Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Nutrition in Plants
Q. 1: Name some components of food.
Ans: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals.
Q. 2: Define nutrients.
Ans: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals are essential components of food; these components are called nutrients.
Q. 3: Give an example of an autotroph.
Ans: All green plants.
 Green plants
Green plants
Q. 4: Give an example of a heterotroph.
Ans: Animals and human beings.
Q. 5: Plants prepare their food by using raw materials present in their __________________.
Ans: Surroundings.
Q. 6: What do you mean by nutrition?
Ans: Nutrition is the mode of taking food by an organism and its utilisation by the body.
Q. 7: Name the food factories of plants.
Ans: Green leaves.
 Green leaves
Green leaves
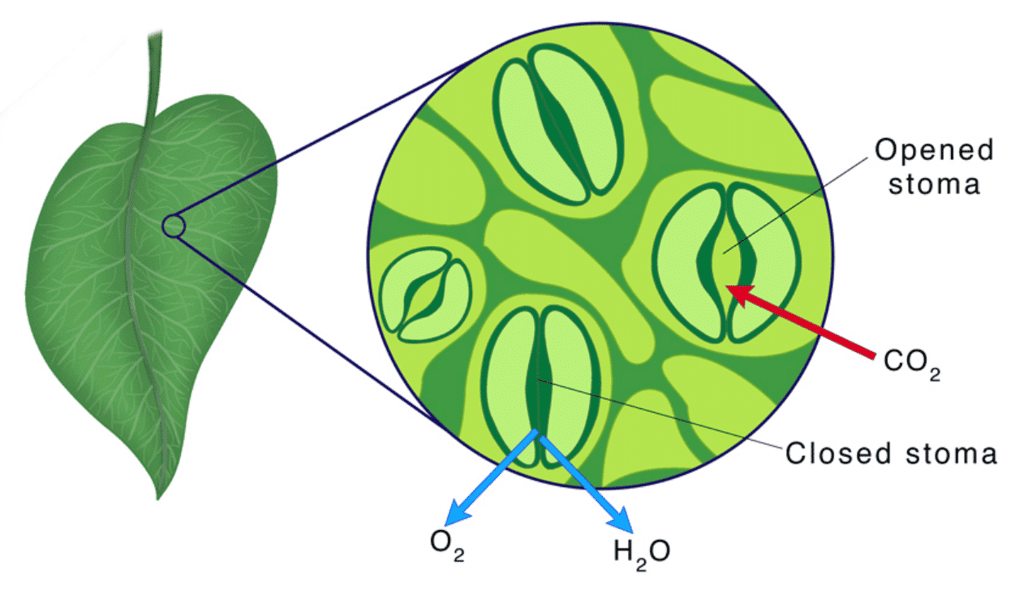
Q. 8: Name the tiny pores present on the surface of leaves.
Ans: Stomata
Q. 9: Name the green pigment present in leaves.
Ans: Chlorophyll
Q. 10: ____________ helps leaves to capture the energy of sunlight
Ans: Chlorophyll
Q. 11: Why is photosynthesis named so?
Ans: Because the synthesis of food occurs in the presence of sunlight.
Q. 12: The Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms. True / False
Ans: True
Q. 13: Where does the nucleus of a cell lie?
Ans: The nucleus lies in the cytoplasm of the cell (not always exactly in the centre).
Cell
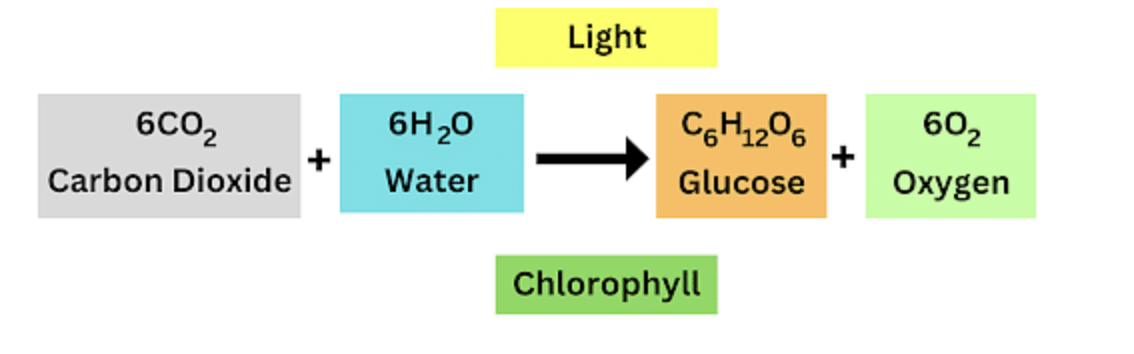
Q. 14: State the equation for the process of photosynthesis.
Ans: Carbon dioxide + water —————> carbohydrate + Oxygen(in the presence of sunlight)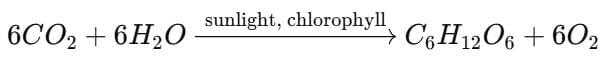
Q. 15: The nucleus in a cell is surrounded by a jelly-like substance called ___________.
Ans: Cytoplasm
Q. 16: Why are algae present in stagnant water bodies green in colour?
Ans: Because they contain green colour pigment chlorophyll.
