JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): The p-Block Elements- 2 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.22. A soluble compound of a poisonous element M, when heated with Zn/H2SO4 gives a colourless and extremely poisonous gaseous compound N, which on passing through a heated tube gives a silvery mirror of element M. Identify M and N. (1997 - 2 Marks)
Ans. M = As,N = AsH3
Solution.
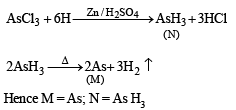
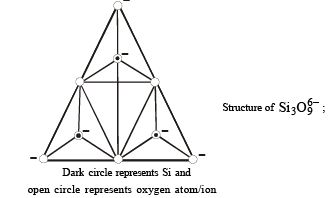
Q.23. Draw the structure of a cyclic silicate, (Si3O9)6– with proper labelling. (1998 - 4 Marks)
Solution. In cyclic 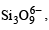 three tetrahedra of
three tetrahedra of 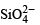 are joined together sharing two oxygen atoms per tetrahedron.
are joined together sharing two oxygen atoms per tetrahedron.
Q.24. Thionyl chloride can be synthesized by chlorinating SO2 using PCI5. Thionyl chloride is used to prepare anhydrous ferric chloride starting from its hexahydrated salt.
Alternatively, the anhydrous ferric chloride can also be prepared from its hexahydrated salt by treating with 2, 2 – dimethoxypropane. Discuss all this using balanced chemical equations. (1998 - 6 Marks)
Solution.
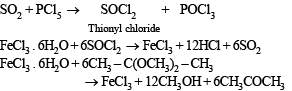
Q.25. Reaction of phosphoric acid with Ca5(PO4)3F yields a fertilizer “triple superphosphate”. Represent the same through balanced chemical equation. (1998 - 2 Marks)
Solution. 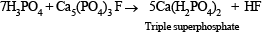
Q.26. In the following equation, (1999 - 6 Marks)
A + 2B + H2O → C + 2D
(A = HNO2, B = H2SO3, C = NH2OH). Identify D. Draw the structures of A, B, C and D.
Solution. The reaction is
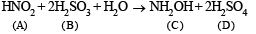
The structures of A, B, C and D are as follows.
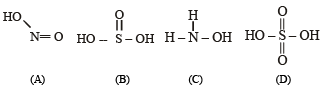
Q.27. In the contact process for industrial manufacture of sulphuric acid some amount of sulphuric acid is used as a starting material. Explain briefly. What is the catalyst used in the oxidation of SO2? (1999 - 4 Marks)
Solution. Sulphur trioxide produced in the contact process is absorbed by sulphuric acid forming H2S2O7. It is not dissolved in water as it gives a dense fog of sulphuric acid particles.
The catalyst used in the contact process is vanadium pentoxide.
Q.28. The Haber process can be represented by the following scheme;
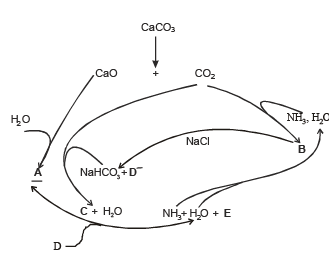
Identify A, B, C, D and E. (1999 - 5 Marks)
Ans. 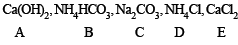
Solution. In such a case
A = Ca(OH)2, B = NH4HCO3, C = Na2CO3, D = NH4Cl and E = CaCl2
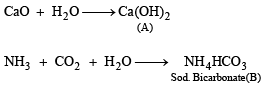
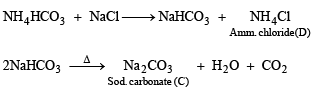
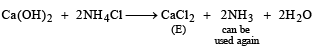
Q.29. Give an example of oxidation of one halide by another halogen. Explain the feasibility of the reaction (2000 - 2 Marks).
