JEE Advanced (Subjective Type Questions): Modern Physics- 2 | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.19. The element Curium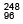 Cm has a mean life of 1013 seconds.
Cm has a mean life of 1013 seconds.
Its pirmary decay modes are spontaneous fission and adecay, the former with a probability of 8% and the latter with a probability of 92%. Each fission releases 200 MeV of energy. The masses involved in a-decay are as follows: 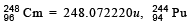 = 244.064100 u and
= 244.064100 u and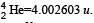 . Calculate the power output from a sample of 1020 Cm atoms. (1 u = 931 MeV/c2.) (1997 - 5 Marks)
. Calculate the power output from a sample of 1020 Cm atoms. (1 u = 931 MeV/c2.) (1997 - 5 Marks)
Ans. 3.32 × 10–5 W
Solution. The reaction involved in a-decay is
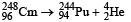
Mass defect
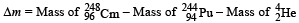
= (248.072220 – 244.064100 – 4.002603) u
= 0.005517u
Therefore, energy released in a-decay will be
Eα = (0.005517 × 931) MeV = 5.136 MeV
Similarly, Efission = 200 MeV (given)
Mean life is given as tmean 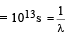
∴ Disintegration constant λ = 10–13 s–1
Rate of decay at the moment when number of nuclei are 1020 is
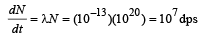
Of these distintegrations, 8% are in fission and 92% are in a-decay.
Therefore, energy released per second
= (0.08 × 107 × 200 + 0.92 × 107 × 5.136) MeV
= 2.074 × 108 MeV
∴ Power output (in watt) = Energy released per second (J/s)
= (2.074 × 108) (1.6 × 10–13)
Q.20. Nuclei of a radioactive element A are being produced at a constant rate α. The element has a decay constant λ. At time t = 0, there are N0 nuclei of the element. (1998 - 8 Marks)
(a) Calculate the number N of nuclei of A at time t.
(b) If α = 2N0λ, calculate the number of nuclei of A after one half-life of A, and also the limiting value of N as t →∞ .
Ans.
Solution.
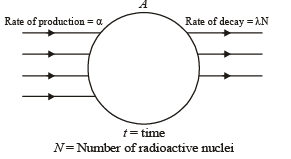
(a) Let at time ‘t’ number of radioactive nuclei are N.
Net rate of formation of nuclei of A.
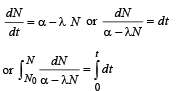
Solving this equation, we get
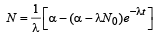 ........(1)
........(1)
(b) Substituting a = 2λN0 and
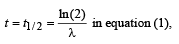
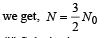
(ii) Substituting α = 2λ N0 and t → ∞ in equation (1), we get
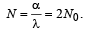
Q.21. Photoelectrons are emitted when 40 nm radiation is incident on a surface of work function 1.9 eV. These photoelectrons pass through a region containing α-particles. A maximum energy electron combines with an α–particle to form a He+ ion, emitting a single photon in this process. He+ ions thus formed are in their fourth excited state. Find the energies in eV of the photons, lying in the 2 to 4 eV range, that are likely to be emitted during and after the combination. [Take h = 4.14×10–15 eV.s.] (1999 - 5 Marks)
Ans. 3.4 eV, 3.84 eV and 2.64 eV
Solution. The energy of the incident photon is
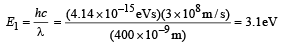
The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is Emax = E1 – W = 3.1 eV – 1.9 eV = 1.2eV
It is given that,
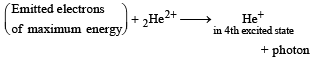
The fourth excited state implies that the electron enters in the n = 5 state.
In this state its energy is
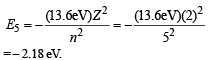
The energy of the emitted photon in the above combination reaction is E = Emax + (– E5) = 1.2 eV + 2.18 eV = 3.4 eV
Note : After the recombination reaction, the electron may undergo transition from a higher level to a lower level thereby emitting photons.
The energies in the electronic levels of He+ are
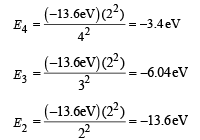
The possible transitions are n = 5 → n = 4
ΔE = E5 – E4 = [– 2.18 – (– 3.4)] eV = 1.28 eV
n = 5 → n = 3
ΔE = E5– E3 = [– 2.18 – (– 6.04)] eV = 3.84 eV
n = 5 → n = 2
ΔE = E5 – E2 = [– 2.18 – (– 13.6)] eV = 11.4 eV
n = 4 → n = 3
ΔE = E4 – E3 = [– 3.4 – (– 6.04)] eV = 2.64 eV
Hence, the photons that are likely to be emitted in the range of 2 eV to 4 eV are 3.4 eV, 3.84 eV and 2.64 eV.
