JEE Advanced (Matrix Match & Integer Answer): States of Matter | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Each question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column-I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column-II are labelled p, q, r, s and t. Any given statement in Column-I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column-II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as illustrated in the following example :
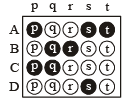
If the correct matches are A-p, s and t; B-q and r; C-p and q; and D-s then the correct darkening of bubbles will look like the given.
Q.1. Match gases under specified conditions listed in Column I with their properties/laws in Column II. Indicate your answer by darkening the appropriate bubbles of the 4 × 4 matrix given in the ORS. (2007)
Column I Column II
(A) Hydrogen gas (P = 200 atm, T = 273 K) (p) Compressibility factor ≠ 1
(B) Hydrogen gas (P ~ 0, T = 273 K) (q) Attractive forces are dominant
(C) CO2 (P = 1 atm, T = 273 K) (r) PV = nRT
(D) Real gas with very large molar volume (s) P(V – nb) = nRT
Ans. (A) - (p, s); (B) - (r); (C) - (p, q); (D) - (r);
Sol. (A) : (p) and (s) Because 200 atm pressure is very large.
For H2 gas, at very high pressure Z > 1.
(B) : (r) Since P ~ 0, it means very low presure, so ideal behaviour is observed.
(C) : (p) and (q) Since P is 1 atm, Z for CO2 would be less than 1.
(D) : (r) In real gas with very high molar volume, molecules will be very far apart from each other due to which van der Waal's forces as well as actual volume occupied by molecules will be negligible.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