Chlorophyll cellsQ. 17: Name a component of food other than carbohydrate synthesised by plants.
Ans: Proteins and Fats
Q. 18: Name some insectivorous plants.
Ans: Pitcher plants and Venus flytraps are insectivorous plants.
Q. 19: In the saprotrophic mode of nutrition, organisms take in nutrients from
a. Oxygen mask
b. Water mask
c. Pollution mask
d. None of these
Ans: d. None of these
(They take nutrients from dead and decaying matter.)
Q. 20: During photosynthesis plants take in _______________ and releases _______________.
Ans: Carbon dioxide and oxygen
Q. 21: Some organisms live together and share shelter and nutrients, this type of relationship is called
Ans: Symbiotic relationship.
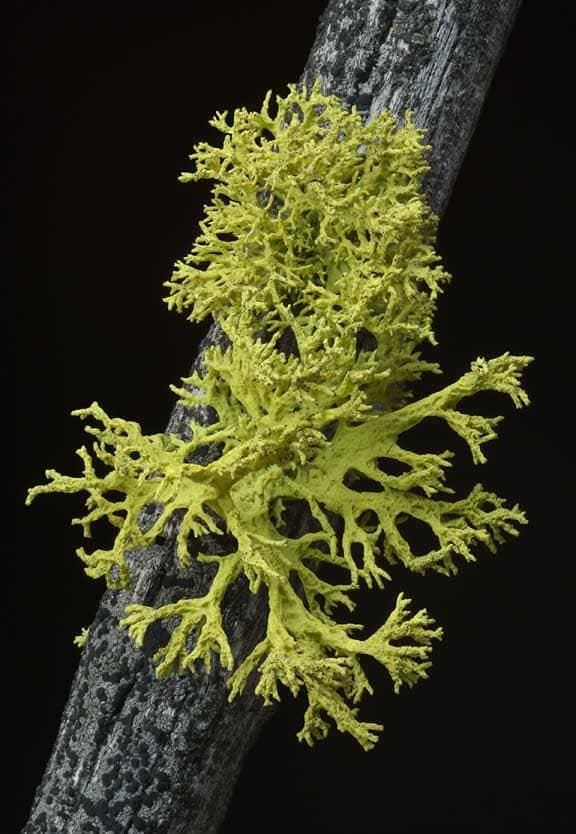
Q. 22: Lichen is a symbiotic association between __________ and Fungi.
Ans: Algae and Fungi.

Q. 23: Name the edible fungi.
Ans: Mushroom.
Q. 24: Name the organism responsible for converting atmospheric nitrogen into soluble forms.
Ans: Rhizobium bacteria.
 Q. 25: Where can we see Rhizobium bacteria?
Q. 25: Where can we see Rhizobium bacteria?
a. Dead matter
b. Decaying matter
c. Both a and b
d. None of these
Ans: d. None of these
Rhizobium bacteria are found in root nodules of leguminous plants, not in dead or decaying matter.
Q. 26: Give an example of parasites.
Ans: Cuscuta plants.
 Cuscuta Plant
Cuscuta Plant
Q. 27: Give an example of saprotrophs.
Ans: Fungi
Q. 28: Amarbel is an example of
a. Parasite
b. Host
c. Autotrophs
d. Saprotrophs
Ans: Parasite
Q. 29: Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. True/ False.
Ans: False
Q. 30: During photosynthesis solar energy is converted into chemical energy. True/ False.
Ans: True
Q. 31: The product of photosynthesis is
a. Carbohydrate
b. Protein
c. Fats
d. All of these
Ans: a. Carbohydrate
Q. 32: Name a plant that has both autotrophic and heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
Ans: Insectivorous plants
Q. 33: Name a parasitic plant with a yellow, slender and tubular type of stem.
Ans: Amarbel (Cuscuta).
Q. 34: Name the pores present in leaves through which exchange of gas takes place.
Ans: Stomata
Q. 35: Animals are autotrophs. True/ False.
Ans: False
|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Nutrition in Plants
| 1. What is the process of nutrition in plants? |  |
| 2. How do plants obtain nutrients from the soil? |  |
| 3. What is the role of chlorophyll in plant nutrition? |  |
| 4. How do plants use the nutrients obtained through photosynthesis? |  |
| 5. Why is photosynthesis important for plant nutrition? |  |

















