Preposition-1 | English Grammar Basic - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Preposition |

|
| Kinds of Preposition |

|
| A list of Phrasal Preposition |

|
Introduction
Prepositions are essential components of English grammar. They serve as connectors that link nouns, pronouns, or phrases to other words within a sentence. They provide critical information about relationships, indicating direction, location, time, and other connections between elements in a sentence. Prepositions help clarify the meaning of sentences, making them more precise and informative.
In English, prepositions are small but powerful words that play a significant role in expressing complex ideas and relationships. They help answer questions like "where?" "When?" "how?" and "why?" by indicating spatial, temporal, and logical relationships.
For example, prepositions can specify the location of an object ("on the table"), the time of an event ("at noon"), or how something is done ("by car"). Understanding and using prepositions correctly is crucial for clear and effective communication.
Preposition
A Preposition is a word placed before a noun or a pronoun to show in what relation the person or thing denoted by it stands regarding something else.
Examples:
- The cat is under the table.
- "under" is the preposition, showing the relationship between the cat and the table.
- She walked through the park.
- "through" is the preposition, showing the path she took.
- The book is on the shelf.
- "on" shows where the book is in relation to the shelf.
Kinds of Preposition

Simple Preposition
Simple Prepositions include at, by, for, from, in, on, of, off, to, through, up, with, out, till, etc.
Of these, at, by, with, in, and on are used after verbs indicating rest in a place.
Examples:
- Moni is in Darjeeling.
- I sat by John.
- I was in the garden.
- The keys were with me.
- The book was on the table.
- To, from, of, through, and up are used after verbs indicating motion.
- I went to London.
- Tom came from his house.
- We went through the field.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill.
Compound Prepositions
Compound Prepositions include above, across, along, amidst, around, about, among, amongst, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, into, inside, outside, underneath, within, without, etc.
Compound Prepositions are formed by combining a preposition with a noun, adjective, or adverb.
Examples:
- above = on + by + up
- across = on + cross
- into = in + to
Participial Prepositions
Participial Prepositions including barring, concerning, considering, during, expecting, judging, notwithstanding, regarding, respecting, etc., are the present participles of verbs. These participles have acquired the character of prepositions, no longer needing the prop of a noun to cling to.
Example:
- Barring accident, the mail will arrive in time.
- "Barring" means expecting or apart from, showing an exception.
Concerning yesterday's murder, many persons were arrested.
- "Concerning" is similar to about, referring to the subject of the sentence (yesterday's murder).
Considering the quality, the price is too high.
- "Considering" here means taking into account, and focusing on the quality when evaluating the price.
Touching this matter, I have not as yet made up my mind.
- "Touching" means with regard to, referring to a specific matter or subject.
Double Preposition
Double Prepositions include from behind, from beyond, from within, etc., where, often two prepositions are used with the same object.
Example:
- The mischief was done from behind the screen.
- The news came from beyond the Atlantic.
- Somebody shouted from within the room.
Disguised Prepositions
Disguised Prepositions include hunting, ashore (a = on), o'clock (o' = of), once a week, two rupees a day (a = on)
Example: We jumped overboard at 3 o'clock and swam ashore.
Detached Prepositions
Detached Prepositions are those which are far removed from their objects.
Example: Whom did you speak to?
Phrasal Prepositions
Phrasal Prepositions or Phrase Prepositions are the groups of words that are used with the force of a single preposition.
Example:
- Jack succeeded by means of hard labour.
- "by means of" or simply "by" shows the method or way Jack succeeded, indicating that his success was achieved through hard labour.
James failed on account of his negligence.
- "on account of" is similar to for or because of, showing the reason or cause for James's failure, which was his negligence.
The object to a Preposition may also be a Descriptive adverb, an Adverbial phrase, or a Noun clause
Adverbs as objects to a Preposition:
- John is by far the best boy in his class.
- He will have reached home by then.
- Much might happen between now and then.
- He left at once to come back before now.
- From here to there is a long distance.
Adverbial phrases as objects to a Preposition:
- The ship suddenly came into view from beyond the horizon.
- He did not reach till long after midnight.
Noun clauses as objects to a Preposition:
- He informed me of what had happened there.
- It depends on whether you can go or not.
A list of Phrasal Preposition
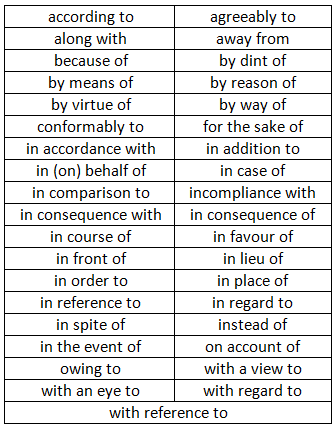
Several words are used sometimes as adverbs and sometimes as prepositions. A word is a preposition when it governs a noun or pronoun and it is an adverb when it does not.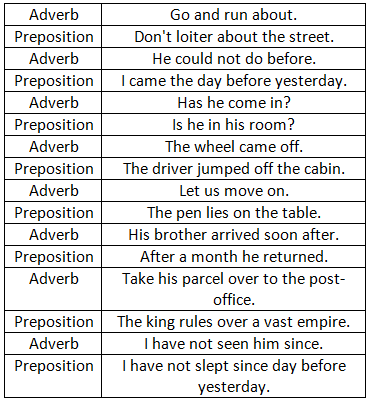
|
20 videos|143 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Preposition-1 - English Grammar Basic - Class 10
| 1. What are prepositions and why are they important in English? |  |
| 2. What are the different kinds of prepositions? |  |
| 3. Can you provide examples of phrasal prepositions? |  |
| 4. How do prepositions affect the meaning of sentences? |  |
| 5. Are there any common mistakes to avoid when using prepositions? |  |





















