JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): The d & f-Block Elements & Coordination Compounds- 2 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.16. Compare qualitatively the first and secon d ion isation potentials of copper and zinc. Explain the observation. (1996 - 2 Marks)
Solution.
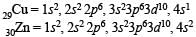
On the basis of configuration of Cu and Zn, first ionisation potential of Zn is greater than that of copper because in zinc the electron is removed from 4s2 configuration while in copper it is removed from 4s1 configuration. So more amount of energy is required for the removal of electron of 4s2 (completely filled orbital) than that of 4s1 while the second ionisation potential of Cu is higher than that of zinc because Cu+ has 3d10 (stable configuration) in comparison to Zn+ (4s1 configuration).
Q.17. Write the formulae of the following complexes :
(i) Pentamminechlorocobalt(III) (1997 - 1 Mark)
(ii) Lithium tetrahydroaluminate(III). (1997 - 1 Mark)
Ans. (i) [CoCl(NH3)5]+2, (ii) LiAlH4
Solution. (i) [CoCl(NH3)5]2+ Formula of pentamminechlorocobalt (III)
(ii) LiAlH4 Formula of lithium tetrahydroaluminate (III)
Q.18. When the ore haematite is burnt in air with coke around 2000°C along with lime, the process not only produces steel but also produces a silicate slag that is useful in making building materials such as cement. Discuss the same and show through balanced chemical equations. (1998 - 4 Marks)
Solution. Haematite(Fe2O3) on burning with coke and lime at 2000°C results in the following reactions.
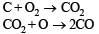
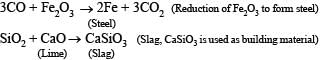
Q.19. Work out the following using chemical equations (1998 - 2 Marks)
In moist air copper corrodes to produce a green layer on the surface.
Solution. 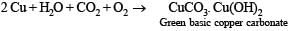
Q. 20. A, B, and C are three complexes of chromium (III) with the empirical formula H12O6Cl3Cr. All the three complexes have water and chloride ion as ligands. Complex A does not react with concentrated H2SO4, whereas complexes B and C lose 6.75% and 13.5% of their original mass, respectively, on treatment with concentrated H2SO4. Identify A, B and C. (1999 - 6 Marks)
Ans. [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3, [Cr(H2O)5Cl](H2O)Cl2, [Cr(H2O)4Cl2](H2O)2Cl
Solution. The complex A does not react with concentrated H2SO4 implying that all water molecules are coordinated with Cr3+ ion. Hence, its structure would be [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3.
The compound B loses 6.75% of its original mass when treated with concentrated H2SO4. This loss is due to the removal of water molecules which is/are not directly coordinated to Cr3+ ion.
The mass of water molecules removed per mole of the complex
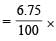 molar mass of the complex
molar mass of the complex 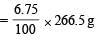
= 17.98 g This corresponds to one mole of water. Hence, the structure of the compound B will be [Cr(H2O)5Cl](H2O)Cl2
NOTE : The compound C loses 13.5% of its mass when treated with concentrated H2SO4 which is twice of the mass lost by the compound B. Hence, the structure of the compound C will be [Cr(H2O)4Cl2](H2O)2 Cl.
Q. 21. Write the chemical reaction associated with the 'brown ring test'. (2000 - 2 Marks)
Solution. NaNO3 + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HNO3
6FeSO4 + 2HNO3 + 3H2SO4 → 3Fe2 (SO4)3 + 4H2O + 2NO
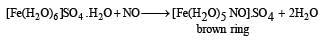
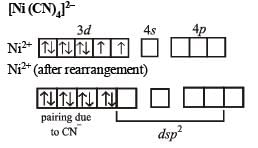
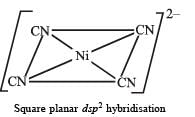
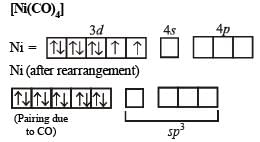
Q.22. Draw the structures of [Co(NH3)6]3+ , [Ni(CN)4]2- and [Ni(CO)4]. Write the hybridisation of atomic orbitals of the transition metal in each case. (2000 - 4 Marks)
Solution.
