Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Sound
Q1. Discuss the importance of sound in our life.
Ans: The significance of sound in our lives includes:
- Communication: Sound is essential for effective interaction between people.
- Awareness: It keeps us informed about events and activities beyond our direct attention.
- Animal Alertness: Animals depend on sound to stay aware of their surroundings, regardless of their focus.
Q2. How is sound produced?
Ans: Sound is produced by the vibrations of an object. These vibrations create pressure waves that travel through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. The process involves:
- Condensations: This is when molecules in the medium are pushed together.
- Rarefactions: This occurs when molecules are pulled apart.
These alternating condensations and rarefactions form the sound waves that we hear.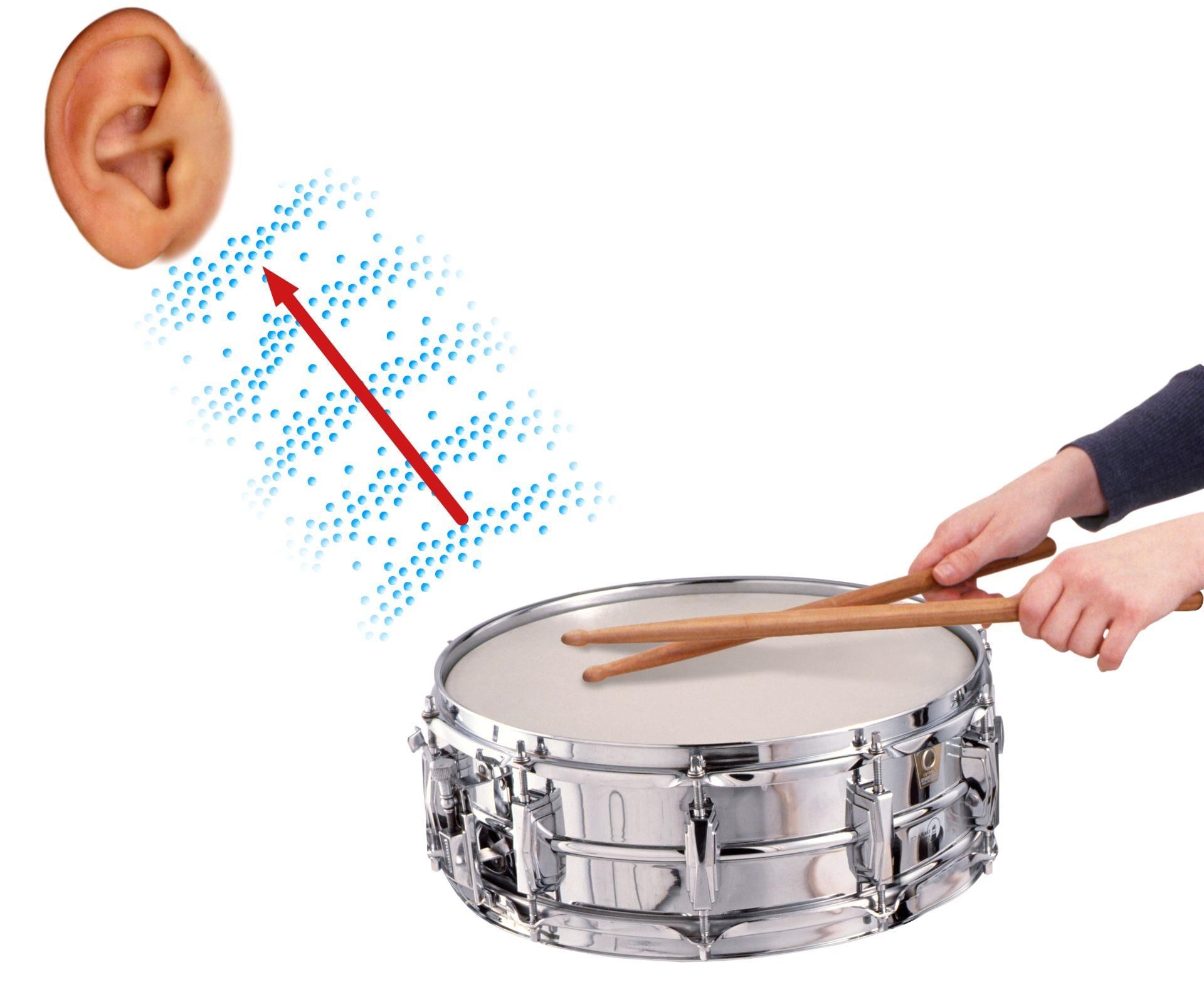
Q3. How does sound travel from one place to another?
