Short & Long Answer Questions: Surface Chemistry | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
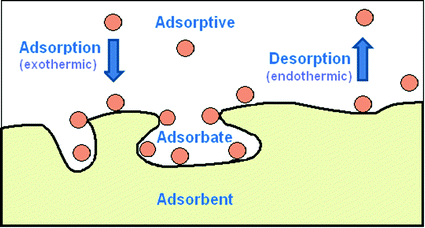
Q.1 What is desorption?
Answer: The process of removing an adsorbed substance from the surface on which it is adsorbed is called desorption.
Q.2 What is sorption?
Answer: Both adsorption and absorption are simultaneously called sorption.
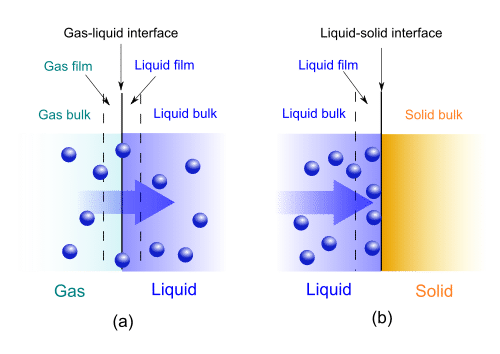 Gas-liquid absorption (a) and liquid-solid adsorption (b) mechanism. Blue spheres are solute molecules.Q.3 What are physical and chemical adsorption?
Gas-liquid absorption (a) and liquid-solid adsorption (b) mechanism. Blue spheres are solute molecules.Q.3 What are physical and chemical adsorption?
Answer: When the accumulation of gas on a solid surface occurs on account of weak van der Waals forces the adsorption is termed physical adsorption. When gas molecules or atoms are held to the solid surface by chemical bonds the adsorption is termed as chemisorptions.
Q.4 What is an adsorption isotherm?
Answer: The curve which describes the variation in the amount of gas adsorbed by the adsorbent with pressure at constant temperature is called adsorption isotherm.
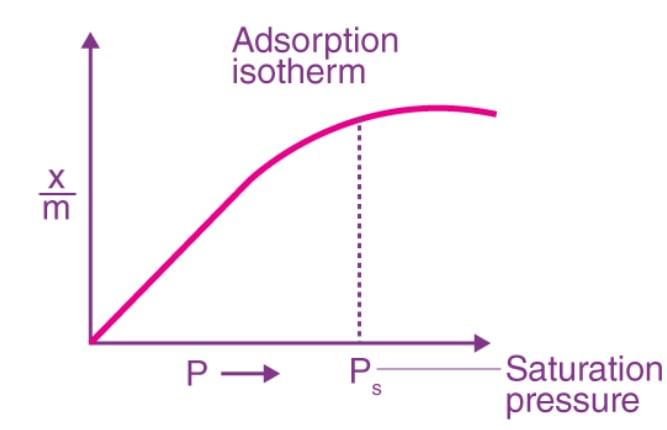
Q.5 Under what condition Freundlich adsorption isotherm fails?
Answer: At high pressure Freundlich adsoption isotherm fails.
Q.6 What is the use of adsorption in metallurgy?
Answer: In metallurgy, adsorption is used for the concentration of ore. It is concentrated by separating it from silica and other earthy matter by the method of froth floatation using pine oil and frothing agent.
Q.7 What is the principle of separation of inert gases from their mixture?
Answer: The separation of inert gases from a mixture is based on the difference in the degree of adsorption of gases by the coconut charcoal.
Q.8 Which catalysis involves adsorption?
Answer: Heterogeneous catalysis involves the adsorption of the substrate on the surface of the adsorbent.
Q.9 Why silica and alumina gels are used for removing moisture and controlling humidity?
Answer: Alumina and silica are good adsorbents. They can absorb even a small amount of moisture present in the atmosphere.
Q.10 Which substance is used in a gas mask?
Answer: Activated charcoal or a mixture of adsorbents is used as an adsorbent in a gas mask.
