Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Force and Pressure
Short Answer Questions
Q1. What is force? What is its unit?
Ans: A force is defined as a push or pull exerted on an object. It arises from the interaction between two objects and possesses both magnitude and direction. A force can cause a change in the state of motion of an object or alter its shape. The unit of force is the Newton.
Q2. What is change in state of motion? What brings change in state of motion?
Ans: A change in either the speed of an object, its direction of motion, or both, is referred to as a change in its state of motion. Such changes are brought about by a force, which can alter the state of motion of an object.
Q3. What is the difference between contact forces and non-contact forces?
Ans: Contact forces are forces that act only when there is physical contact between two interacting objects. An example of this is muscular force. In contrast, non-contact forces, also known as field forces, can act without physical contact between objects. These forces can exert influence from a distance, such as in the case of magnetic force. 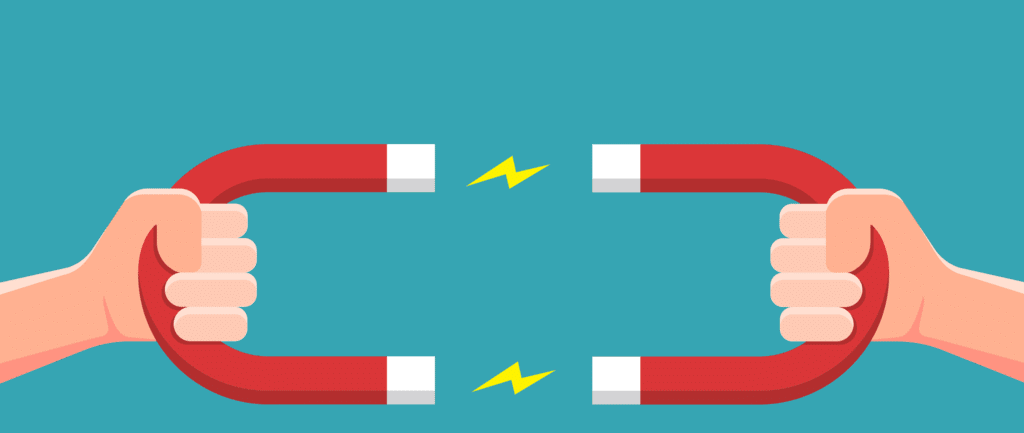 Magnetic Force
Magnetic Force
Q4. Give two example each of the situation in which you apply force to change state of motion of an object and to change shape of an object?
Ans: Here are two examples of situations where force is applied:
- A goalkeeper applies force to save a goal by attempting to stop a moving ball. This action alters the state of motion of the ball.
- Force is applied to the shape of a ball of dough when it is rolled out to make a chapatti.
Q5. Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string?
Ans: It is difficult to hold a school bag with a strap made of a thin and strong string because it applies a large amount of pressure on the shoulders. This is due to the very small contact surface area. Pressure is inversely proportional to the surface area over which the force acts; therefore, pressure decreases as the surface area increases.
Q6. Why Porters wear turbans when they have to carry heavy loads on their heads?
Ans: Porters wear turbans when carrying heavy loads on their heads to increase the area of contact. This reduces the pressure on the head, making it more comfortable to support the weight.
Q7. Force applied on an object may change its speed. How?
Ans: The force applied on an object can change its speed. If the force is applied in the same direction as the object's motion, the speed of the object increases. Conversely, if the force is applied in the opposite direction, it results in a decrease in the object's speed.
Q8. Why Lorries and trucks carrying heavy loads have 8 tyres instead of four?
Ans: Lorries and trucks carrying heavy loads typically have eight tyres instead of four. This design choice is essential for several reasons:
- The additional tyres help to distribute the weight more evenly across the ground.
- Broader tyres increase the area of contact with the ground, which reduces the pressure exerted on the surface.
By having more tyres, these vehicles can operate safely and effectively, minimising the risk of damage to the road and improving stability during transport.
Q9. Why the sucker sticks to the surface over which it is pressed?
Ans: When we press the sucker, most of the air between its cup and the surface escapes. The sucker adheres to the surface because the atmospheric pressure acts on it. To remove the sucker from the surface, the applied force must be sufficient to overcome this atmospheric pressure.
Q10. What is pressure? How is pressure related to the surface area on which it acts?
Ans: Pressure is defined as the force per unit area. It is important to note that pressure is inversely proportional to the surface area on which it acts. This means that the smaller the area, the greater the pressure exerted on that surface for the same amount of force.
Q11. When we stop pedalling the bicycle, it slows down and gradually stops. Why?
Ans: When we stop pedalling the bicycle, it slows down and gradually stops due to the force of friction between the tyres of the bicycle and the ground. This frictional force acts in a direction that is always opposite to the direction of motion, effectively bringing the moving bicycle to a rest.