Ans: Sound travels from one place to another by moving through a medium, which can be a solid, liquid, or gas. The process involves:
- Generation of vibrations at the source.
- Creation of compressions (high-pressure areas) and rarefactions (low-pressure areas) in the medium.
- Collisions between particles in the medium, transferring energy from one particle to another.
This transfer of energy allows the sound wave to travel effectively.
Q4. Why some sounds are louder than others?
Ans: The variation in the loudness of sounds is primarily determined by their amplitude. Key points include:
- A higher amplitude means that particles in the medium vibrate more intensely.
- This leads to a greater displacement of air molecules.
- More displacement causes increased compression and rarefaction in the sound wave.
- The result is more intense variations in air pressure, which our ears perceive as a louder sound.
Q5. Explain with an activity that vibrating object produces sound.
Ans: Take a metal dish and fill it with water. Then, strike the edge of the dish with a spoon. You will hear a sound. Next, strike the edge of the dish again and observe the surface of the water.
- You will see waves forming in the water.
- This demonstrates that the vibrating dish is producing sound.
- The vibrations in the dish create sound waves that travel through the air.
This activity clearly shows how a vibrating object can produce sound.
Q6. What are vibrating parts of Veena and Tabla?
Ans: The vibrating parts that produce sound in the Veena and Tabla are:
- Veena: The sound is produced by the stretched string.
- Tabla: The sound comes from the stretched membrane.
Q7. What are vibrating parts of Flute?
Ans: The vibrating part of a flute that produces sound is the air column.
Q8. Name some musical instrument which are simply beaten or struck to produce melodious music.
Ans: Manjira, ghatam, nagada, and kartal are some musical instruments that are simply beaten or struck to produce melodious music.
Q9. How sound is produced from a guitar?
Ans: The sound from a guitar is produced as follows:
- When a string is plucked, it vibrates.
- This vibration causes the surrounding air to move, creating sound waves.
- Other parts of the guitar, like the body, also vibrate, enhancing the sound.
- The combination of vibrations from the strings and the body results in the sound we hear.

Q10. Does any part of human body vibrate while speaking or singing a song?
Ans: Yes, when we speak or sing, the larynx, or voice box, vibrates. It is situated at the upper end of the windpipe and plays a crucial role in producing sound.
Q11. Why the larynx in human body does vibrate while speaking or singing a song?
Ans: The human larynx contains two vocal cords that are stretched across it, creating a narrow opening for air to pass through. When air from the lungs is pushed through this opening, it causes the vocal cords to vibrate, which produces sound.
- The vocal cords are essential for sound production.
- Air pressure from the lungs forces the cords apart.
- The vibration of the cords generates different pitches.
Q12. Explain via an activity that sound travels in liquids.
Ans: To demonstrate that sound travels in liquids, follow this simple activity:
- Fill a bucket with water.
- Hold a bell underwater with one hand, ensuring it does not touch the bucket's sides.
- Gently place your ear near the water surface.
You will hear the sound of the ringing bell. This shows that sound can travel through water.
Q13. Explain via an activity that sound travels in solids.
Ans: To demonstrate that sound travels in solids, follow this simple activity:
- Take a metal rod and hold one end against your ear.
- Ask a friend to tap the other end of the rod.
- You will hear the sound of the tapping clearly.
This activity shows that sound can travel through solids, as you can hear the sound despite being some distance away from the source.
Q14. How water animals communicate in water?
Ans: Water animals primarily communicate using sound, as it travels efficiently through water. Here’s how it works:
- When a sound is made underwater, it travels in waves.
- For example, if you fill a bucket with water and shake a bell underneath, you can hear it ring.
- This demonstrates that sound can travel through water effectively.
Thus, many aquatic animals use sound to communicate with each other.
Q15. Explain the function of eardrum in human beings.
Ans: The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its main functions include:
- Acting like a stretched rubber sheet that vibrates in response to sound waves.
- Transmitting these vibrations to the inner ear.
- Facilitating the conversion of sound vibrations into signals sent to the brain, enabling us to hear.
In summary, the eardrum plays a crucial role in our ability to hear by responding to sound and passing information to the brain.
Q16. What is eardrum?
Ans: The eardrum, also known as the tympanic membrane, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear.
Key features of the eardrum include:
- It resembles a stretched rubber sheet.
- Sound vibrations cause it to vibrate.
- These vibrations are transmitted to the inner ear.
