JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Compounds Containing Nitrogen- 1 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Fill in the Blanks
Q.1. In an acidic medium, ................. behaves as the strongest base. (1981 - 1 Mark)
(nitrobenzene, aniline, phenol)
Ans. aniline
Solution. aniline.
Q.2. Amongst the three isomers of nitrophenol, the one that is least soluble in water is ............... . (1992 - 1 Mark)
Ans. o-nitrophenol
Solution. o-Nitrophenol; this isomer involves intramolecular hydrogen bonding whereas the other two isomers have intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Because of this, the former is less polar and hence least soluble in polar solvent water.
Q.3. The high melting point and insolubility in organic solvents of sulphanilic acid are due to its........structure. (1994 - 1 Mark)
Ans. dipolar ion
Solution. Dipolar ion. (Salt like)
Subjective Problems
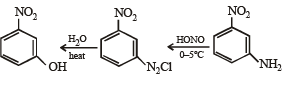
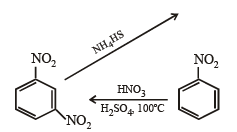
Q.1. Show with equations how the following compounds are prepared (equations need not be balanced) :
(i) n-propyl amine from ethyl chloride (in two steps) (1982 - 1 Mark)
(ii) chlorobenzene from aniline (in two steps). (1982 - 1 Mark)
(iii) Aniline from benzene (1983 - 1 Mark)
(iv) Acetoxime from acetaldehyde using the reagents, [K2Cr2O7/H+, Ca(OH)2 and NH2OH.HCl]. (1984 - 2 Marks)
(v) aniline to chlorobenzene (1985 - 1 Mark)
(vi) benzaldehyde to cyanobenzene. (in not more than 6 steps) (1986 - 2 Marks)
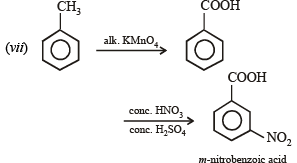
(vii) toluene to m-nitrobenzoic acid? (1987 - 1 Mark)
(viii) 4-nitroaniline to 1, 2, 3-tribromobenzene. (1990 - 2 Marks)
(ix) p-bromonitrobenzene from benzene in two steps. (1993 - 2 Marks)
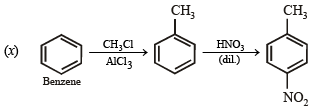
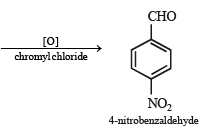
(x) 4-nitrobenzaldehyde from benzene. (1994 - 2 Marks)
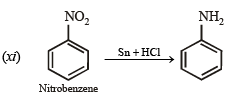
(xi) benzamide from nitrobenzene (1994 - 2 Marks)
(xii) Aniline → Benzylamine (in 3 steps) (2000 - 3 Marks)
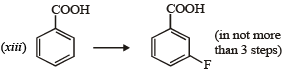 (2003 - 2 Marks)
(2003 - 2 Marks)
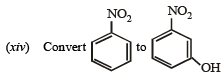 in not more than four steps. (2004 - 4 Marks)
in not more than four steps. (2004 - 4 Marks)
Solution. (i)
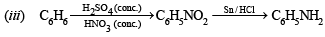
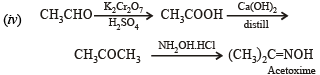
(v) Consult (ii)
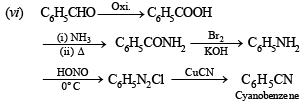
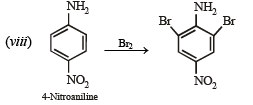
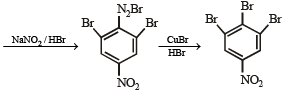
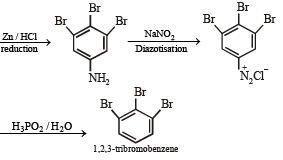
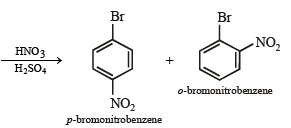
On fractional crystallization para isomer crystallizes first.
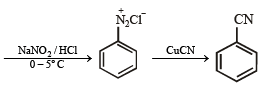
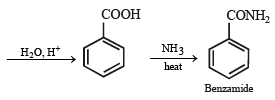

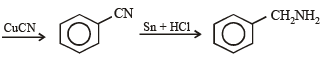
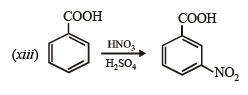
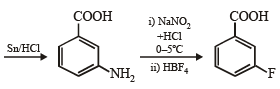
(xiv) Going backward, we can easily solve the problem.