Q.22. A hydrogen-like atom of atomic number Z is in an excited state of quantum number 2n. It can emit a maximum energy photon of 204 eV. If it makes a transition to quantum state n, a photon of energy 40.8 eV is emitted. Find n, Z and the ground state energy (in eV) for this atom. Also calculate the minimum energy (in eV) that can be emitted by this atom during de-excitation. Ground state energy of hydrogen atom is –13.6 eV. (2000 - 6 Marks)
Ans. 2, 4, 10.5 eV
Solution. Energy for an orbit of hydrogen like atoms is
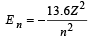
For transition from 2n orbit to 1 orbit
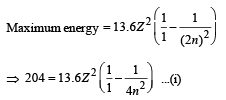
Also for transition 2n → n.
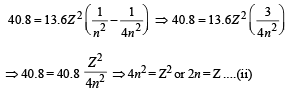
From (i) and (ii)
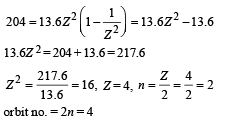
For minimum energy = Transition from 4 to 3.
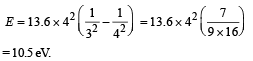
Hence n = 2, Z = 4, Emin = 10.5 eV
Q.23. When a beam of 10.6 eV photons of intensity 2.0 W/m2 falls on a platinum surface of area 1.0 × 10-4 m2 and work function 5.6 eV, 0.53% of the incident photons eject photoelectrons.
Find the number of photoelectrons emitted per second and their minimum and maximum energies (in eV). Take 1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J. (2000 - 4 Marks)
Ans. 6.25 × 1011, 0 eV, 5 eV
Solution. No. of photons/sec
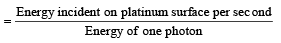
No. of photons incident per second
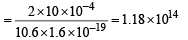
As 0.53% of incident photon can eject photoelectrons
∴ No. of photoelectrons ejected per second
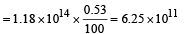
Minimum energy = 0 eV,
Maximum energy = (10.6 – 5.6) eV = 5 eV
Q.24. In a nuclear reaction 235U undergoes fission liberating 200 MeV of energy. The reactor has a 10% efficiency and produces 1000 MW power. If the reactor is to function for 10 years, find the total mass of uranium required. (2001 - 5 Marks)
Ans. 38451 Kg
Solution. The formula for η of power will be
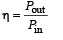
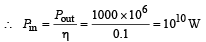
Energy required for this power is given by
E = P × t
= 1010 × 86,400 × 365 × 10
= 3.1536 × 1018 J
200 × 1.6 × 10–13 J of energy is released by 1 fission
∴ 3.1536 × 1018 J of energy is released by
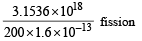
= 0.9855 × 1029 fission
= 0.985 × 1029 of U235 atoms.
6.023 × 1023 atoms of Uranium has mass 235g
∴ 0.9855 × 1029 atoms of Uranium has
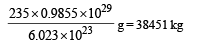
Q.25. A nucleus at rest undergoes a decay emitting an a particle of de-Broglie wavelength λ = 5.76 × 10-15 m. If the mass of the daughter nucleus is 223.610 amu and that of the a particles is 4.002 amu, determine the total kinetic energy in the final state. Hence, obtain the mass of the parent nucleus in amu. (1 amu = 931.470 MeV/c2) (2001-5 Marks)
Ans. 10–12 J, 227.62 amu
Solution. Let the reaction be
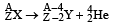
Here, my = 223.61 amu and mα = 4.002 amu
We know that
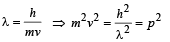

Applying eq. (i) for Y and α, we get
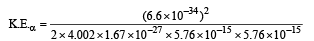
= 0.0982243 × 10–11 = 0.982 × 10–12J
Similarly (K.E.)Y = 0.0178 × 10–12 J
Total energy = 10–12 J
We know that E = Δmc2
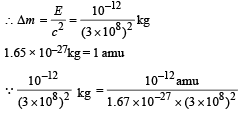
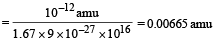
The mass of the parent nucleus X will be
mx = my + ma + Δm
= 223.61 + 4.002 + 0.00665 = 227.62 amu
Q.26. A radioactive nucleus X decays to a nucleus Y with a decay constant λx = 0.1 s-1. Y further decays to a stable nucleus Z with a decay constant λY = 1/30 s-1. Initially, there are only X nuclei and their number is No = 1020. Set up the rate equations for the populations of X, Y and Z. The population of Y nucleus as a function of time is given by NY(t) = (NoλX/ (λX - λY)){exp(-λYt)-exp(-λxt)}. Find the time at which NY is maximum and determine the populations X and Z at that instant. (2001-5 Marks)
Ans.