- Finally, signals are sent to the brain, allowing us to hear sounds.
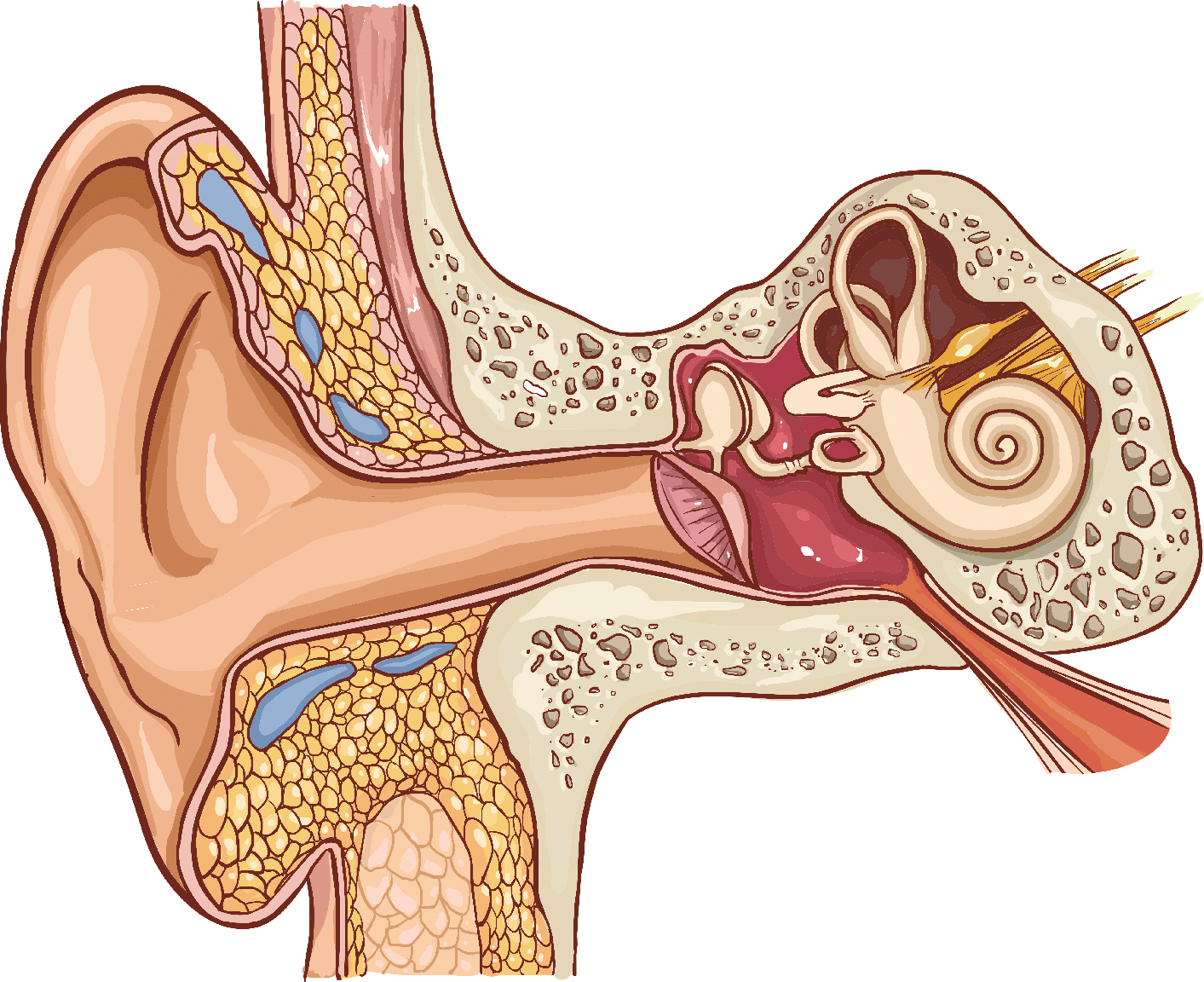
Q17. Explain the functioning of human ear.
Ans: The eardrum, also known as the tympanic membrane, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. It functions like a stretched rubber sheet:
- Sound vibrations cause the eardrum to vibrate.
- These vibrations are then transmitted to the inner ear.
- From the inner ear, signals are sent to the brain.
This process allows us to hear the sounds around us.
Q18. Why are sound waves called mechanical waves?
Ans: Sound waves are referred to as mechanical waves because they require a medium, such as air, water, or solids, to travel through. Here’s why:
- Sound waves cause the particles of the medium to vibrate.
