JEE Advanced (Matrix Match & Integer Answer): Units & Measurements | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Match the Following
DIRECTIONS (Q. No. 1) : Each question contains statements given in two columns, which have to be matched. The statements in Column-I are labelled A, B, C and D, while the statements in Column-II are labelled p, q, r and s. Any given statement in Column-I can have correct matching with ONE OR MORE statement(s) in Column-II. The appropriate bubbles corresponding to the answers to these questions have to be darkened as illustrated in the following example :
If the correct matches are A-p, s and t; B-q and r; C-p and q; and D-s then the correct darkening of bubbles will look like the given.
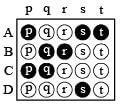
Q.1. Some physical quantities are given in Column I and some possible SI units in which these quantities may be expressed are given in Column II. Match the physical quantities in Column I with the units in Column II and indicate your answer by darkening appropriate bubbles in the 4 × 4 matrix given in the ORS. (2007)
| Column I | Column II |
| (A) GMeMs , G – universal gravitational constant, Me – mass of the earth, Ms – mass of the Sun | (p) (volt) (coulomb)(metre) |
| (B) 3RT/M , R – universal gas constant, T – absolute temperature, M – molar mass | (q) (kilogram) (metre)3(second)–2 |
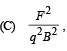 F – Force, q – charge, B – magnetic field F – Force, q – charge, B – magnetic field | (r) (metre)2 (second)–2 |
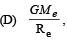 Me – mass of the earth, Re – radius of the earth Me – mass of the earth, Re – radius of the earth | (s) (farad) (volt)2 (kg)–1 |
Ans. (A) → p, q ; (B) → r, s ; (C) → r, s ; (D) → r,s
Solution. A : p → q
Reason : Unit of GMeMs = Fr2 = Nm2
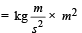
= kg m3s–2
Also (volt) (coulomb) (metre) = (joule) (metre)
= (N - m) (m) = Nm2 = kg m3s–2
B : r → s
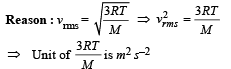
C : r → s
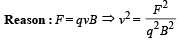
∴ Unit of v2 is m2s–2 which is further equal to FV2 kg–1.
D : r → s
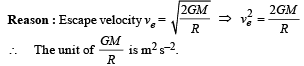
DIRECTIONS (Q. No. 2) : Following question has matching lists. The codes for the lists have choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.2. Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: (JEE Adv. 2013)
| List I | List II |
| P. Boltzmann constant | 1. [ML2T-1] |
| Q. Coefficient of viscosity | 2. [ML–1T–1] |
| R. Planck constant | 3. [MLT–3K–1] |
| S. Thermal conductivity | 4. [ML2T–2K–1] |
Codes:
| P | Q | R | S | |
| (a) | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| (b) | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| (c) | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| (d) | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Ans. (c)
Solution.
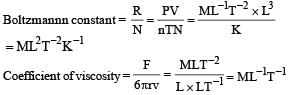
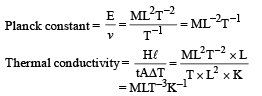
(c) is the correct option.
Integer Value Correct Type
Q.1. To find the distance d over which a signal can be seen clearly in foggy conditions, a railways-engineer uses dimensions and assumes that the distance depends on the mass density ρ of the fog, intensity (power/area) S of the light from the signal and its frequency f. The engineer finds that d is proportional to S1/n. The value of n is (JEE Adv. 2014)
Ans. (3)
Solution.
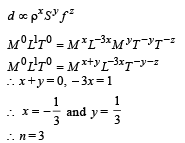
Q.2. During Searle’s experiment, zero of the Vernier scale lies between 3.20 × 10–2 m and 3.25 × 10–2 m of the main scale. The 20th division of the Vernier scale exactly coincides with one of the main scale divisions. When an additional load of 2 kg is applied to the wire, the zero of the Vernier scale still lies between 3.20 × 10–2 m and 3.25 × 10–2 m of the main scale but now the 45th division of Vernier scale coincides with one of the main scale divisions. The length of the thin metallic wire is 2 m and its cross-sectional area is 8 × 10–7 m2. The least count of the Vernier scale is 1.0 × 10–5 m. The maximum percentage error in the Young’s modulus of the wire is (JEE Adv. 2014)
Ans. (4)
Solution.
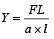
Here F, a and L are accurately known.
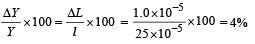
Q.3. The energy of a system as a function of time t is given as E(t) = A2 exp(–αt,) where a = 0.2 s–1. The measurement of A has an error of 1.25%. If the error in the measurement of time is 1.50%, the percentage error in the value of E(t) at t = 5 s is (JEE Adv. 2015)
Ans. (4)
Solution. E = A2 e–0.2t
∴ loge E = 2 loge A –0.2t
On differentiating we get
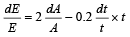
As errors always add up therefore
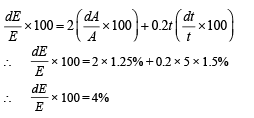
|
446 docs|929 tests
|





