Solution. More electronegative halogen displaces lesser electronegative halogen from its halide. Thus,
Cl2 + 2KBr (or 2 KI) → 2KCl + Br2 (or I2)
Q.30. Draw the molecular structures of XeF2, XeF4 and XeO2F2 indicating the location of lone pair(s) of electrons. (2000 - 3 Marks)
Solution. TIPS/Formulae :
Use the formula
H (hydridisation) 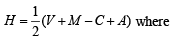
V = number of electron in valence shell of central atom
M = number of monovalent atoms surrounding the central atom
C = Charge on cation
A = Charge on anion
XeF2 : 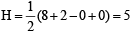 Hence hybridisation is sp3d, and thus its structure is linear.
Hence hybridisation is sp3d, and thus its structure is linear.
XeF, : 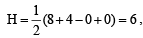 Hence hybridisation is sp3d2. and thus its structure is square planar.
Hence hybridisation is sp3d2. and thus its structure is square planar.
XeO2F2 : 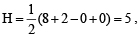 Hence hybridisation is sp3d. and shape is see saw.
Hence hybridisation is sp3d. and shape is see saw.
Q.31. Give reason(s) why elemental nitrogen exists as a diatomic molecule whereas elemental phosphorus as a tetraatomic molecule. (2000 - 2 Marks)
Solution. Elemental nitrogen exists as a diatomic molecule because nitrogen can form pπ - pπ multiple bonds which is not possible in case of phosphorus due to repulsion between non-bonded electrons of the inner core. There is no such repulsion in case of smaller nitrogen atoms as they have only 1s2 electrons in their inner core.
Q.32. Compound (X) on reduction with LiAlH4 gives a hydride (Y) containing 21.72% hydrogen along with other products. The compound (Y) reacts with air explosively resulting in boron trioxide. Identify (X) and (Y). Give balanced reactions involved in the formation of (Y) and its reaction with air.
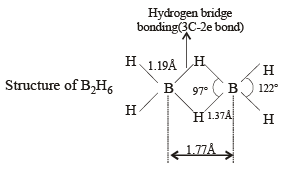
Draw the structure of (Y). (2001 - 5 Marks)
Ans. BCl3 or BBr3, B2H6
Solution. Since B2O3 is formed by reaction of (Y) with air, (Y) therefore should be B2H6 in which % of hydrogen is 21.72. The compound (X) on reduction with LiAlH4 gives B2H6. Thus it is boron trihalide. The reactions are shown as:
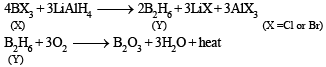
Structure of B2H6 is as follows:
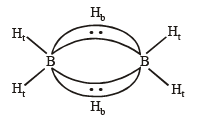
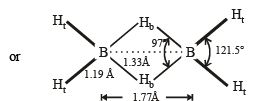
Thus the diborane molecule has four two-centre- two -electron bonds (2c – 2e bonds) also called usual bonds and two three-centre-two -electron bonds (3c – 2e) also called banana bonds. Hydrogen attached to usual and banana bonds are called Ht (terminal H) and Hb (bridged H) respectively.
Q.33. Starting from SiCl4, prepare the followin g in steps not exceeding the number given in parentheses (give reactions only):
(i) Silicon (1)
(ii) Linear silicone containing methyl groups only (4)
(iii) Na2SiO3 (3)
Solution. (i) SiCl4 + 2Mg(or Zn) → Si + 2MgCl2 (or ZnCl2)
(ii) SiCl4 + 2CH3MgCl → (CH3)2SiCl2 + 2MgCl2
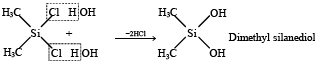
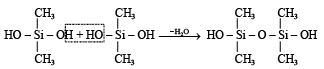
Polymerisation continues on both ends to give linear silicone.
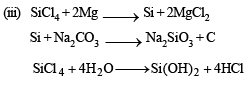
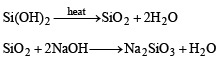
Q.34. Write balanced equations for the reactions of the following compounds with water : (2002 - 5 Marks)
(i) Al4C3
(ii) CaNCN
(iii) BF3
(iv) NCl3
(v) XeF4
Solution.
