Fill in the Blanks: Electrostatics | JEE Advanced | Question Bank for JEE Main & Advanced (350+ Tests) PDF Download
Fill in the Blanks
Q.1. Five identical capacitor plates, each of area A, are arranged such that adjacent plates are at a distance d apart, the plates are connected to a source of emf V as shown in the figure (1984- 2 Marks)
The charge on plate 1 is ..... and on plate 4 is ....
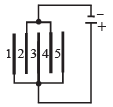
Ans.
Solution. On the plate 1 there is +ve charge
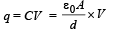
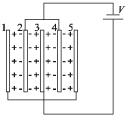
On the plate 4 the charge is
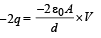
Q.2. Figure shows li ne of c onstant potential in a region in which an electric field is present. The values of the potential are written in brackets. Of the points A, B and C, the magnitude of the electric field is greatest at the point ... (1984- 2 Marks)
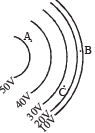
Ans. B
Solution. It is greatest at point B because at B the equipotential surfaces are closest.
Q.3. Two small balls having equal positive charges Q (coulomb) on each are suspended by two insulating strings of equal length L (metre) from a hook fixed to a stand. The whole set up is taken in a satellite into space where there is no gravity (state of weightlessness). The angle between the two strings is ........... and the tension in each string is ........ newtons. (1986 - 2 Marks)
Ans.
Solution. There is no gravitational force acting. Only electrostatic force of repulsion is acting which will take the two balls as far as possible. The angle between the two strings will be 180°. The tension in the string will be equal to the electrostatic force of repulsion
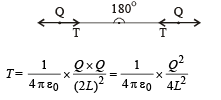
Q.4. Two parallel plate capacitors of capacitances C and 2C are connected in parallel and charged to a potential difference V. The battery is then disconnected and the region between the plates of the capacitor C is completely filled with a material of dielectric constant K. The potential differences across the capacitors now becomes............. (1988 - 2 Marks)
Ans.
Solution. Initially charge on capacitance C = q1 = CV
Charge on capacitance C = q2 = 2CV
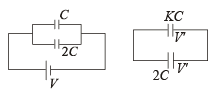
Finally charge on capacitance C = q,' = KCV '
Charge on capacitance 2C = q2' = 2CV '
Total charge will remain conserved
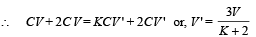
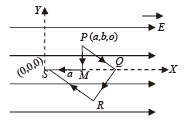
Q.5. A point charge q moves from point P to point S along the path PQRS (fig.) in a uniform electric field E pointing parallel to the positive direction of the X-axis. The cooridnates of the points P, Q, R and S are (a, b, O), (2a, O, O) (a, – b, O) and (O, O,O) respectively. The work done by the field in the above process is given by the expression ................ (1989 - 2 Marks)
Ans. –qEa
Solution. NOTE : Since electric field is conservative in nature, the work done by the field along PQRS will be same as along PMS
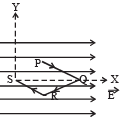
Work done from P to M 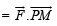
= F (PM) cos 90° = 0
Work done from M to S = 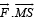
= F (MS) cos 180° [∵F = qE]
= – qEa
Q.6. The electric potential V at any point x, y, z (all in metres) in space is given by V = 4x2 volts. The electric field at the point (1m, 0, 2 m) is .................... V/m. (1992 - 1 Mark)
Ans. –8
Solution. Electric potential V = 4x2 volts
The electric potential changes only along x-axis, We know that
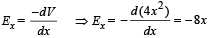
The electric field at point (1, 0, 2) will be (here x = 1)
Ex = – 8 volt/m.
Q.7. Five point charges, each of value + q coul, are placed on five vertices of a regular hexagon of side L metres. The magnitude of the force on the point charge of value – q coul. placed at the centre of the hexagen is .................... newton. (1992 - 1 Mark)
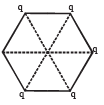
Ans.
Solution.
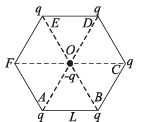
Force on (–q) due to charge at D will get cancelled out by force on (–q) due to change on A. Similarly force on –q due to charge at E will get cancelled out due to charge on B. So the net force will be because of charge on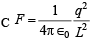 directed from O to C.
directed from O to C.
FAQs on Fill in the Blanks: Electrostatics - JEE Advanced - Question Bank for JEE Main & Advanced (350+ Tests)
| 1. What is electrostatics? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of electrostatics in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 3. How can I prepare for electrostatics in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 4. What are some common applications of electrostatics? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the concept of electric field in electrostatics? |  |
















