JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Alcohols, Phenols & Ethers- 1 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
1. An organic liquid (A), containing C, H and O with boiling point : 78°C, and possessing a rather pleasant odour, on heating with concentrated sulphuric acid gives a gaseous product (B) – with the empirical formula, CH2. ‘B’ decolourises bromine water as well as alkaline KMnO4 solution and takes up one mole of H2 (per mole of ‘B’) in the presence of finely divided nickel at high temperature. Identify the substances ‘A’ and ‘B’. (1979)
Solution:
‘A’ is C2H5OH and ‘B’ is C2H4
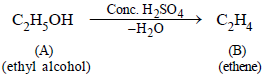
2. A compound (X) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It does not add bromine. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydriodic acid, (X) yields only one organic product (Y). On hydrolysis, (Y) yields a new compound (Z) which can be converted into (Y) by reaction with red phosphorus and iodine. The compound (Z) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid. The equivalent weight of this acid is 60. What are the compounds (X), (Y) and (Z)? Write chemical equations leading to the conversion of (X) to (Y). (1981 - 3 Marks)
Solution:
TIPS/Formulae :
The unreactivity of the compound (X) towards sodium indicates that it is neither an acid nor an alcohol, further its unreactivity towards Schiff’s base indicates that it is not an
aldehyde. The reaction of compound (X) with excess of HI to form only one product indicates that it should be an ether.
Hence its other reactions are sketched as below.
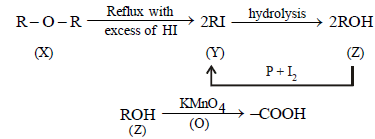
Since the carboxylic acid has equivalent weight of 60, it must be acetic acid (CH3COOH), hence Z must be ethyl alcohol, (Y) ethyl iodide and (X) diethyl ether.
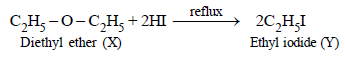
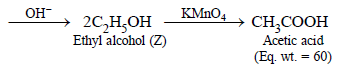
3. Outline the reaction sequence for the conversion of
(i) 1-propanol from 2-propanol (in three steps) (1982 - 1 Mark)
(ii) ethyl alcohol to vinyl acetate. (in not more than 6 steps) (1986 - 3 Marks)
(iii) phenol to acetophenone (1989 - 1½ Marks)
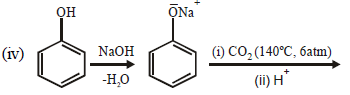
(iv)  (2003 - 2 Marks)
(2003 - 2 Marks)
Solution :
(i) 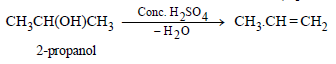
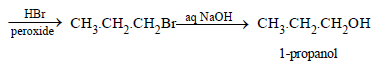
(ii) 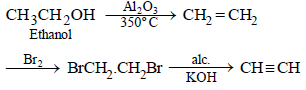
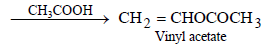
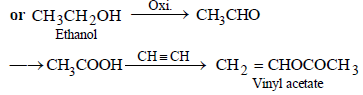
(iii) 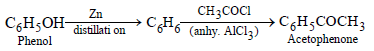
4. State with balanced equations what happens when :
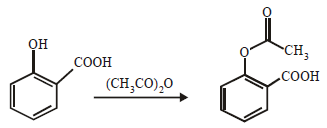
(i) acetic anhydride reacts with phenol in presence of a base. (1982 - 1 Mark)
(ii) Ethylene glycol is obtained by the reaction of ethylene with potassium permanganate. (1991 - 1 Mark)
Solution :
(i) 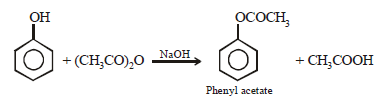
(ii) 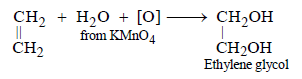
5. Give reasons for the following :
(i) Sodium metal can be used for drying diethyl ether but not ethanol. (1982 - 1 Mark)
(ii) Phenol is an acid but it does not react with sodium bicarbonate. (1987 - 1 Mark)
(iii) Acid catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than that of n-butanol. (1998 - 2 Marks)
Solution :
(i) Ethanol (due to the presence of active hydrogen atom, C2H5 – O – H) reacts with sodium metal, while ether and benzene have no such hydrogen atom and hence
do not react with sodium and thus can be dried by metallic sodium.
