JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): The s-Block Elements | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Sodium carbonate is made by Solvay process but the same process is not extended to the manufacture of potassium carbonate.
(ii) Hydrogen peroxide is a better oxidising agent than water.
(iii) Magnesium oxide is used for the lining of steel making furnace.
(iv) Why is sodium chloride added during electrolysis of fused anhydrous magnesium chloride?
(v) Hydrogen peroxide acts as an oxidising as well as a reducing agent.
(vi) The crystalline salts of alkaline earth metals contain more water of crystallisation than the corresponding alkali metal salts.
(vii) BeCl2 can be easily hydrolysed.
Solution. (i) Potassium ca r bon ate can n ot be man u factur ed by Solvay process, since, unlike sodium hydrogen carbonate, potassium hydrogen carbonate is rather too soluble in water to be precipitated like NaHCO3.
(ii) H2O2 is a better oxidising agent than H2O because oxidation number of oxygen in H2O2 is –1 and that in water it is –2. So H2O2 easily reduces to –2 oxidation number.
(iii) MgO is used for the lining of steel making furnace because it acts as basic flux and facilitates the removal of acidic impurities of Si, P and S from steel through slag formation.
(iv) The anhydrous magnesium chloride is fused with NaCl to provide conductivity to the electrolyte and to lower the fusion temperature of anhydrous MgCl2.
NOTE : NaCl prevents hydrolysis of MgCl2.
(v) The oxidation state of oxygen in H2O2 (i.e. –1) can be changed to 0 or –2 i.e oxygen in H2O2 exists in an intermediate oxidation state with respect to O2 and O2–.
Hence it acts both as an oxidising and reducing agent.
(vi) NOTE : Smaller the size of cation, higher will be hydration tendency because hydration energy of cation is inversely proportional to size of cation.
The size of alkaline earth metal ions are smaller than the size of alkali metal ions. So in crystalline form the salts of alkaline earth metals have more water molecules than those of alkali metals.
(vii) BeCl2 is hydrolysed due to high polarising power and presence of vacant p-orbitals in Be-atom.
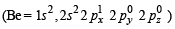
Q.2. How will you prepare bleaching powder from slaked lime
Solution. Bleaching powder, Ca(OCl)2, can be prepared by passing chlorine through Ca(OH)2 solution.
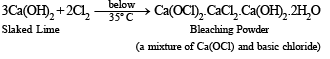
Q.3. Write down the balanced equations for the reactions when:
(i) Calcum phosphate is heated with a mixture of sand and carbon;
(ii) An alkalin e solution of potassium fer ricyan ide is reacted with hydrogen peroxide.
(iii) Car bon dioxide is passed th rough a concen tr ated aqueous solution of sodium chloride saturated with ammonia.
(iv) Potassium ferricyanide reacts with hydrogen peroxide in basic solution.
(v) Carbon dioxide is passed through a suspension of lime stone in water.
Solution. (i)
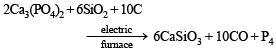
This is the electrothermal process to extract phosphorus from phosphorite or bone ash [Ca3(PO4)2].
(ii) Ferricyanide is oxidised to ferrocyanide on treatment with alkali
2K3[Fe(CN)6] + H2O2 + 2KOH → 2K4[Fe(CN)6] + 2H2O + O2
(iii) NaCl + NH4OH + CO2 → NH4Cl + NaHCO3
(iv) 2K3[Fe(CN)6] + H2O2 + 2KOH → 2K4[Fe(CN)6] + 2H2O + O2
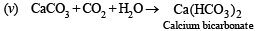
NOTE : Suspension oif lime stone is CaCO3.
Q.4. Give briefly the isolation of magnesium from sea water by the Dow process. Give equations for the steps involved.
Solution. In sea water Mg exists as MgCl2.
On treating sea water with slaked lime Mg(OH)2 is obtained.
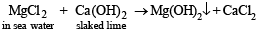
On reacting Mg(OH)2 with HCl, MgCl2 is obtained.
Mg(OH)2 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O
From MgCl2, Mg is obtained by reduction of MgCl2 with CaC2.
MgCl2 + CaC2 → Mg + CaCl2 + 2C
Q.5. Complete and balance the following reactions :
Ca5 (PO4)3 F + H2SO4+ H2O 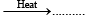 + 5CaSO4 .2H2O+ ......... .
+ 5CaSO4 .2H2O+ ......... .