Q.2. Give reasons for the following :
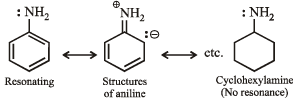
(i) Cyclohexylamine is a stronger base than aniline. (1982 - 1 Mark)
(ii) o-Nitrophenol is steam volatile whereas p-nitrophenol is not; (1985 - 1 Mark)
(iii) Dimethylamine is a stronger base than trimethylamine. (1998 - 2 Marks)
(iv) Nitrobenzene does not undergo Friedel - Craft salkylation (1998 - 2 Marks)
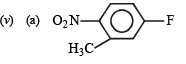
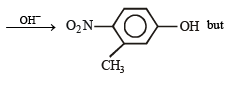
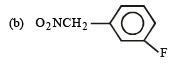 (2005 - 1 Mark)
(2005 - 1 Mark)
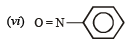
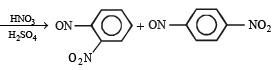
but
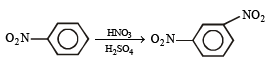 (2005 - 1 Mark)
(2005 - 1 Mark)
Solution. (i) Aniline is weak base than cyclohexylamine because of resonance while there is no resonance in cyclohexylamine
(ii) o-nitrophenol shows intramolecular H-bonding and p-nitrophenol shows intermolecular H- bonding and thus its several molecules associate with each other.
The ortho isomer goes with the steam due to its low boiling point.
(iii) TIPS/Formulae : Two factors operate in deciding the basicity of alkyl amines.
(a) Inductive effect
(b) Solvation effect
(a) Inductive effect. The alkyl group being electron releasing increases the charge density on nitrogen. This in turn increases the basicity of amines. The expected order of basicity is
R3N > R2NH > RNH2 > NH3
(b) Solvation effect. Because of the positive charge carried by the conjugate acid of an amine, it is stabilised by the hydrogen bonding with the solvent water. The larger the number of hydrogens attrached to the nitrogen in the conjugate acid, the larger is its stability and thus larger is the basicity of the corresponding base. The expected order of basicity of the alkylamines will be
NH3 > RNH2 > R2NH > R3N
he inductive and solvent effects predict the opposite trend in the basicity of alkyl amines. In going from R2NH to R3N the solvation effect plays a more dominating role as compared to the inductive effect making R2NH more basic than R3N.
A simple explanation is that the steric factor in R3N makes the availability of a lone pair of electrons on nitrogen poor than in the dialkylamine, predicting R2NH a stronger base than R3N.
(iv) The nitro group in nitrobenzene strongly deactivates the benzene ring due to – I and – M effects. This decreases the reactivity of benzene ring towards Friedel - Crafts alkylation.
(v) TIPS/Formulae : –NO2 group is electron withdrawing, hence m-directing whereas –CH2NO2 is not.
(a) Given compound is an aryl fluoride having electronwithdrawing –NO2 group at para position of fluoride atom which activates the fluoride due to – M and – E effects for nucleophilic substitution (SNAr), hence reaction with NaOH will liberate F– as NaF.
(b) The given compound is an aryl fluoride having –CH2NO2 group in the meta position which is not capable of activating aryl fluoride (absence of –M and –E effects because NO2 group is present in m-position and also not conjugated to benzene ring) for nucleophilic substitution, hence aq. NaOH will not displace fluorine here, i.e. no F- will be formed
(vi) (a) 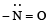 group is electron releasing, henceo-, p-directing
group is electron releasing, henceo-, p-directing
(b) 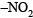 group is electron withdrawing, hence m-directing
group is electron withdrawing, hence m-directing
Q.3. Arrange the following :
(i) p-toluidine, N, N-dimethyl-p-toluidine, p-nitroaniline, aniline in increasing basicity (1986 - 1 Mark)
(ii) methylamine, dimethylamine, aniline, N-methylaniline in incerasing order of base strength. (1988 - 1 Mark)
Ans. (i) N, N-dimethyl-p-toluidine, < p-nitroaniline < aniline < p-toluidine.
(ii) aniline-N-methylamine < methylaniline < dimethylaniline
Solution. (i) TIPS/Formulae : Presence of +I group increases the basicity whereas presence of –I group decreases the basicity.
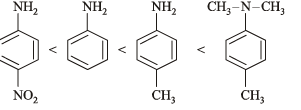
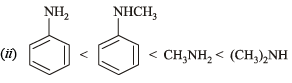
The ease with which the lone pair of electron (unshared) on the N-atom co-ordinates with a proton determines the relative basic strength of amines.
