Central Banking in India: Functions of RBI - UPSC PDF Download
Ref: https://edurev.in/question/463149/The-central-banking-functions-in-India-are-performed-by-theI-Central-Bank-of-IndiaII-Reserve-Bank-
Key Facts:
- In the monetary system of all countries, the central bank occupies a most important place.
- The Central Bank is an apex institution of the monetary system which regulates the functioning of the commercial banks of a country.
- The Central Bank of India is ‘Reserve Bank of India’.
- A Central Bank is primarily meant to promote the financial and economic stability of the country.
- The Central Bank of a country promotes economic growth and stability and controls inflation
Functions of the Central Banks/RBI
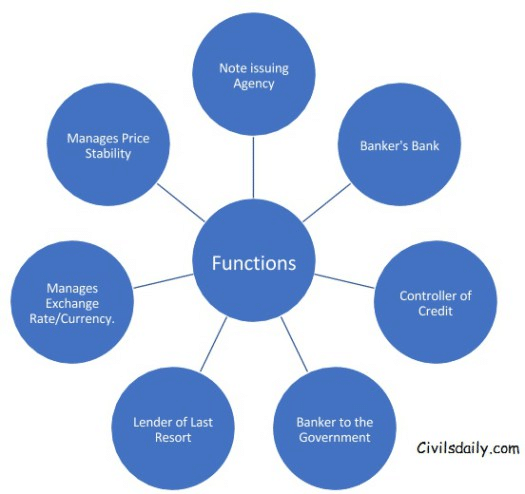
Issue of Currency Notes
- Under section 22 of RBI Act, the bank has the sole right to issue currency notes of all denominations except one-rupee coins and notes.
- The one-rupee notes and coins and small coins are issued by Central Government, and their distribution is undertaken by RBI as the agent of the government.
- The RBI has a separate issue department which is entrusted with the issue of currency notes.
Banker to The Government
- The RBI acts as a banker agent and adviser to the government. It has an obligation to transact the banking business of Central Government as well as State Governments.
- Example, RBI receives and makes all payments on behalf of the government, remits its funds, buys and sells foreign currencies for it and gives it advice on all banking matters.
- RBI helps the Government – both Central and state – to float new loans and manage public debt.
- On behalf of the central government, it sells treasury bills and thereby provides short-term finance.
Banker’s bank And Lender of Last Resort
- RBI acts as a banker to other banks. It provides financial assistance to scheduled banks and state co-operative banks in the form of rediscounting of eligible bills and loans and advances against approved securities.
- RBI acts as a lender of last resort. It provides funds to the bank when they fail to get it from any other source.
- It also acts as a clearing house. Through RBI, banks make inter-banks payments.
Controller of Credit
- RBI has the power to control the volume of credit created by banks. The RBI through its various quantitative and qualitative measures regulates the money supply and bank credit in an economy.
- RBI pumps in money during recessions and slowdowns and withdraws money supply during an inflationary period.
Manages Exchange Rate and Is Custodian of the Foreign Exchange Reserve
- RBI has the responsibility of removing fluctuations from the exchange rate market and maintaining a competitive and stable exchange rate.
- RBI functions as custodian of nations foreign exchange reserves.
- It has to maintain a fair external value of Rupee.
- RBI achieves its objective through appropriate monetary and exchange rate policies.
Collection and Publication of Data
- The RBI collects and compiles statistical/data information on banking and financial operations, prices, FDIs, FPIs, BOP, Exchange Rate and industries etc., of the economy.
- The Reserve Bank of India publishes a monthly Bulletin/publication for the same.
- It not only provides information but also highlights important studies and investigations conducted by RBI.
Regulator and Supervisor of Commercial Banks
- The RBI has wide powers to supervise and regulate the commercial and co-operative banks in India.
- RBI issues licenses regulate branch expansion, manages liquidity and Assets, management and methods of working of commercial banks and amalgamation, reconstruction and liquidation of the banks.
Clearing House Functions
- The RBI acts as a clearing house for all member banks. This avoids unnecessary transfer of funds between the various banks.
Measures of Credit Control in India
The management of the money supply and credit control is an important function of the Reserve Bank of India. The money supply has an important bearing on the functioning of the economy.
FAQs on Central Banking in India: Functions of RBI - UPSC
| 1. What are the functions of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)? |  |
| 2. How does the Reserve Bank of India control inflation? |  |
| 3. How does the Reserve Bank of India regulate banks and financial institutions? |  |
| 4. How does the Reserve Bank of India manage the currency in circulation? |  |
| 5. How does the Reserve Bank of India promote the development of financial markets? |  |



