- The vibration of these particles is what allows sound to be transmitted.
- Without a medium, sound cannot propagate, as there are no particles to carry the wave.
In summary, sound waves are mechanical because they depend on the physical movement of particles in a medium to transmit energy.
Q19. Why there is difference in sound of a baby and an adult?
Ans: The difference in the sound of a baby and an adult can be attributed to the amplitude of vibration in their vocal cords and eardrums:
- A higher amplitude of vibration produces a louder sound.
- A lower amplitude results in a softer sound.
- Babies have a smaller amplitude of vibration in their eardrums, which leads to a quieter sound compared to adults.
Q20. Name the factor which determines shrillness or pitch of a sound?
Ans:
The factor that determines the pitch of a sound is its frequency of vibration:
- A higher frequency results in a high pitch.
- A lower frequency leads to a low pitch.
Q21. Which of the two a drum or a whistle will produce sound with higher pitch and why?
Ans: A whistle produces a sound with a higher pitch compared to a drum. This is due to the following reasons:
- The frequency of vibration is key to pitch.
- A whistle vibrates at a higher frequency, resulting in a high pitch.
- In contrast, a drum has a lower frequency, which leads to a lower pitch.
Thus, the higher the frequency of vibration, the higher the pitch of the sound.
Q22. Which of the two a man or a woman will produce sound with higher pitch and why?
Ans: Women generally produce sound with a higher pitch than men. This difference is due to the following factors:
- The frequency of vibration in women's vocal cords is typically higher.
- A higher frequency results in a higher pitch of sound.
- Conversely, men usually have a lower frequency of vibration, leading to a lower pitch.
In summary, the pitch of sound is directly related to the frequency of vibration: higher frequency equals higher pitch.
Q23. Differentiate between audible and in audible sounds.
Ans: Audible sounds are defined as sounds that fall within the frequency range of 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. These sounds are easily heard by humans. In contrast, inaudible sounds are those that fall outside this range:
- Frequencies below 20 Hz are considered inaudible.
- Frequencies above 20,000 Hz are also inaudible.
In summary:
- Audible sounds: 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz
- Inaudible sounds: Below 20 Hz and above 20,000 Hz

Q24. Is there any animal that can hear sound of frequencies higher than 20000 Hz?
Ans: Yes, dogs can hear sounds at frequencies higher than 20,000 Hz. This ability makes them valuable for various tasks, including:
- Police investigations
- Search and rescue operations
- Detecting certain medical conditions
Dogs' acute hearing enhances their roles in these important areas.
Q25. Name some equipment that works at frequencies higher than 20000 Hz.
Ans: The ultrasound equipment is commonly used in medical settings and operates at frequencies exceeding 20,000 Hz. It is effective for:
- Tracking various medical conditions
- Investigating internal organs
- Assisting in diagnostic imaging
This technology harnesses high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the body, making it invaluable in modern medicine.
Q26. Define noise along with examples.
Ans: Noise refers to unpleasant or unwanted sounds that can be disruptive or irritating. Common examples include:
- Horns from vehicles
- Sounds from construction sites
- Noises from factory machinery
Q27. Explain noise pollution and its causes.
Ans: Noise pollution refers to the presence of excessive or unwanted sounds in the environment.
The main causes of noise pollution include:
- Traffic noise from vehicle horns.
- Construction sounds from building sites.
- Industrial noise from factory machinery.
- Domestic sources such as televisions, radios at high volume, air conditioners, and kitchen appliances like pressure cookers.
Q28. Your friend's parents are going to buy a house; they have been offered one nearby a factory and another 50 km away from the factory in a less crowded place. Which house you would suggest your friend's parents should buy, and why?
Ans: I would suggest choosing the house that is 50 km away from the factory, located in a less crowded area. Here are the reasons:
- The house near the factory is likely to experience noise pollution from industrial machines.
- There may also be air pollution issues due to emissions from the factory.
- A quieter, less crowded environment can contribute to better health and well-being.
Q29. How noise pollution is harmful to human beings?
Ans: Noise pollution can cause a variety of health issues, including:
- Hearing loss
- Sleep disturbances
- Hypertension
- Severe headaches
- Increased stress
These effects can significantly impact overall well-being and quality of life.
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Question Answers - Sound
| 1. What is sound and how is it produced? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of sound waves? |  |
| 3. How do we perceive sound? |  |
| 4. What factors affect the speed of sound? |  |
| 5. What is the relationship between frequency and pitch in sound? |  |

