Solution. Ca5(PO4)3F + 5H2SO4 + 10H2O 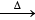 3H3PO4 + 5CaSO4.2H2O + HF
3H3PO4 + 5CaSO4.2H2O + HF
Q.6. A 5.0 cm3 solution of H2O2 liberates 0.508 g of iodine from an acidified KI solution. Calculate the strength of H2O2 solution in terms of volume strength at STP.
Ans. 4.48 volumes
Solution.
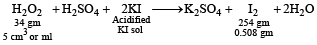
i.e. 254 gm of I2 is released by 34 gm H2O2
∴ 0.508 gm of I2 will be released by
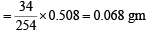
5 ml of H2O2 sol. contains 0.068 gm of H2O2.
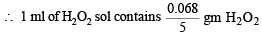
NOTE : The strength of H2O2 is generally calculated in terms of volume strength. According to which 10 volume of H2O2 means that 1 ml of H2O2 sol gives 10 ml of O2 at STP.
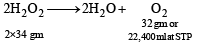
i.e., 68 gm of H2O2 gives 22,400 ml of O2 at STP or 1 ml of H2O2 sol
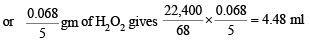
or 1 ml of H2O2 sol gives 4.48 ml of O2 i.e. strength of H2O2 sol is 4.48 volumes
Q.7. Explain the difference in the nature of bonding in LiF and LiI.
Solution. LiF has more ionic character while LiI has more covalent character. The latter is due to the greater polarizability of larger iodide ion than the fluoride ion.
Q.8. To a 25ml H2O2 solution, excess of acidified solution of potassium iodide was added. The iodine liberated required 20 ml of 0.3 N sodium thiosulphate Solution. Calculate the volume strength of H2O2 solution.
Ans. 1.344
Solution. Meq. of H2O2 = Meq.of Na2S2O3
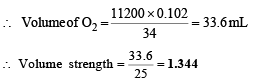
Q.9. Give reactions for the oxidation of hydrogen peroxide with potassium permanganate in acidic medium.
Solution. 2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2MnSO4 + 3H2O + 5 [O]
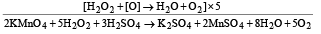
Q.10. Element A burns in nitrogen to give an ionic compound B. Compound B reacts with water to give C and D. A solution of C becomes ‘milky’ on bubbling carbon dioxide. Identify A, B, C and D.
Ans. Ba, Ba3N2, Ba(OH)2, BaCO3
Solution.
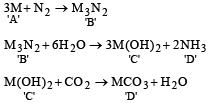
M may be either Ca or Ba.
NOTE : It is not magnesium because Mg(OH)2 has very low solubility in water.
If we consider Ba as M then A is Ba, B is Ba3N2, C is Ba(OH)2, D is BaCO3.
Q.11. Arrange the following sulphates of alkaline earth metals in or der of decreasing th ermal stability : BeSO4, MgSO4, CaSO4, SrSO4
Ans. SrSO4 > CaSO4 > MgSO4 > BeSO4
Solution. SrSO4 > CaSO4 > MgSO4 > BeSO4 (Based upon size of cation or ionic character)
Q.12. Work out the following using chemical equation: Chlorination of calcium hydroxide produces bleaching powder.
Solution.
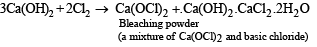
Q.13. Hydr ogen per oxide acts both as an oxidising and as a reducing agent in alkaline solution towards certain first row transition metal ions. Illustrate both these properties of H2O2 using chemical equations.
Solution. When H2O2 acts as oxidising agent, following reaction takes place:
H2O2 + 2e– → 2OH–
While regarding its action as reducing agent, the following reaction takes place:
H2O2 + 2OH– → O2 + 2H2O + 2e–
Examples of oxidising character of H2O2 in alkaline medium
2Cr(OH)3 + 4NaOH + 3H2O2 → 2Na2CrO4 + 8H2O
Here Cr3+ (Cr is a first row transition metal) is oxidised to Cr6+.
Example of reducing character of H2O2 in alkaline medium
2K3[Fe(CN)6]+2KOH+H2O2 → 2K4[Fe(CN)6]+2H2O+O2
Here Fe3+ (Fe is a first row transition metal) is reduced to Fe2+.
|
481 docs|964 tests
|





