(ii) Phenol (a weaker acid) reacts with NaHCO3 (a weaker base) to form phenoxide ion (a stronger base) and carbonic acid (a stronger acid).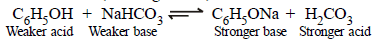
Since acid-base equilibria lie towards the weaker acid and weaker base, phenol does not decompose NaHCO3
(difference from carboxylic acids).
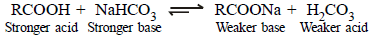
(iii) Since 3º carbocation (formed in case of t-butanol) is more stable than 1º (formed in n-butanol), the dehydration in the former proceeds faster than in the
latter.
6. An alcohol A, when heated with conc. H2SO4 gives an alkene B. When B is bubbled through bromine water and the product obtained is dehydrohalogenated with excess of
sodamide, a new compound C is obtained. The compound C gives D when treated with warm dilute H2SO4 in presence of HgSO4. D can also be obtained either by oxidizing A with KMnO4 or from acetic acid through its calcium salt. Identify A, B, C and D. (1983 - 4 Marks)
Solution : The given problem can be sketched as below.
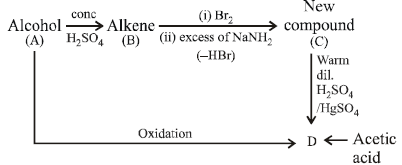
NOTE THIS STEP : From the problem it appears that the compound C is an alkyne, hence D must be an aldehyde or ketone. Further since D can be obtained from acetic acid
through its calcium salt it may be either acetaldehyde or acetone. Hence going back, A may be either ethyl alcohol or iso-propanol both of which explains the given set of
reactions.
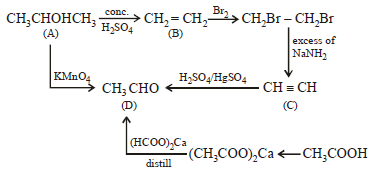
Hence
A is ethyl alcohol, CH3CH2OH
B is ethylene, CH2 = CH2
C is acetylene, CH ≡ CH
D is acetaldehyde, CH3 . CHO
7. A compound of molecular formula C7H8O is insoluble in water and dilute sodium bicarbonate but dissolves in dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide. On treatment with bromine
water, it readily gives a precipitate of C7H5OBr3. Write down the structure of the compound. (1985 - 2 Marks)
Solution:
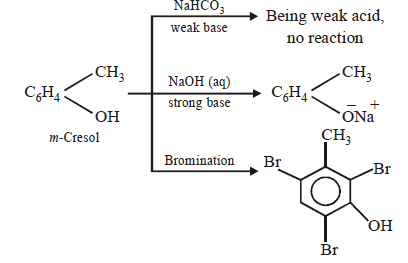
(i) The compound (C7H8O) is soluble in aq. NaOH but insoluble in NaHCO3, indicating it to have a phenolic group.
(ii) The compound, on treatment with Br2 water, gives C7H5OBr3. Taking into account of molecular formulae of the two compounds, the parent compound seems to
be cresol.
(iii) Bromination of the compound reveals that it is m-cresol as it forms tribromo derivative.
(iv) The reactions are
8. Give a chemical test/suggest a reagent to distinguish between methanol and ethanol. (1985 - 1 Mark)
Solution :
TIPS/Formulae :
Iodoform test is used to distinguish methanol and ethanol. Ethanol gives iodoform test while methanol does not respond.
