Class 7 History Chapter 3 Question Answers - The Delhi Sultans
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Discuss briefly the types of taxes in Delhi Sultanate.
Ans: During the Delhi Sultanate, there were three main types of taxes:
- Kharaj: A tax on crops, amounting to about 50% of a peasant's produce.
- Cattle tax: Levied on livestock owned by farmers.
- House tax: Imposed on residential properties.
Additionally, there were other taxes:
- Khums: One-fifth of war booty and treasure.
- Zakat: A religious duty for Muslims to give a portion of their savings to the needy.
- Jizyah: A tax on non-Muslims, initially collected with the land tax but later as a separate tax.
Q2: What was the difference between the administrative system of Alauddin Khilji and Muhammad Tughluq?
Ans: 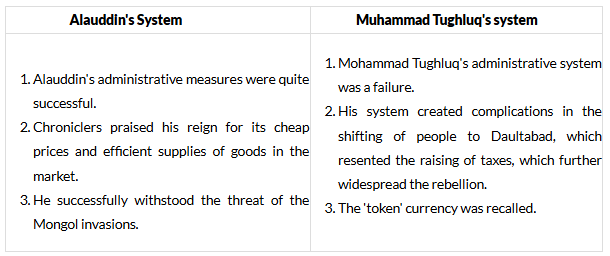
Q3: State the conditions under which Delhi became an important commercial centre.
Ans: Delhi became an important commercial centre primarily in the twelfth century under the following conditions:
- Delhi was established as a capital by the Tomara Rajputs.
- In the mid-twelfth century, the Chauhans (or Chahamanas) from Ajmer defeated the Tomaras.
- Many wealthy Jaina merchants settled in the city.
- These merchants built significant temples and contributed to the city's economy.
- Coins minted in Delhi, known as dehliwal, circulated widely.
Q4: Discuss briefly why the admistrative character and methods of Muhammad Tughluq were a failure?
Ans: Muhammad Tughluq's administrative character and methods were marked by significant failures due to several key reasons:
- Kashmir Campaign: His military campaign into Kashmir ended disastrously, leading him to abandon plans for invading Transoxiana.
- Capital Shift: The decision to move the capital from Delhi to Daulatabad proved to be a poor choice.
- Tax Increases: The rise in taxes, coupled with famine in the Ganga-Yamuna region, resulted in widespread rebellion.
- Token Currency: The introduction of 'token' currency had to be retracted due to its failure.
Q5: Mention all the ways in which the chieftains arranged themselves for their defense?
Ans: Ibn Battuta, a fourteenth-century traveller, described how chieftains arranged their defences in various ways:
- They fortified themselves in mountains and rocky, uneven terrains.
- They established strongholds in bamboo groves, which provided natural protection.
- These forests acted as ramparts, housing their cattle and crops.
- Water, mainly collected rainwater, was available within these areas.
- They could only be subdued by powerful armies that had to cut through the bamboo using special tools.
Q6: Why did the rulers of the Delhi Sultanate fail to control the hinterlands initially?
Ans: The rulers of the Delhi Sultanate initially struggled to control the hinterlands due to several key factors:
- Long distances made communication and governance challenging.
- Frequent rebellions and wars undermined their authority.
- The constant threat of Mongol invasions from Afghanistan diverted resources and attention.
- Rebellions led by local governors further weakened central control.
Q7: Why was Raziya, daughter of Sultan Iltutmish removed from the throne of Delhi?
Ans: In 1236, Raziya, the daughter of Sultan Iltutmish, became the Sultan of Delhi. Although the chronicler Minhaj-i-Siraj acknowledged her superior qualifications compared to her brothers, societal norms and gender biases made her position difficult.
- Minhaj-i-Siraj believed that a woman ruling contradicted the established social order.
- The nobles were also dissatisfied with her attempts to govern independently.
- As a result, Raziya was removed from the throne in 1240.
Q8: What forced the two rulers Allauddin Khilji and Muhammed Tughluq to mobilise a large standing army in Delhi?
Ans: The Mongols, led by Genghis Khan, invaded the Delhi Sultanate starting in 1219. This invasion:
- Increased during the reign of Alauddin Khilji.
- Continued to escalate in the early years of Muhammad Tughluq's rule.
As a result, both rulers were compelled to mobilise a large standing army in Delhi to defend against these threats, which created significant administrative challenges.
Q9: When did Delhi become the capital city under the Delhi Sultanate?
Ans: Delhi became the capital city under the Delhi Sultanate in the 13th century.
Q10: What are the important historical sources to study the history of the Delhi Sultanate?
