JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Units & Measurements | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. Give the MKS units for each of the following quantities. (1980)
(i) Young’s modulus
(ii) Magnetic Induction
(iii) Power of a lens
Ans. (i) N/m2;
(ii) Tesla;
(iii) Dioptre;
Solution. The M.K.S. unit of Young’s modulus is Nm–2.
The M.K.S. unit of magnetic induction is Tesla.
The M.K.S. unit of power of lens is Dioptre.
Q.2. A gas bubble, from an explosion under water, oscillates with a period T proportional to padbEc. Where ‘P’ is the static pressure, ‘d’ is the density of water and ‘E’ is the total energy of the explosion. Find the values of a, b and c.
Ans. a = – 5/6, b = 1/2, c = 1/3
Solution. Given that T ∝ PadbEc
⇒ [M0L0T1] = [ML–1T–2]a [ML–3]b [ML2T–2]c
∴ [M0L0T1] = [Ma + b + c L–a –3b + 2c T–2a – 2c]
∴ a + b + c = 0, – a – 3b + 2c = 0
– 2a – 2c = 1
On solving, we get
a = – 5/6, b = 1/2, c = 1/3
Q.3. Write the dimensions of the following in terms of mass, time, length and charge (1982 - 2 Marks)
(i) magnetic flux
(ii) rigidity modulus
Ans. (i) [M1L2T–1Q–1] (ii) [ML–1T–2]
Solution. Magnetic Flux = [M1L2T–1Q–1]
Modulus of Rigidity = [ML–1T–2]
Q.4. Match the ph ysical quan tities given in column I with dimensions expressed in terms of mass (M), length (L), time (T), and charge (Q) given in column II and write the correct answer against the matched quantity in a tabular form in your answer book.
Column I Column II
Angular momentum ML2T–2
Latent heat ML2Q–2
Torque ML2T–1
Capacitance ML3T–1Q–2
In ductan ce M–1 L–2 T2 Q2
Resistivity L2T–2
Solution.. Angular Momentum [ML2T–1] ;
Latent heat [L2T –2] ;
Torque [ML2T–2]
Capacitance [M–1L–2T2Q2] ;
Inductance [ML2Q–2];
Resistivity [ML3T–1Q–2]
Q.5. Column -I gives three physical quant ities. Select the appropriate units for the choices given in Column-II. Some of the physical quantities may have more than one choice correct :
Column I Column II
Capacitance (i) ohm-second
In ductan ce (ii) coulomb2–joule–1
Magnetic Induction (iii) coulomb (volt)–1
(iv) newton (amp-metre)–1
(v) volt-second (ampere)–1
Ans. Capacitance coulomb-volt–1, coulomb2-joule–1
In ductance ohm-sec, volt-second (ampere)–1
Magnetic Induction newton (ampere-metre)–1
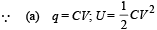
(b) Refer to solution of Q. 3, type D
Q.6. If nth division of main scale coincides with (n+1)th divisions of vernier scale. Given one main scale division is equal to ‘a’ units. Find the least count of the vernier. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Ans. a/n + 1 units
Solution. (n + 1) divisions of vernier scale = n divisions of main scale.
∴ One vernier division = a/n + 1 main scale division

Q.7. A screw gauge having 100 equal divisions and a pitch of length 1 mm is used to measure the diameter of a wire of length 5.6 cm. The main scale reading is 1 mm and 47th circular division coincides with the main scale. Find the curved surface area of wire in cm2 to appropriate significant figure.
(use π = 22/7)
Ans. 2.6 cm2
Solution.
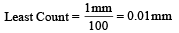
Diameter = MSR + CSR × (least count)
= 1 mm + 47 × (0.01) mm = 1.47 mm Surface Area = πDl
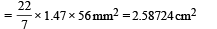
= 2.6 cm2 (Rounding off to two significant figures)
Q.8. In Searle’s exper iment, which is used to find Young’s Modulus of elasticity, the diameter of experimental wire is D = 0.05 cm (measured by a scale of least count 0.001 cm) and length is L = 110 cm (measured by a scale of least count 0.1 cm). A weight of 50 N causes an extension of X = 0.125 cm (measured by a micrometer of least count 0.001cm). Find maximum possible error in the values of Young’s modulus.
Screw gauge and meter scale are free from error. (2004 - 2 Marks)
Ans. 1.09 × 1010 Nm -2
Solution. 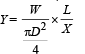
KEY CONCEPT : Maximum error in Y is given by
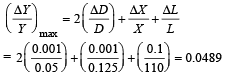
It is given that W = 50 N; D = 0.05 cm = 0.05 × 10–2m;
X = 0.125 cm = 0.125 × 10–2m;
L = 110 cm = 110 × 10–2m
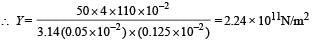
∴ Maximum possible error in the value of
Y = DY = 0.0489 × 2.24 × 1011
= 1.09× 1010 N/m2
Q.9. The side of a cube is measured by vernier callipers (10 divisions of a vernier scale coincide with 9 divisions of main scale, where 1 division of main scale is 1 mm). The main scale reads 10 mm and first division of vernier scale coincides with the main scale. Mass of the cube is 2.736 g. Find the density of the cube in appropriate significant figures.
Ans. 2.66 gm/cm3
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