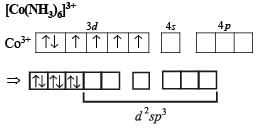
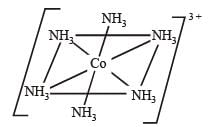
Octa hedral compl ex, d2sp3 hybridisation
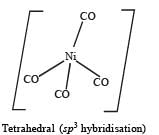
Q.23. (i) Write the chemical reactions involved in the extraction of metallic silver from argentite.
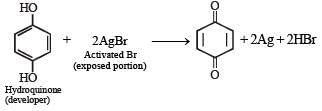
(ii) Write the balanced chemical equation for developing photographic films. (2000 - 4 Marks)
Solution.(i) Argentite is Ag2S. Silver is extracted from its ore argentite (silver glance, Ag2S) as follows :
(1) Silver glance is concentrated by froth flotation.
(2) Leaching : The concentrated ore is ground to fine powder and dissolved in dilute solution of sodium cyanide.
Ag2S + 4 NaCN → 2 NaAg(CN)2 + Na2S
Oxygen of air converts Na2S to Na2SO4 thereby preventing reaction to take place in the reversible direction.
(3) Recovery of silver.
Silver is precipitated out by adding electropositive metal, Zn.
2Na[Ag(CN)2] + Zn → Na2[Zn(CN)4]+ 2Ag
(ii) For development, activated grains are preferentially reduced by mild reducing agents like hydroquinone
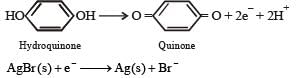
(Reduction of activated AgBr to elemental silver.) The photographic film is permanently fixed by immediately washing out any non activated AgBr grains in hypo emulsion.
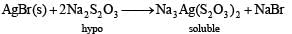
Q.24. A metal complex having composition Cr(NH3)4Cl2Br has been isolated in two forms (A) and (B). The form (A) reacts with AgNO3 to give a white precipitate readily soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia, whereas (B) gives a pale yellow precipitate soluble in concentrated ammonia. Write the formula of (A) and (B) and state the hybridization of chromium in each. Calculate their magnetic moments (spin– only value). (2001 - 5 Marks)
Ans. [Cr(NH3)4BrCl]Cl : (d2sp3); [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Br : (d2sp3); 3.87 BM, 3.87 BM
Solution. Compound (A) on treatmen t with AgNO3 gives wh ite precipitate of AgCl, which is readily soluble in dil.aq.
NH3.Therefore it has at least one Cl– ion in the ionization sphere furthermore chromium has coordination number equal to 6. So its formula is [Cr(NH3)4BrCl]Cl.
Compound (B) on treatment with AgNO3 gives pale yellow precipitate of AgBr soluble in conc. NH3. Therefore it has Br– in the ionization sphere. So its formula is [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Br
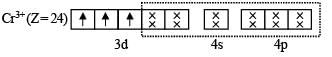
State of hybridization of chromium in both (A) and (B) is d2sp3.
Spin magnetic moment of (A) or (B),
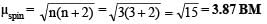
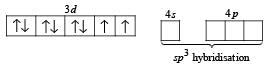
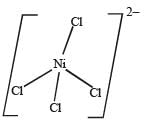
Q.25. Deduce the structure of [NiCl4]2- and [Ni (CN)4]2- considering the hybridization of the metal ion. Calculate the magnetic moment (spin only) of the species. (2002 - 5 Marks)
Solution. Cl– is a weak ligand which is unable to pair the electrons of Ni2+. Therefore, here hybridisation is sp3 and shape will be tetrahedral.
Electronic configuration of Ni+2 (No. of electrons = 26) in presence of Cl– ion, a weak ligand.
Magnetic moment of 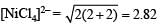 BM
BM
On the other hand, CN– is a stong ligand which pairs up the electrons of Ni2+. Therefore, here hybridisation is dsp2 and shape will be square planar.
Electronic configuration of Ni2+ in presence of CN– ion, a strong ligand.
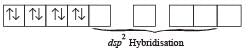
For structure of [Ni(CN)4]2–, refer question 24 in Section (E).
Magnetic moment of 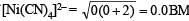
Q.26. Write the IUPAC nomenclature of the given complex along with its hybridisation and structure.
K2 [Cr(NO)(NH3)(CN)4], μ = 1.73 BM (2003 - 4 Marks)
Ans. Potassium amminotetracyanonitrosoniumchromate (I), (d2sp3), octahedral shape.
