Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - How Do Organisms Reproduce
Q1: Name the various types of asexual reproduction.
Ans: The various types of asexual reproduction are:
(a) Fission– binary and multiple
(b) Budding
(c) Spore formation
(d) Regeneration
(e) Vegetative propagation – It is a process by which new organisms arise without production of seeds or spores. It can occur naturally or be induced by horticulturists.
Q2: Why are budding, fragmentation and regeneration all considered as asexual types of reproduction? With neat diagrams explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
Ans: They are considered as asexual types of reproduction as all of them involve a single parent and no fusion of gametes take place in them.
They are considered as asexual types of reproduction as all of them involve a single parent and no fusion of gametes take place in them.
Q3: Differentiate between binary fission and multiple fission.
Ans: Binary Fission:
1.In this type of fission, the parent cell gives rise to two daughter cells.
2.It is expressed by organisms like amoeba, paramecium, etc.
Multiple Fission: 1.In this type of fission, the parent cell gives rise to more than two daughter cells.
1.In this type of fission, the parent cell gives rise to more than two daughter cells.
2.It is expressed by organisms like plasmodium.
Q4: List the advantages of vegetative propagation.
Ans: The advantages of vegetative propagation are as follows (a) It helps in the easy propagation of non–flowering plants.
(a) It helps in the easy propagation of non–flowering plants.
(b) It helps in producing hybrids of various plants, with improved qualities.
(c) It helps in the propagation of a large number of population in a very short duration.
(d) It helps in the propagation of plants that do not produce seeds or produce them in very small quantities.
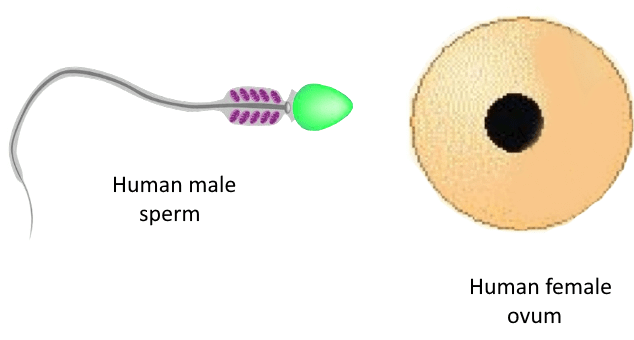
Q5: Name the male and the female gametes in human beings.
Ans: The male gamete is called sperm and the female gamete is called ovum in human beings.
Q6: Define fertilization.
Ans: The process of fusion of the male gamete with the female gamete of the same species, i.e., the sperm with the ovum is known as fertilization. After fertilization, the product obtained is the zygote, which eventually develops into a complete organism.
Q7: Define sexual reproduction.
Ans: The type of reproduction that involves both the sexes of the species is known as sexual reproduction. This kind of reproduction requires the fertilization of the gametes of both the sexes.
Q8: Mention any two functions of human ovary.
Ans: The two functions of human ovary are as follows:
(i) It is responsible for the production of the female gamete, ovum.
(ii) It secretes hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Q9: Distinguish between pollination and fertilisation. Mention the site and product of fertilisation in a flower. Draw a neat, labelled diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth and its entry into the ovule.
Ans:
- Pollination: The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
- Fertilisation: The process of fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote is called fertilisation.
- The site of fertilisation is ovule. The product of fertilisation is zygote.

Q10: What is syngamy?
Ans: The process of fusion of the two gametes is known as syngamy. It is the initial step in the process of fertilization.
Q11: Where does fertilization take place in human females?
Ans: Fertilization in the case of humans is internal. The process of fertilization takes place inside the fallopian tube of females.
Q12: Define menopause.
Ans: At the age of around 45-50 years, the ovaries of the females stop producing ova.
The stoppage of menstrual flow and other events like the changes in the hormonal composition is known as menopause.
Q13: Describe asexual reproduction in amoeba.