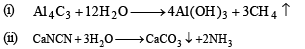
Ammonia formed dissolves in water to form NH4OH
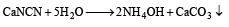
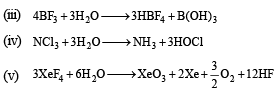
Q.35. How is boron obtained from borax? Give chemical equations with reaction conditions. Write the structure of B2H6 and its reaction with HCl. (2002 - 5 Marks)
Solution. NOTE : When hot con centr ated HCl is added to borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O) the sparingly soluble H3BO3 is formed which on subsequent heating gives B2O3 which is reduced to boron on heating with Mg, Na or K
Na2B4O7 (anhydrous) + 2HCl( hot, conc.)
→ 2NaCl+ H2B4O7
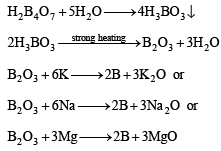
B2H6 + HCl → B2H5Cl + H2
[NOTE : Normally this reaction takes place in the presence of Lewis acid (AlCl3)]
Q.36. Write down reactions involved in the extraction of Pb. What is the oxidation number of lead in litharge? (2003 - 2 Marks)
Ans. O.N. of Pb in PbO is +2
Solution.
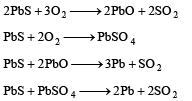
Q.37. Identify the following:
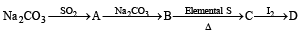
Also mention the oxidation state of S in all the compounds.
Ans. 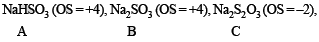
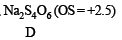
Solution.
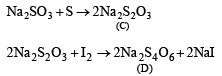
Oxidation states of ‘S’ are : + 4 in (A) , (+ 6) in B and + 2 in (C), + 2.5 in (D)
Q.38. AlF3 is insoluble in anhydrous HF but it becomes soluble in presence of little amount of KF. Addition of boron trifluoride to the resulting solution causes reprecipitation of AlF3.
Explain with balanced chemical equations. (2004 - 2 Marks)
Solution. HF is weakly dissociated, while KF is highly dissociated giving a high concentration of F– which leads to the formation of soluble AlF63–.
AlF3 + 3 KF → K3[AlF6]
Since BF3 is more acidic than AlF3, it pulls out F– from AlF63– reprecipitating AlF3.
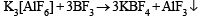
Q.39. How many grams of CaO are required to neutralize 852 gm of P4O10 ? Draw structure of P4O10 molecule. (2005 - 2 Marks)
Ans. 1008 g
Solution.
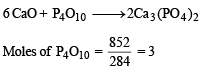
Moles of CaO = 3 × 6 = 18; wt. of CaO = 18 × 56 = 1008 g
For structure of P4O10 : See question 20 of this section.
Q.40. Write the structures of (CH3)3 N and (Me3Si)3 N . Are they isostructural? Justify your answer. (2005 - 2 Marks)
Solution. (CH3)3 N and (Me3Si)3 N are not isostructural, the former is pyramidal while the latter is trigonal planar. Silicon has vacant d orbitals which can accommodate lone pair of electrons from N (back bonding) leading to planar shape.
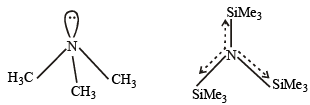
Q.41.
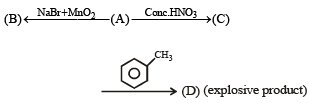
Ans. 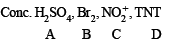
Solution.
A. Conc. H2SO4
B. Br2
C. 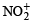
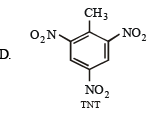
Reactions involved are

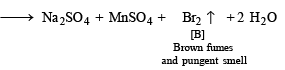
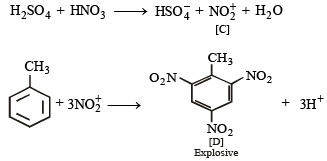
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