Q12. What is frictional force? How it arises?
Ans: The force acting against the relative motion of surfaces in contact is known as frictional force or simply friction. Friction is a type of contact force that arises due to the interaction between these surfaces. Specifically, the force of friction occurs when two surfaces come into contact, leading to resistance against their movement. This resistance is influenced by several factors, including the nature of the surfaces and the amount of force pressing them together.
Q13. What is magnetic force? What happens when we bring like poles of two magnets closer?
Ans: A magnet can exert a force on another magnet without being in contact with it; this force is known as magnetic force. When we bring like poles of two magnets closer, they repel each other. Conversely, unlike poles of two magnets attract each other.
Q14. What is gravitational force? Is gravity the property of earth alone?
Ans: Gravitational force is the force that every object in the universe exerts on every other object. This means that all objects, regardless of their size, contribute to this force. Therefore, gravity is not exclusive to the Earth; it exists between all objects in the universe, whether they are large like planets or small like dust particles. In summary:
- Every object exerts a gravitational force on others.
- Gravity is not limited to Earth; it applies universally.
Q15. A rocket has been fired upwards to launch a satellite in its orbit. Name the two forces acting on the rocket just after leaving of the launching pad.
Ans: The forces acting on a rocket just after it leaves the launching pad are:
- Frictional force due to air resistance.
- Force of gravity acting in the downward direction.
Q16. What will be the effect of force while squeezing a piece of lemon between the fingers?
Ans: Agent exerting pressure: Fingers.
Object: Lemon. The effect of force is observed in the following ways:
- Lemon juice is released.
- There is a change in the shape of the lemon.
Q17. What will be the effect of force while taking out toothpaste from toothpaste tube?
Ans: Agent exerting pressure: Fingers. Object: Toothpaste tube. Effect of force: When pressure is applied, toothpaste is expelled from the tube, resulting in a change in shape of the toothpaste.
Q18. A blacksmith is hammering a hot piece of copper for making a tool, how does the force due to affect the piece of copper?
Ans: The force exerted by the hammer during the process of hammering affects the shape of the hot piece of copper. As the blacksmith strikes the copper, the metal becomes malleable due to its high temperature, allowing it to change form. Through repeated blows, the following occurs:
- The shape of the copper is altered, enabling the creation of various tools.
- The molecular structure of the copper is modified, enhancing its properties.
- The technique improves the strength and durability of the finished tool.
Q19. What are the effects of the force while making high jump by an athlete?
Ans: Agent: An athlete applies force during a high jump. Object: The athlete's body is the object being acted upon by this force. Effect of Force: The primary effect of this force is jumping, which allows the athlete to gain height and clear the bar. During the jump, the athlete pushes against the ground. This action generates an upward force that propels the body into the air. The key factors influencing the height achieved include:
- Strength: The athlete's physical strength helps in generating more force.
- Technique: Proper jumping technique ensures that the force is effectively transferred to achieve maximum height.
- Gravity: The force of gravity acts on the athlete, pulling them back down after the jump.
In conclusion, the interaction of these forces determines the success of the high jump.
Q20. Differentiate between atmosphere and atmospheric pressure.
Ans: Atmosphere refers to the layer of air that surrounds our Earth, while atmospheric pressure is the force exerted by this air on a given surface. In other words, the atmosphere is the medium, and atmospheric pressure is the measurable effect of that medium.
Q21. Differentiate between friction and contact force.
Ans: Friction is the force that opposes the motion of objects, affecting their state of movement. In contrast, a contact force refers to the forces that act only when there is direct physical contact between two interacting objects.
Q22. What is a force? Explain with the help of some examples.
Ans: Force is defined as a pull or push applied to an object. Various actions demonstrate force, including:
- Pushing
- Pulling
- Picking
- Hitting
- Lifting
- Running
- Bending
Force is responsible for moving or stopping a body, as well as changing its shape and direction of motion. These actions clearly illustrate the concept of force in practice.
Q23. How do we feel force in our daily life?
Ans: We experience force in various big and small actions throughout our daily lives. For instance:
- We hit or catch many objects daily.
- A moving ball stops on its own due to the effects of force.
- The direction of a ball's motion changes when it is hit with a bat.
- We make lassi by churning curd, which also demonstrates the application of force.
These actions illustrate how force is exerted in our everyday activities.
Q24. Explain that forces are due to an interaction between objects.
Ans: Imagine, a man is standing behind a stationary car. The car does not move due to his presence.

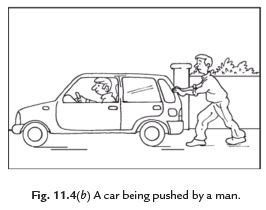
Now allow the man to push the car, it means he applies a force on the car. The car may begin to move in the direction of the applied force. Note that the man has to push the car to make it move. This example shows that at least two objects must interact with each other for a force to come into play.