Ans: Important historical sources to study the history of the Delhi Sultanate include:
- Coins - These provide insights into the economy and trade.
- Inscriptions - These record significant events and achievements.
- Architecture - The structures built during this period reflect cultural and artistic values.
- Histories - Known as tarikh (singular) or tawarikh (plural), these were written in Persian.
The authors of tawarikh were often learned individuals such as secretaries, poets, and courtiers, who documented events and advised rulers on governance.
Q11: Why was Razziya, the Sultana of Delhi Sultanate dethroned?
Ans: Razziya, the daughter of Iltutmish, became the Sultana of Delhi in 1236. However, her reign faced significant challenges:
- Chronicler Minhaj-I-Siraj believed women should be subordinate to men.
- Religious leaders opposed a woman ruling the state.
- These factors contributed to her removal from the throne in 1240.
Q12: Write briefly about the invasion of the Mongols and its results ?
Ans: The Mongol invasion began under Genghis Khan in 1219, targeting Transoxiana in north-east Iran. Shortly after, the Delhi Sultanate faced Mongol attacks.
- The invasions intensified during the reigns of Alauddin Khalji and Muhammad Tughluq.
- This prompted the Sultanate to mobilise a large standing army in Delhi.
- The need for military readiness posed significant administrative challenges for the rulers.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Explain the significance of Delhi during the 12th to 15th century, highlighting its political, cultural, and economic importance.
Ans: During the 12th to 15th centuries, Delhi became a crucial political hub in India, serving as the capital for several influential dynasties:
- Slave Dynasty
- Khalji Dynasty
- Tughlaq Dynasty
- Lodhi Dynasty
As the heart of the Delhi Sultanate, it governed vast regions of the subcontinent. Its significance can be summarised as follows:
- Political Importance: Delhi was the seat of power, enabling the ruling dynasties to exert control over large territories.
- Cultural Influence: The city attracted numerous scholars, poets, and artists, fostering a rich blend of Persian, Arabic, and Indian cultures.
- Architectural Achievements: Iconic structures like the Qutub Minar and various mosques were built, showcasing the architectural prowess of the time.
- Economic Growth: Delhi thrived as a trade centre, strategically located on key trade routes, linking it with Central Asia and beyond.
Overall, Delhi played a pivotal role in shaping the history of medieval India.
Q2: Write a brief note on the administration of Delhi Sultanate provinces under the Tughlaqs and the Khaljis.
Ans: The Khalji and Tughlaq rulers appointed military leaders as governors to manage different areas of land, called "iqtas". These governors were known as "iqtadars" or "muqtis". Their job was to provide military support to the Sultan of Delhi. In return, they were allowed to collect taxes from the land and keep a portion as their salary. They also used this money to pay their soldiers.
The government made sure the muqtis followed the rules by appointing accountants to check how much tax was collected. The muqtis were only allowed to collect the taxes decided by the government, and they had to maintain a certain number of soldiers. The kings also made sure that the local aristocrats, called "samantas", accepted their rule and authority.
Q3: What is meant by the “internal” and “external” frontiers of sultanates?
Ans: The internal frontiers of the Delhi Sultanate referred to regions within the empire that were not directly under Sultanate control, such as areas occupied by forest tribes, local chieftains, and autonomous rulers. To consolidate power over these regions, the Sultans encouraged the expansion of agriculture by clearing forests and settling people in these areas. This helped bring them into the Sultanate's economic and administrative fold.
The external frontiers, on the other hand, referred to regions outside the core territories of the Sultanate, which were acquired through military campaigns. These included areas such as Bengal, Gujarat, and South India. The Sultans sought to expand their empire into these territories to gain control over important resources and trade routes, thereby extending the Sultanate's influence.
|
63 videos|552 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 History Chapter 3 Question Answers - The Delhi Sultans
| 1. दिल्ली में 12वीं से 15वीं सदी के दौरान प्रमुख साम्राज्य कौन से थे? |  |
| 2. 12वीं से 15वीं सदी के दौरान दिल्ली में धार्मिक और सांस्कृतिक परिवर्तनों के क्या मुख्य पहलू थे? |  |
| 3. तुगलक साम्राज्य की स्थापना कब हुई थी और इसके प्रमुख शासक कौन थे? |  |
| 4. दिल्ली सल्तनत के प्रशासनिक ढांचे की विशेषताएँ क्या थीं? |  |
| 5. 12वीं से 15वीं सदी में दिल्ली में सामाजिक संरचना कैसी थी? |  |

