Q.4. Complete the following with appropriate structures :
 (1986 - 1 Mark)
(1986 - 1 Mark)
 (1992 - 1 Mark)
(1992 - 1 Mark)
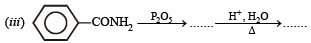 (1992 - 1 Mark)
(1992 - 1 Mark)
(iv) 2, 4-Dinitroaniline
 (1995 - 1 Mark)
(1995 - 1 Mark)
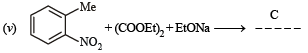 (1997 - 1 Mark)
(1997 - 1 Mark)
 (1998 - 2 Marks)
(1998 - 2 Marks)
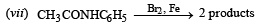 (1998 - 2 Marks)
(1998 - 2 Marks)
Solution.
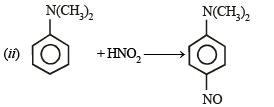
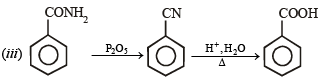
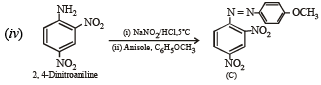
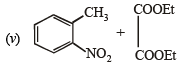
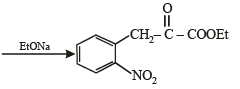
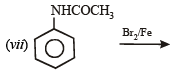
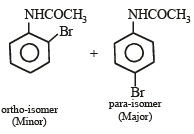
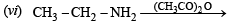 CH3 - CH2 - NH - COCH3 + CH3COOH
CH3 - CH2 - NH - COCH3 + CH3COOH
Q.5. Write balanced equations for the following reaction : Acetamide is reacted with bromine in the presence of potassium hydroxide. (1987 - 1 Mark)
Solution. Hoffmann degradation reaction.
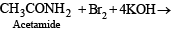
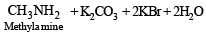
Q.6. Give a chemical test and the reagents used to distinguish between the following pair of compounds : Ethylamine and diethylamine. (1988 - 1 Mark)
Solution. NOTE : Carbylamine reaction is a distinction test for primary amines. All primary amines (alphatic or aromatic) on heating with alcoholic KOH and CHCl3 give unpleasant or foul smell of isocyanide which is easily detected.
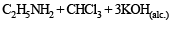
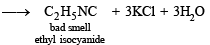
Diethylamine , a 2° amine, does not respond this test.
Q.7. An organic compound A, containing C, H, N and O, on analysis gives 49.32% carbon, 9.59% hydrogen and 19.18% nitrogen. A on boiling with NaOH gives off NH3 and a salt which on acidification gives a monobasic nitrogen free acid B. The silver salt of B contains 59.67% silver. Deduce the structures of A and B. (1988 - 3 Marks)
Ans. CH3CH2CONH2,CH3CH2COOH
Solution. Determination of empirical formula :
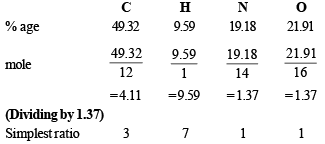
∴Empirical formula of A will be C3H7NO and empirical formula wt = 73
Calculation of molecular wt. of (B)
We know,meq. of Ag = meq. of Ag salt
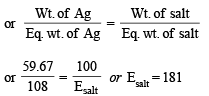
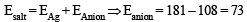
For monobasic acid (B), adding one H,
Mol. wt. = Eq. wt. + 1 = 73 + 1 = 74
B being monobasic can be represented as Cn H2n + 1 COOH
⇒ 74 = 12n + (2n + 1).1 + 12 + 16 + 16 + 1 ⇒ n = 2
∴ B = C2H5COOH
Nature of A : Since B is obtained by the action of A with NaOH followed by hydrolysis, so A is an amide, CH3CH2CONH2.
Reaction :
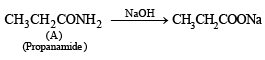
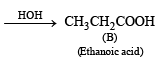
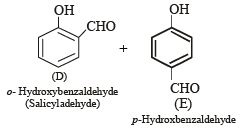
Q.8. A mixture of two aromatic compounds A and B was separated by dissolving a chloroform followed by extraction with aqueous KOH solution. The organic layer containing compound A, when heated with alcoholic solution of KOH produced a compound C(C7H5N) associated with an unpleasant odour. The alkaline aqueous layer on the other hand, when heated with chloroform and then acidified gave a mixture of two isomeric compounds D and E of molecular formula C7H6O2. Identify the compounds A, B, C, D, E and write their structures. (1990 - 4 Marks)
Ans. 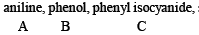
Solution. TIPS/Formulae :
(i) Carbylamine reaction involves reaction of a primary amine with alc. KOH and CHCl3 which results a product containing isocyanide group with unpleasant smell.