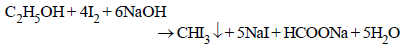
9. Complete the following with appropriate structures :
Solution
(i) 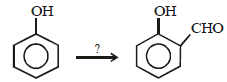
(ii) 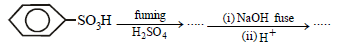
Solution:
(i) 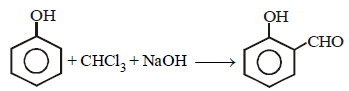
(ii) 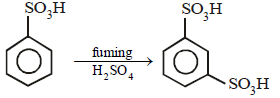
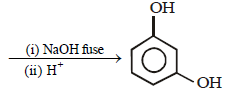
10. Compound ‘X’ (molecular formula, C5H8O) does not react appreciably with Lucas reagent at room temperature but gives a precipitate with ammonical silver nitrate. With excess of MeMgBr, 0.42 g of ‘X’ gives 224 ml of CH4 at STP. Treatment of ‘X’ with H2 in presence of Pt catalyst followed by boiling with excess HI, gives n-pentane. Suggest
structure for ‘X’ and write the equation involved. (1992 - 5 Marks)
Solution :
(i) Since the compound X (C5H8O) does not react appreciably with Lucas reagent, it indicates that the compound has a primary alcoholic group (–CH2OH).
(ii) Reaction of the compound X with ammonical silver nitrate to give a precipitate indicates that it has an acetylenic hydrogen atom, i.e., ≡C – H grouping is
present.
(iii) Treatment of X with H2/Pt followed by boiling with excess of HI gives n-pentane. It indicates that the compound does not have any branch.
On the basis of the above points, compound X (C5H8O) may be assigned following structure.
HC ≡ C – CH2 – CH2 – CH2OH
(X) 4-Pentyn-1-ol (Mol. wt. 84, Eq. wt. = 42)
The above structure for the compound X is in accordance with its equivalent weight obtained from the given data.
224 ml. of CH4 at STP is obtained from 0.42 g
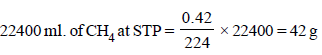
∴ Eq. wt. of the compound X = 42
Reactions of the compound X :
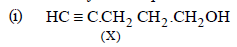
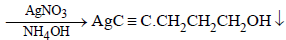
(ii)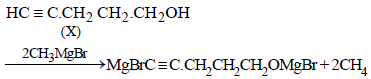
(iii)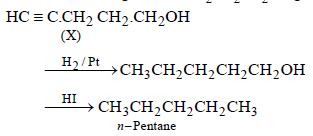
11. When t-butanol and n-butanol are separately treated with a few drops of dilute KMnO4, in one case only the purple colour disappears and a brown precipitate is formed. Which of the two alcohols gives the above reaction and what is the brown precipitate? (1994 - 2 Marks)
solution :
n-Butanol gives the following reaction in which the purple colour of KMnO4 changes to brown. tert-Alcohols are not oxidisable easily, hence purple colour of KMnO4 remains same.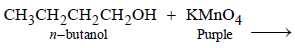
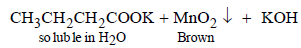
The brown precipitate is of MnO2
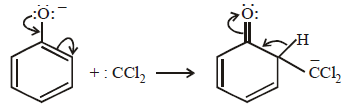
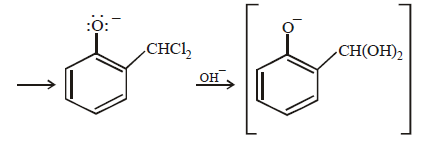
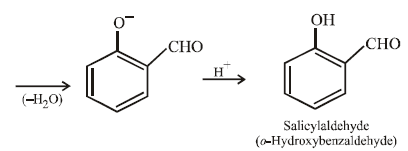
12. When phenol is reacted with CHCl3 and NaOH followed by acidification, salicylaldehyde is obtained. Which of the following species are involved in the above mentioned reaction as intermediates? (1995 - 2 Marks)
(i) 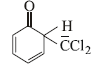
(ii) 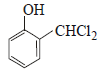
(iii) 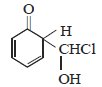
(iv) 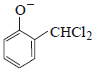
Solution :
TIPS/Formulae :
The reaction involves electrophilic substitution on the highly reactive phenoxide ion.
Here the electrophile is dichlorocarbene formed by the action of strong alkali on chloroform.
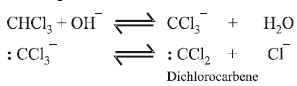
|
446 docs|929 tests
|





















