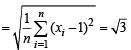
{using the given value}
Q.10. The marks obtained by 40 students are grouped in a frequency table in class intervals of 10 maks each. The mean and the variance obtained from this distribution are found to be 40 and 49 respectively. It was later discovered that two observations belonging to the class interval (21–30) were included in the class interval (31–40) by mistake. Find the mean and the variance after correcting the error. (1982 - 3 Marks)
Ans. Sol. n = 40 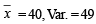
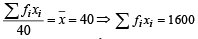 ....(1)
....(1)
Also Var. = 49 =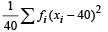
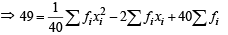
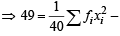 2 x 1600 x 40 x 40
2 x 1600 x 40 x 40
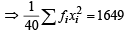 ...(2)
...(2)
Let 21 – 30 and 31 – 40 denote the kth and (k + 1)th class intervals respectively.
Then if before correction fk and fk+1 are the frequencies of these intervals then after correction (2 observations are shifted from 31 – 40 to 21 – 30), frequency of kth intervals becomes fk + 2 and frequency of (k + 1)th interval becomes fk+1 – 2.
Then, we get
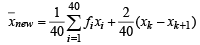
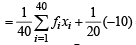 = 40 – 0.5 = 39.5
= 40 – 0.5 = 39.5
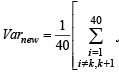
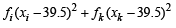
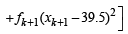
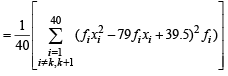
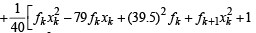
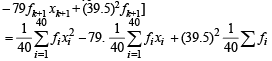
= 1649 – 3160 + 1560.25 = 49.25 [Using eqn. (1) and (2)]
Q.11. A relation R on the set of complex numbers is defined by z1 R z2 if and only if
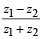 is real. Show that R is an equivalence relation. (1982 - 2 Marks)
is real. Show that R is an equivalence relation. (1982 - 2 Marks)
Ans. Sol. Given that 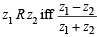 is real.
is real.
To show that R is an equivalence relation.
Reflexivity : For z1 = z2 = z (say)
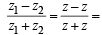 0 which is real
0 which is real
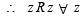 ∴ R is reflexive.
∴ R is reflexive.
Symmetric : Let z1 R z2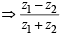 is real
is real 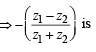 also real
also real
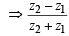 is real ⇒ z2 R z1 ⇒ R is symmetric.
is real ⇒ z2 R z1 ⇒ R is symmetric.
Transitivity : Let z1 R z2 and z2 R z3
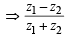 is real and
is real and 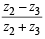 is also real
is also real
Now, 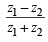 is real ⇒
is real ⇒ 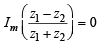
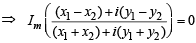
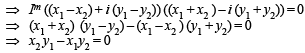
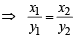 ...(1)
...(1)
Similarly,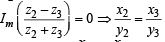 ...(2)
...(2)
From (1) and (2) we get 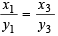
⇒ 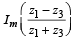 = 0 ⇒
= 0 ⇒ 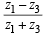 is real
is real
⇒ z1R z3 ∴ R is transitive.
Thus R is reflexive, symmetric and transitive.
Hence R is an equivalence relation.
|
347 docs|185 tests
|
FAQs on Subjective Type Questions: Miscellaneous (Sets, Relations, Statistics & Mathematical - JEE Advanced - 35 Years Chapter wise Previous Year Solved Papers for JEE
| 1. What is the definition of a set in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What is a relation in mathematics? |  |
| 3. How is statistics used in real-life applications? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between mean, median, and mode in statistics? |  |
| 5. How is mathematical reasoning important in problem-solving? |  |
