Solution. 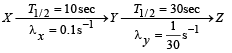
The rate of equation for the population of X, Y and Z will be
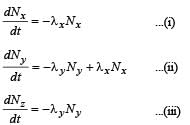
⇒ On integration, we get
Nx = N0e -λxt ...(iv)
Given
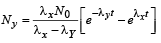
To determine the maximum NY, we find
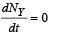
From (ii)
-λy Ny + λxNx = 0
⇒ λx Nx = λyNy .......(v)
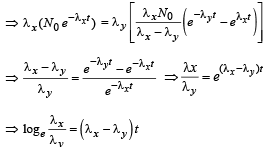
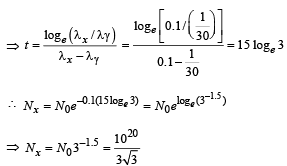
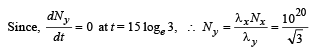
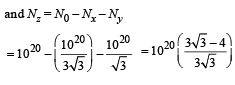
Q.27. A hydrogen-like atom (descr ibed by the Bohr model) is observed to emit six wavelengths, originating from all possible transitions between a group of levels. These levels have energies between -0.85 eV and -0.544 eV (including both th ese values). (2002 - 5 Marks)
(a) Find the atomic number of the atom.
(b) Calculate the smallest wavelength emitted in th ese transitions.
(Take hc = 1240 eV-nm, ground state energy of hydrogen atom = –13.6 eV)
Ans. (a) 3 (b) 4052 nm
Solution. If x is the difference in quantum number of the states than x+1C2 = 6 ⇒ x = 3
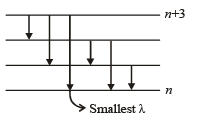
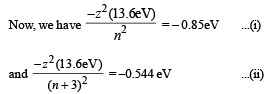
Solving (i) and (ii) we get n = 12 and z = 3
(b) Smallest wavelength λ is given by
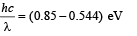
Solving, we get λ = 4052 nm.
Q.28. Two metallic plates A an d B, each of area 5 × 10–4 m2, are placed parallel to each other at a separation of 1 cm. Plate B carries a positive charge of 33.7 × 10–12 C. A monochromatic beam of light, with photons of energy 5 eV each, starts falling on plate A at t = 0 so that 1016 photons fall on it per square meter per second. Assume that one photoelectron is emitted for every 106 incident photons. Also assume that all the emitted photoelectrons are collected by plate B and the work function of plate A remains constant at the value 2eV. Determine (2002 - 5 Marks)
(a) the number of photoelectrons emitted up to t = 10 s,
(b) the magnitude of the electric field between the plates A and B at t = 10 s, and
(c) the kinetic energy of the most energetic photoelectron emitted at t = 10 s when it reaches plate B.
Neglect the time taken by the photoelectron to reach plate B.
Take ε0 = 8.85 × 10–12 C2/N-m2
Ans. (a) 5 × 107
(b) 2000 N/C
(c) 23 eV
Solution. Number of electrons falling on the metal plate A = 1016 × (5 × 10–4)
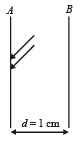
∴ Number of photoelectrons emitted from metal plate A upto 10 seconds is
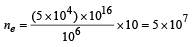
(b) Charge on plate B at t = 10 sec
Qb = 33.7 × 10–12 – 5 × 107 × 1.6 × 10–19 = 25.7 × 10–12 C
also Qa = 8 × 10–12 C
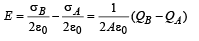
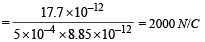
(c) K.E. of most energetic particles
= (hv –φ) + e (Ed) = 23 eV
Note : (hv – φ) is energy of photoelectrons due to light e (Ed) is the energy of photoelectrons due to work done by photoelectrons between the plates.
Q.29. Frequency of a photon emitted due to transition of electron of a certain element from L to K shell is found to be 4.2 × 1018 Hz. Using Moseley’s law, find the atomic number of the element, given that the Rydberg’s constant R = 1.1 × 107 m–1. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Ans. 42
Solution. According to Bohr ’s model, the energy released during transition from n2 to n1 is given by
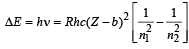
For transition from L shell to K shell
b = 1, n2 = 2, n1 = 1
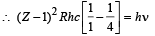
On putting the value of R = 1.1 × 107 m–1 (given),
c = 3 × 108 m/s, we get Z = 42
Q.30. A radioactive sample emits n β-particles in 2 sec. In next 2 sec it emits 0.75 n β-particle, what is the mean life of the sample? (2003 - 2 Marks)
Ans.
Solution.