Q25. What happens when (i) Two forces are exerted in same direction? (ii) Two forces are exerted in opposite directions?
Ans: (i) When two forces are exerted in same direction on an object, then the forces are added and action becomes easy.
(ii) When two forces act in the opposite directions on an object, the net force acting on it is the difference between the two forces.
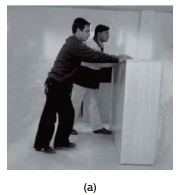
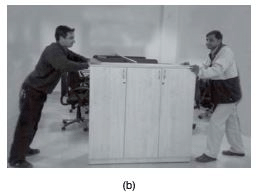
Fig. 11.5 Two friends pushing a heavy load (a) in the same direction, (b) in opposite directions.
Q26. What are the two factors on which effect of force depends?
Ans: There are two factors on which the effect of force depends:
- Magnitude: The strength of the force is expressed by its magnitude.
- Direction of force: It is essential to specify the direction in which the force acts.
If either the direction or magnitude of the force changes, its effect will also change.
Q27. What are the effects of force?
Ans: A force can change or attempt to change the following:
- Speed of a moving body.
- Direction of motion of a body.
- Shape of a body.
Q28. What are states of motion?
Ans: An object can be in two states of motion: at rest or in motion. Any change in this position, whether from rest to motion or vice versa, is referred to as a change in the state of motion. The state of motion of an object is characterised by its speed and the direction of its movement.
Q29. How can a force change the states of motion?
Ans: There are two states of an object:
- Rest
- Motion
When a force is applied to a body, it can cause the body to move. Additionally, a force can change the direction of a moving object as well as its speed. It can also stop a moving object. If the force is applied in the direction of motion, the object's speed is increased. Conversely, if the force acts in the opposite direction, the speed of the object decreases.
Q30. What is the effect of force on the shape of an object?
Ans: A force can change or attempt to change the shape of an object. When a force is applied to an object, a change in shape occurs. This change may be minor or significant. In summary, we can say that the application of force to an object may alter its shape.
Q31. Explain contact and non-contact forces.
Ans: Contact forces are the forces that occur only when two objects are in physical contact with each other. Examples include friction, tension, and normal force. These forces are essential in understanding how objects interact in our physical world. In contrast, non-contact forces are those that act on objects without the need for direct contact. Examples include gravitational force, magnetic force, and electrostatic force. These forces can influence objects over a distance, demonstrating the fundamental interactions that can occur even when objects are not touching.
Q32. What is muscular force? Why is it called contact force?
Ans: Muscular force is the force generated by the action of muscles. It is classified as a contact force because it only takes effect when two bodies are in contact with each other.
Q33. What do you understand by the force of friction?
Ans: The force of friction is a force that acts on all moving objects, always opposing their direction of motion. It arises due to the contact between surfaces, which is why it is also referred to as a contact force.
Q34. What is electrostatic force? Why is it called non-contact force?
Ans: The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or uncharged body is known as electrostatic force. This force acts even when the bodies are not in contact, which is why it is referred to as a non-contact force.
Q35. Explain force of gravity.
Ans: The force of gravity is the reason objects fall towards the Earth. This force, known as gravity, is an attractive force that acts on all objects. It pulls them towards the centre of the Earth, causing them to fall.
Q36. What is pressure? What happens to the pressure when area on which it is applied increases?
Ans: Pressure is defined as the force acting on a unit area of a surface. The formula for calculating pressure is: Pressure = Force / Area on which it acts. Pressure is inversely proportional to the area over which the force is applied. This means that as the area increases, the pressure decreases. Conversely, we can say that pressure increases when the area decreases.
Q37. We observe that the wheels of buses and trucks are heavier than the wheels of cars or scooters. Why?
Ans: The wheels of buses and trucks are heavier than those of cars or scooters because they need to support more weight. To exert less pressure on the ground, their tyres are designed to be broader. This is based on the principle that pressure decreases as the area of contact increases. If these vehicles had narrower wheels, they would exert more pressure and risk sinking into the ground. In contrast, scooters and cars have narrower wheels as they require more pressure for better gripping on the road surface. This design choice enhances their stability and handling, especially at higher speeds.
Q38. What is atmospheric pressure?
Ans: The envelope of air surrounding the Earth is known as the atmosphere. This atmospheric air extends up to several kilometres above the Earth's surface. The pressure exerted by this air is referred to as atmospheric pressure.
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Force and Pressure
| 1. What is force? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of forces? |  |
| 3. How is pressure defined? |  |
| 4. What is the relationship between force and pressure? |  |
| 5. How does pressure affect the behavior of objects? |  |

