Solution. The spin magnetic moment, μ of the complex is 1.73 BM.
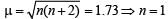
It means that nucleus of the complex, chromium ion has one unpaired electron. So the ligand NO is unit positively charged.
IUPAC name :
Potassium amminetetracyanonitrosochr (I)
(a) Electronic configuration of Cr+ :
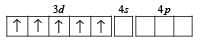
(b) Electronic configuration of Cr+ under the influence of strong field ligand CN–
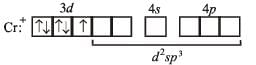
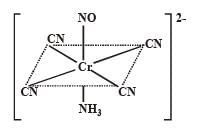
So, Hybridization : d2sp3; Shape : Octahedral
Q.27. Nickel chloride, when treated with dimethylgyloxime in presence of ammonium hydroxide, a bright red precipitate is obtained. Answer the following. (2004 - 4 Marks)
(a) Draw the structure of the complex showing H-bonds
(b) Give oxidation state of nickel and its hybridisation
(c) Predict the magnetic behaviour of the complex
Ans. (b)+2, dsp2; (c) diamagnetic
Solution.
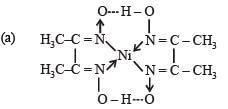
(b) Charge on Ni in the complex is +2 and it is dsp2 hybridised
(c) Since number of unpaired electrons in Ni2+ is zero, the complex is diamagnetic.
Q.28. Some reactions of two ores, A1 and A2 of the metal M are given below. (2004 - 4 Marks)
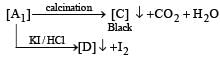
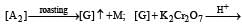 Green solution
Green solution
Identify A1, A2, M, C, D, and G, and explain using the required chemical reactions.
Ans. 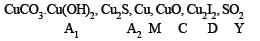
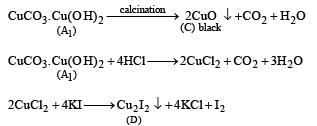
Solution. Calcination of th e ore A1 to form CO2 in dicates that A1 should be a carbonate. Further, reaction of A1 with HCl and KI to evolve I2 indicates that A1 would also be hydroxide.
So the possible formula for the ore, should be CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 which explains all the given reactions
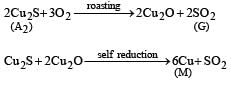
Roasting of A2 gives gas G whose nature is identified as SO2 as it gives green colour with acidified K2Cr2O7. So A2 should be sulphide of copper.
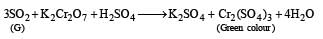
Q.29. 
What are (A) and (B)? Give IUPAC name of (A). Find the spin only magnetic moment of (B). (2005 - 4 Marks)
Ans. 
Solution.
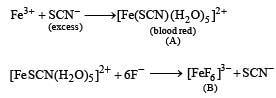
IUPAC name of A is pentaaquathiocyanatoferrate (III) ion
IUPAC name of B is hexafluoroferrate (III)
In [FeF6]3– coordination no. of Fe = 6
In [FeF6]3– oxidation state of Fe = + 3
∴ It has 5 unpaired electrons, n = 5, Fe3+ is 3d5
Q.30. Write the chemical reaction involved in developing of a black and white photographic film. An aqueous Na2S2O3 solution is acidified to give a milky white turbitity. Identify the product and write the balanced half chemical reaction for it. (2005 - 4 Marks)
Solution. Reaction in volved in developing of a black and white photographic film.
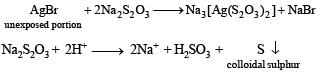
Q.31. 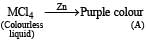 compound; M Transition metal
compound; M Transition metal
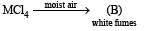
Identify (A), (B) and MCl4. Also explain colour difference between MCl4 and (A).
Ans. 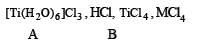
Solution. [A] = [Ti(H2O)6]Cl3 [B] = HCl
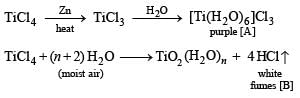

TiCl4 is colourless since Ti4+ has no d electrons, hence d-d transition is impossible. On the other hand, Ti3+ is coloured due to d-d transition. Ti3+ absorbs greenish yellow compound of white light, hence its aqueous solution is purple which is complementary colour of greenish yellow in white light.
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