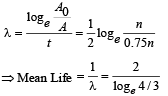
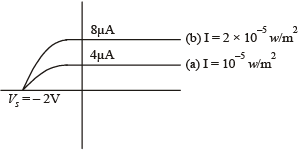
Q.31. In a photoelectric experiment set up, photons of energy 5 eV falls on the cathode having work function 3 eV. (a) If the saturation current is iA = 4μA for intensity 10–5 W/m2, then plot a graph between anode potential and current. (b) Also draw a graph for intensity of incident radiation 2 × 10–5 W/m2. (2003 - 2 Marks)
Solution. (a) eV0 = hv – hv0 = 5 – 3 = 2 eV
∴ V0 = 2 volt
(b) Note : When the intensity is doubled, the saturation current is also doubled.
Q.32. A radioactive sample of 238U decays to Pb through a process for which the half-life is 4.5×109 years. Find the ratio of number of nuclei of Pb to 238U after a time of 1.5×109 years.
Given (2)1/3 = 1.26. (2004 - 2 Marks)
Ans. 0.26
Solution. a = Initial Uranium atom
(a – x) = Uranium atoms left
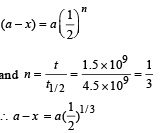
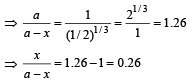
Q.33. The photons from the Balmer series in Hydrogen spectrum having wavelength between 450 nm to 700 nm are incident on a metal surface of work function 2 eV. Find the maximum kinetic energy of ejected electron. (Given hc = 1242 eV nm) (2004 - 4 Marks)
Ans. 0.55 eV
Solution. KEY CONCEPT :
The wavelength λ, of photon for different lines of Balmer series is given by
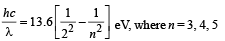
Using above relation, we get the value of λ = 657nm, 487 nm between 450 nm and 700 nm. Since 487 nm, is smaller than 657 nm, electron of max. K.E. will be emitted for photon corresponding to wavelength 487 nm with
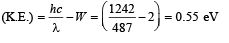
Q.34. The potential energy of a particle of mass m is given by 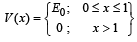 λ1 and λ2 are the de-Broglie wavelengths of the particle, when 0 < x < 1 and x > 1 respectively. If the total energy of particle is 2E0, find λ1 / λ2. (2005 - 2 Marks)
λ1 and λ2 are the de-Broglie wavelengths of the particle, when 0 < x < 1 and x > 1 respectively. If the total energy of particle is 2E0, find λ1 / λ2. (2005 - 2 Marks)
Ans. √2
Solution. The de Broglie wave length is given by
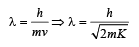
Case (i) 0 < x < 1
For this, potential energy is E0 (given)
Total energy = 2E0 (given)
∴ Kinetic energy = 2E0 – E0 = E0
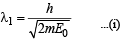
Case (ii) x > 1
For this, potential energy = 0 (given)
Here also total energy = 2E0 (given)
∴ Kinetic energy = 2E0
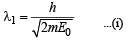
Dividing (i) and (ii)
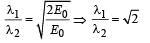
Q.35. Highly energetic electrons are bombarded on a target of an element containing 30 neutrons. The ratio of radii of nucleus to that of Helium nucleus is (14)1/3. Find (a) atomic number of the nucleus. (b) the frequency of Kα line of the X-ray produced. (R = 1.1 × 107 m–1 and c = 3 × 108 m/s) (2005 - 4 Marks)
Ans. (a) 56
(b) 1.546 × 1018 Hz.
Solution. (a) KEY CONCEPT : We know that radius of nucleus is given by formula
r = r0A1/3 where r0 = constt, and A = mass number.
For the nucleus r1 = r041/3
For unknown nucleus r2 = r0 (A)1/3
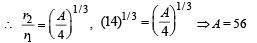
∴ No of proton = A – no. of neutrons = 56 – 30 = 26
∴ Atomic number = 26
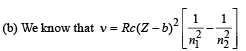
Here, R = 1.1 × 107, c = 3 × 108, Z = 26
b = 1 (for Kα), n1 = 1, n2 = 2
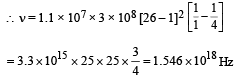
Q.36. In hydrogen-like atom (z = 11), nth line of Lyman series has wavelength λ. The de-Broglie's wavelength of electron in the level from which it originated is also λ. Find the value of n ? (2006 - 6M)
Ans. 24
Solution. Note : nth line of Lyman series means electron jumping from (n + 1)th orbit to 1st orbit.
For an electron to revolve in (n + 1)th orbit. 2πr = (n + 1)λ
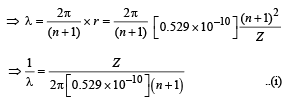
Also we know that when electron jumps from (n + 1)th orbit to 1st orbit.
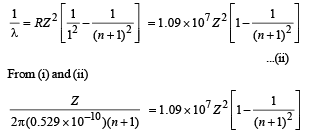
On solving, we get n = 24
|
481 docs|964 tests
|
















