JEE Advanced (Matrix Match & Integer Answer): Mechanical Properties of Solids & Fluids | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Match the Following
DIRECTIONS (Q. No. 1) : Following question has matching lists. The codes for the lists have choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.1. A person in lift is holding a water jar, which has a small hole at the lower end of its side. When the lift is at rest, the water jet coming out of the hole hits the floor of the lift at a distance d of 1.2 m from the person. In the following, state of the lift’s motion is given in List-I and the distance where the water jet hits the floor of the lift is given in List-II. Match the statements from List-I with those in List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists. (JEE Adv. 2014)
| List - I | List - II |
| P. Lift is accelerating vertically up | 1. d = 1.2 m |
| Q. Lift is accelerating vertically down with an acceleration less than the gravitational acceleration | 2. d > 1.2 m |
| R. Lift is moving vertically up with constant speed | 3. d < 1.2 m |
| S. Lift is falling freely | 4. No water leaks out of the jar |
Code:
(a) P-2, Q-3, R-2, S-4
(b) P-2, Q-3, R-1, S-4
(c) P-1, Q-1, R-1, S-4
(d) P-2, Q-3, R-1, S-1
Ans. (c)
Solution.
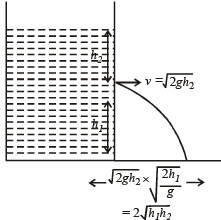
If geff > g
geff = g
geff < g
In all the three cases
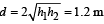
If geff = 0, then no water leaks out
Integer Value Correct Type
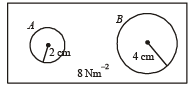
Q.1. Two soap bubbles A and B are kept in a closed chamber where the air is maintained at pressure 8 N/m2. The radii of bubbles A and B are 2 cm and 4 cm, respectively. Surface tension of the soap-water used to make bubbles is 0.04 N/m.
Find the ratio nB/nA, where nA and nB are the number of moles of air in bubbles A and B, respectively. [Neglect the effect of gravity.] (2009)
Ans. 6
Solution. For bubble A :
If PA is the pressure inside the bubble then
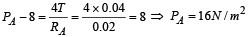
According to ideal gas equation,
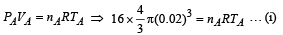
For bubble B :
If PB is the pressure inside the bubble then
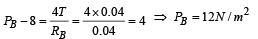
According to ideal gas equation
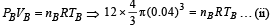
Dividing (ii) by (i) we get
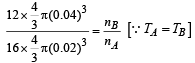
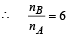
Q.2. A cylindrical vessel of height 500 mm has an orifice (small hole) at its bottom. The orifice is initially closed and water is filled in it up to height H. Now the top is completely sealed with a cap and the orifice at the bottom is opened. Some water comes out from the orifice and the water level in the vessel becomes steady with height of water column being 200 mm. Find the fall in height (in mm) of water level due to opening of the orifice.
[Take atmospheric pressure = 1.0 × 105 N/m2, density of water = 1000 kg/m3 and g = 10 m/s2. Neglect any effect of surface tension.]
Ans. 6
Solution. Initially, the pressure of air column above water is P1 = 105 Nm–2 and volume V1 = (500- H)A , where A is the area of cross-section of the vessel.
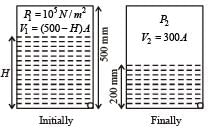
Finally, the volume of air column above water is 300 A. If P2 is the pressure of air then
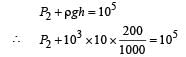
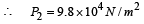
As the temperature remains constant, according to Boyle’s law
P1V1 = P2V2
∴ 105 × (500 - H) A = (9.8 × 104)× 300A ⇒ H = 206 mm
∴ The fall of height of water level due to the opening of orifice = 206 – 200 = 6 mm
Q.3. A 0.1 kg mass is suspended from a wire of negligible mass.
The length of the wire is 1m and its crosssectional area is 4.9 × 10–7 m2. If the mass is pulled a little in the vertically downward direction and released, it performs simple harmonic motion of angular frequency 140 rad s–1. If the Young’s modulus of the material of the wire is n × 109 Nm–2, the value of n is (2010)
Ans. 4
Solution.
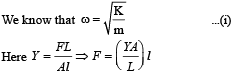
Comparing the above equation with F = kl we get

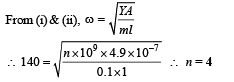 Q.4. Consider two solid spheres P and Q each of density 8 gm cm–3 and diameters 1 cm and 0.5 cm, respectively. Sphere P is dropped into a liquid of density 0.8 gm cm–3 and viscosity η = 3 poiseulles. Sphere Q is dropped into a liquid of density 1.6 gm cm–3 and viscosity η = 2 poiseulles. The ratio of the terminal velocities of P and Q is (JEE Adv. 2016)
Q.4. Consider two solid spheres P and Q each of density 8 gm cm–3 and diameters 1 cm and 0.5 cm, respectively. Sphere P is dropped into a liquid of density 0.8 gm cm–3 and viscosity η = 3 poiseulles. Sphere Q is dropped into a liquid of density 1.6 gm cm–3 and viscosity η = 2 poiseulles. The ratio of the terminal velocities of P and Q is (JEE Adv. 2016)
Ans. 3
Solution.
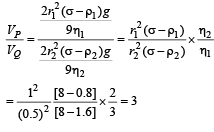
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
















