JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Haloalkanes & Haloarenes | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
1. (a) Show by chemical equations only, how you would prepare the following from the indicated starting materials. Specify the reagents in each step of the
synthesis.
(i) Hexachlorethane, C2Cl6, from calcium carbide.
(ii) Chloroform from carbon disulphide.
(b) Give one chemical test which would distinguish between C2H5OH from CHCl3. (1979)
Solution :
(a)
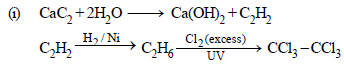
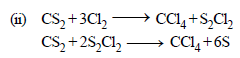

(b) Carbylamine test.
CHCl3 + aq KOH + aniline (i.e. primary amine) → bad smelling isocyanide
C2H5OH + aq KOH + aniline → No reaction
2. Write the structural formula of the major product in each of the following cases :
(i) chloroform reacts with aniline in the presence of excess alkali (1981 - ½ Mark)
(ii) bromoethane reacts with one-half of the molar quantity
of silver carbonate. (1981 - ½ Mark)
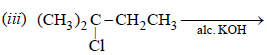
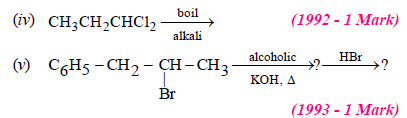
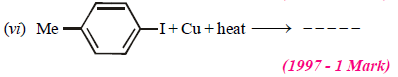
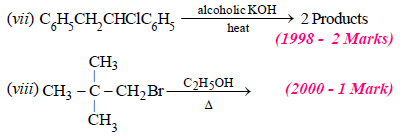
Solution :
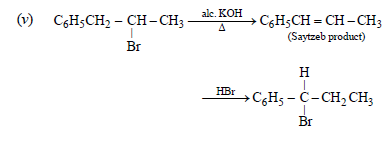
 carbocations are formed on addition of HBr on C6H5CH=CHCH3, the latter being benzylic carbocation,
carbocations are formed on addition of HBr on C6H5CH=CHCH3, the latter being benzylic carbocation,
is stabilised due to resonance and hence Br– adds on it forming C6H5CHBr.CH2CH3 as the final product.]
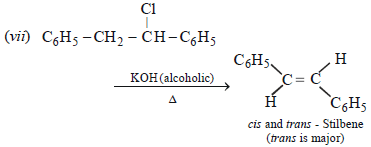
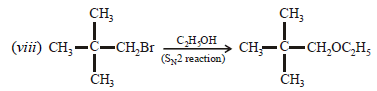
3. Give reasons for the following :
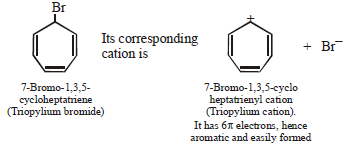
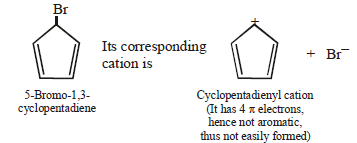
(i) 7-Bromo-1, 3, 5-cycloheptatriene exists as ionic compound, while 5-bromo-1, 3-cyclopentadiene does not ionise even in presence of Ag+ ion. Explain.
(2004 - 2 Marks)
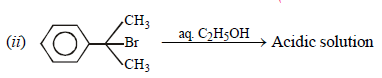
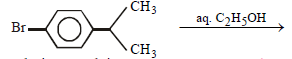 Neutral solution. Explain. (2005 - 1 Mark)
Neutral solution. Explain. (2005 - 1 Mark)
Solution :
(i) TIPS/Formulae :
7-Bromo-1,3,5-cycloheptatriene is aromatic whereas
5-Bromo-1,3-Cycloheptadiene is non aromatic.
(ii) NOTE : The former halide is a 3° halide, hence it undergoes SN1 reaction forming HBr, as one of the products, which make solution acidic
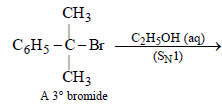
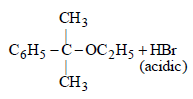
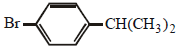 is an aryl halide so it does not undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions. Hence the solution will remain neutral.
is an aryl halide so it does not undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions. Hence the solution will remain neutral.
4. State the conditions under which the following preparation are carried out. Give the necessary equations which need not be balanced :
(i) Lead tetraethyl from sodium-lead alloy (1983 - 1 Mark)
(ii) Methyl chloride from aluminium carbide (1983 - 1 Mark)
solution :
(i) 4C2H5Br + 4(Na–Pb)  Pb(C2H5)4 + 4NaBr + 3Pb
Pb(C2H5)4 + 4NaBr + 3Pb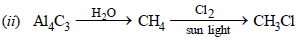
5. Write the structure of all the possible isomers of dichloroethene. Which of them will have zero dipole moment? (1985 - 2 Marks)
Solution :
Dichloroethene exists in three isomeric forms.
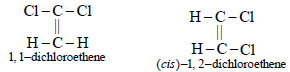
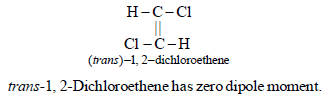
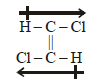
6. What happens when excess chlorine is passed through boiling toluene in the presence of sunlight?(1987 - 1 Mark)
Solution :
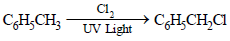
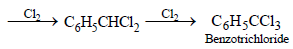
NOTE : This follows free radical mechanism.]