Ans:  Amoeba reproduces by the process of binary fission. During this process, the nucleus divides first, followed by the formation of a constriction in the cellular membrane of amoeba. This gradually increases inwards and divides the cytoplasm into two parts. Finally two daughter organisms are obtained.
Amoeba reproduces by the process of binary fission. During this process, the nucleus divides first, followed by the formation of a constriction in the cellular membrane of amoeba. This gradually increases inwards and divides the cytoplasm into two parts. Finally two daughter organisms are obtained.
Q14: Explain various steps of budding in yeast.
Ans: Budding is a form of asexual reproduction usually observed in yeast. (a) During this process, a small protrusion appears on the upper portion of the body of the organism. This bulge is called a bud.
(a) During this process, a small protrusion appears on the upper portion of the body of the organism. This bulge is called a bud.
(b) The bud gradually grows in size and forms an individual cell.
(c) From this newly budded cell, another bud appears at the tip.
(d) This process continues and a chain of yeast cells is obtained.
Q15: What are the various methods of vegetative propagation? Discuss any one method with example.
Ans: The various types of vegetative propagation are
• Cutting
• Layering
• Grafting
• Parthenogenesis
• Micro-propagation
Grafting
(a) It is a method in which two parts of different plants are joined together in such a way that they unite and grow as one plant.
(b) The portion of the plant that is grafted onto another plant is known as the scion, and the plant on which grafting is performed is known as the stock.
(c) The stock and the scion are tied in such a way that the cambium of the scion and the stock come in contact with each other.
(d) The stock is so chosen that it possesses qualities like disease resistance, high water absorbing capacity, deep penetrating roots for a firm hold, etc. The scion is so chosen that it possesses qualities like high yield of pulp or seeds (as desired) from a single fruit, etc.
(e) For example citrus-root stock is used for a variety of grafts like sweet orange, lime, grape, etc.
Q16: Mention the reproductive parts of a flower.
Ans: The reproductive parts of a flower are as follows: Male reproductive part – Stamens
Male reproductive part – Stamens
Female reproductive part – Pistil.
Q17: What is pollination? Describe cross-pollination.
Ans: The transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called pollination. Pollen grains are shed from the anther and reach the stigma of either the same flower or a different flower.
Cross-pollination
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same species is termed as cross-pollination.
Q18: Describe double fertilization in plants.
Ans:  In the case of plants, the pollen grain releases two male gametes. One fuses with the egg and forms the zygote. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei. This fusion is said to be triple fusion. Thus, inside an embryo sac, two fusions, syngamy and triple fusion, take place. This mechanism of two fusions occurring in an embryo sac is called double fertilization.
In the case of plants, the pollen grain releases two male gametes. One fuses with the egg and forms the zygote. The other male gamete fuses with the two polar nuclei. This fusion is said to be triple fusion. Thus, inside an embryo sac, two fusions, syngamy and triple fusion, take place. This mechanism of two fusions occurring in an embryo sac is called double fertilization.
Q19: What are the male and the female gonads in the human beings? Mention their functions.
Ans: Testes are the male gonads in human beings. Their functions are
(a) To produce male hormones like testosterone.
(b) To produce the male gamete – sperm.
Ovaries are the female gonads in human beings. Their functions are
(c) To produce female hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
(d) To produce the female gamete – ovum.
Q20: Mention the secondary sexual characters in human males and females.
Ans: The male secondary sexual characters are the growth of hair on the chest, near the genitals, on the face in the form of beard and moustache, development of deep hoarse voice, etc.
The female secondary sexual characters are the development of breasts and mammary glands, axial and pubic hair, etc.
|
85 videos|437 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - How Do Organisms Reproduce
| 1. How do organisms reproduce? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of asexual reproduction? |  |
| 3. What is the role of DNA in the process of reproduction? |  |
| 4. How do plants reproduce sexually? |  |
| 5. Can organisms choose between sexual and asexual reproduction? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|

