(ii) Riemer-Tiemann reaction of phenol produces o and p isomers.
Solution of compound A in chloroform when treated with alcoholic KOH yields compound C (C7H5N) having an unpleasant odour which may be due to isocyanide. Hence the above reaction may be an example of carbylamine reaction. Therefore, compound A must be aniline (C6H5NH2) and C must be phenylisocyanide (C6H5NC).
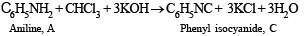
Alkaline aqueous layer of B when heated with chloroform gives D and E which are isomeric with each other and have molecular formula C7H6O2. This indicates the possibility that Reimer-Tiemann reaction would have taken place. Hence compound B must be phenol and compounds D and E are o- and p-hydroxybenzaldehydes. This can be represented in the following way.
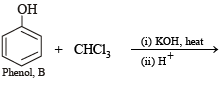
Q.9. A basic, volatile nitrogen compound gave a foul smelling gas when treated with chloroform and alcoholic potash. A 0.295 g sample of the substance. dissolved in aq. HCl and treated with NaNO2 solution at 0°C, liberated a colorless, odourless gas whose volume corresponded to 112 ml at STP. After the evolution of the gas was complete, the aqueous solution was distilled to give an organic liquid which did not contain nitrogen and which on warming with alkali and iodine gave a yellow precipitate. Identify the original substance. Assume that it contains one N atom per molecule. (1993 - 4 Marks)
Ans. isopropylamine
Solution. Let us summarise the given facts.
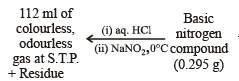
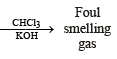
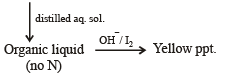
Reaction of the original compound with alcoholic potash and chloroform to give foul smelling gas indicates that it contains a primary –NH2 group.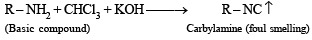
Determination of mol. weight of the amine : 112 ml. of gas is evolved at S.T.P. by 0.295 g of amine
22400 ml. of gas is evolved by 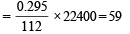
Hence the mol. wt. of the amine = 59
∴ Mol. wt. of the alkyl group = 59 – 16 = 43
Nature of alkyl gp. of mol. wt. 43 = C3H7–
Thus the amine may be either
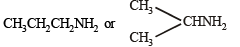
The reaction of amine with NaNO2 at 0ºC and all other reactions may thus be written as below.
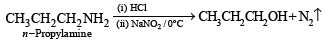
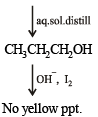
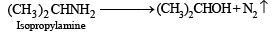
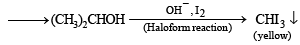
NOTE : Since the given reactions correspond to isopropylamine, the original compound may be propylamine or isopropylamine, (CH3)2CHNH2.
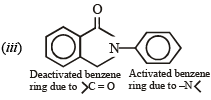
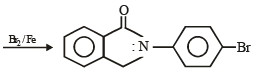
Q.10. Identify the major product in the following reactions :
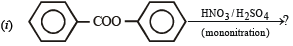 (1993 - 1 Mark)
(1993 - 1 Mark)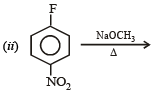 (2000 - 1 Mark)
(2000 - 1 Mark)
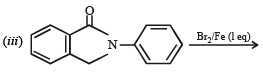 (2000 - 1 Mark)
(2000 - 1 Mark)
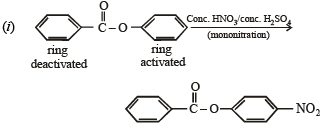
Solution.
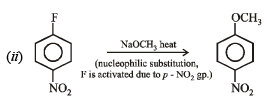
Q.11. Identify, A (C3H9N) which reacts with benzensulphonyl chloride to give a solid, insoluble in alkali. (1993 - 1 Mark)
Ans. ethylmethylamine
Solution. A (C3H9N) is a 2º amine CH3 – NH – C2H5 (ethymethylamine) because the benzene sulphonyl chloride is solid and insoluble in alkali.
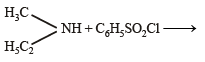
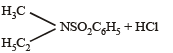
N, N-ethylmethylbenzene sulphonamide
(Insoluble in alkali)
Q.12. Write the structure of the foul-smelling compound obtained when aniline is treated with chloroform in the presence of KOH. (1996 - 1 Mark)
Ans. PhNC
Solution. 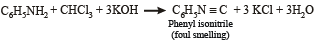
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