7. What effect should the following resonance of vinyl chloride have on its dipole moment? (1987 - 1 Mark)
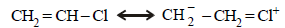
Solution :
TIPS/Formulae :
Resonance decreases the dipole moment of vinyl chloride (CH2 = CHCl). The positive charge on Cl and a negative charge on C (developed by resonance) oppose each other and hence diminish the electronegativity of Cl and thus polarity (and dipole moment) of the bond. The dipole moments of vinyl chloride and chlorobenzene are 1.4D and 1.7D respectively, while the dipole moment of alkyl halides is 2–2.2D.
8. An organic compound X, on analysis gives 24.24 per cent carbon and 4.04 per cent hydrogen. Further, sodium extract of 1.0 g of X gives 2.90 g of silver chloride with acidified silver nitrate solution. The compound X may be represented by two isomeric structures, Y and Z. Y on treatment with aqueous potassium hydroxide solution gives a dihydroxy compound while Z on similar treatment gives ethanal. Find out the molecular formula of X and give the structures of Y and Z. (1989 - 4 Marks)
Solution : 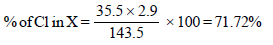
Empirical formula of (X)
| Element | % | Relative no. of atoms | Simplest ratio |
| C | 24.24 | 2.02 | 1 |
| H | 4.04 | 4.04 | 2 |
| Cl | 71.72 | 2.02 | 1 |
∴ Empirical formula of (X) is CH2Cl
Since X has two isomers Y and Z; both react with KOH(aq).
Y  dihydroxy compound i.e. 2Cl atoms on adjacent carbon
dihydroxy compound i.e. 2Cl atoms on adjacent carbon
Z  CH3CHO i.e. Z should have 2Cl atoms on one C atom
CH3CHO i.e. Z should have 2Cl atoms on one C atom
Thus Z should be CH3CHCl2 (1, 1-dichlorethane) and
Y should CH2ClCH2Cl (1, 2-dichloroethane)
Reactions :
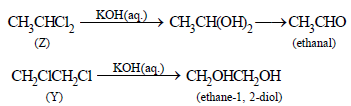
9. Draw the stereochemical structures of the products in the following reaction : (1994 - 4 Marks)
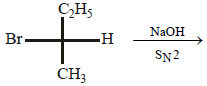
Solution:
SN2 reaction leads to inversion in configuration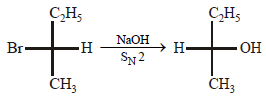
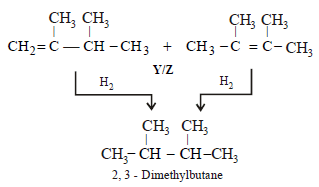
10. An alkyl halide, X, of formula C6H13Cl on treatment with potassium tertiary butoxide gives two isomeric alkenes Y and Z (C6H12). Both alkenes on hydrogenation give 2, 3-dimethylbutane. Predict the structures of X, Y and Z. (1996 - 3 Marks)
Solution :
Summary of the given facts
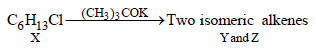
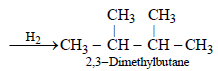
The two isomeric precursors of (Y and Z) of 2, 3-dimethylbutane
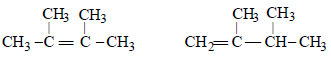
Hence the precursor of Y & Z should have following structure which explains all the given facts
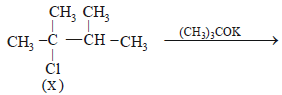
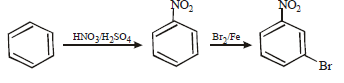
11. How will you prepare m-bromoiodobenzene from benzene (in not more than 5-7 steps)? (1996 - 2 Marks)
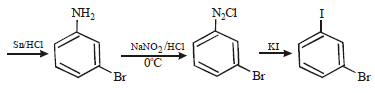
Solution :
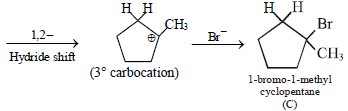
12. Cyclobutyl bromide on treatment with magnesium in dry ether forms an organometallic (A). The organometallic reacts with ethanal to give an alcohol (B) after mild acidification. Prolonged treatment of alcohol (B) with an equivalent amount of HBr gives 1–bromo–1–methylcyclopentane (C). Write the structures of (A), (B) and explain how (C) is obtained from (B). (2001 - 5 Marks)
Solution :
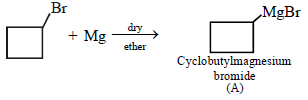
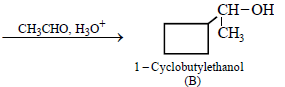
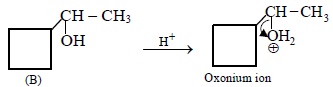
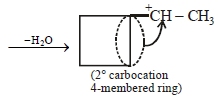
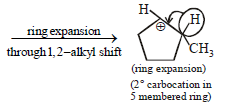
|
446 docs|930 tests
|






