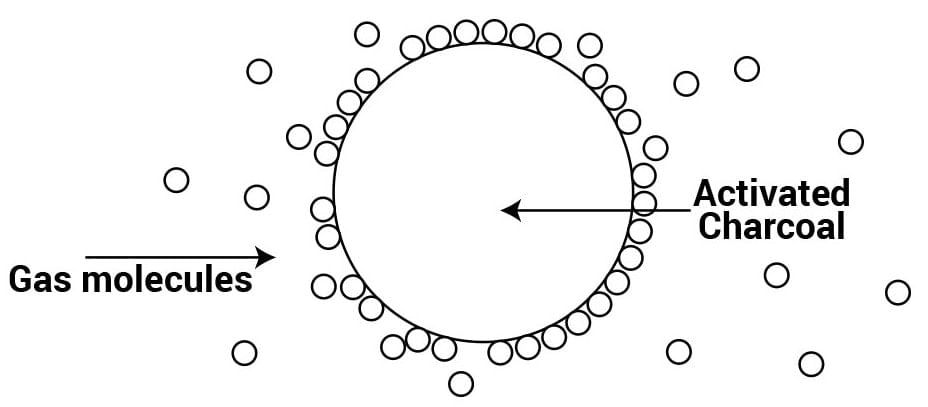
Q.11 How is a high vacuum produced?
Answer: Traces of air are adsorbed by charcoal from a vessel and a high vacuum is produced.
Q.12 How does the adsorption of a gas on a solid surface vary with temperature?
Answer: Adsorption of gas on the solid surface decreases with rising temperature.
Q.13 Give two uses of adsorption.
Answer: Two uses of adsorption
(i) Control of humidity (ii) Producing high vacuum.
Q.14 What is physisorption?
Answer: When the gas molecule or atoms are held together by weak van der Waals forces on the solid surface it is called physisorption.
Q.15 Adsorption is exothermic. Why?
Answer: During adsorption, there is always a decrease in residual force on the surface i. e., there is a decrease in surface energy which appears as heat.
Q.16 What is a catalyst?
Answer: The chemical substance which alters the rate of a chemical reaction but chemically and quantitatively remains unchanged is called a catalyst.
Q.17 Define promoters and poisons for example.
Answer: A substance that enhances the activity of a catalyst is called a promoter while a substance that decreases the activity of the catalyst is called poison. e-g- In Haber's process molybdenum acts as a promoter and carbon monoxide acts as a poison for the catalyst.
Q.18 What do you mean by the selectivity of catalyst?
Answer: The selectivity of a catalyst means its ability to direct a reactant to yield a particular product.
Q.19 Define the activity of the catalyst.
Answer: The ability of a catalyst to absorb the reactant molecule to give a product is called the activity of a catalyst.
Q.20 What are zeolites?
Answer: Zeolites are shape-selective catalysts. These are actually microporous aluminosilicates with a three-dimensional network structure.
Q.21 Give the name of a substance used as a shape-selective catalyst.
Answer: Zeolites are used as shape-selective catalysts.
Q.22 Which catalyst is used to convert alcohols into gasoline in the petroleum industry?
Answer: ZSM-5 is used as a catalyst to convert alcohols into the gasoline petroleum industry.
Q.23 What are enzymes?
Answer: Enzymes are complex nitrogenous organic compounds which are produced by living plants and animals and act as a catalyst.
Q.24 What is biochemical catalysis?
Answer: Enzymes are used to catalyse numerous reactions occurring in the bodies of animals and plants so, they are biochemical catalysts and the phenomenon is called biochemical catalysis.
Q.25 Which enzyme is used in the inversion of cane sugar?
Answer: Invertase enzyme is used in the inversion of cane sugar.
Q.26 Name the enzyme used in the conversion of glucose into ethyl alcohol.
Answer: Zymase acts as a catalyst in the conversion of glucose into ethyl alcohol.
Q.27 What is the role of pepsin and trypsin in the stomach?
Answer: Pepsin converts protein into peptides, try sin converts protein into amino acid by hydrolysis.
Q.28 Name the catalyst which converts milk into curd.
Answer: Lactobacilli convert milk into curd.
Q.29 Name the catalyst used in Ostwald's process for the manufacture of nitric acid.
Answer: Platinised asbestos is used as a catalyst in Ostwald's process for the manufacture of nitric acid.
Q.30 What is the optimum condition for the maximum efficiency of an enzyme catalyst?
Answer: Optimum condition for maximum efficiency of enzyme catalyst (i) Temperature 298-310 K
Q.31 What are co-enzymes? Give example.
Answer: Those substances which increase enzymatic activity are called co-enzymes, e.g. a small non-protein (vitamin) present along with an enzyme enhances its activity.
Q.32 What are enzyme inhibitors and poisons?
Answer: Enzyme inhibitors and poisons are substances that reduce or completely destroy the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
Q.33 What are colloids?
Answer: A colloid is a heterogeneous system in which one substance is dispersed (dispersed phase) as very fine particles in another substance called dispersion medium.
Q.34 What is the diameter of colloidal particles?
Answer: The diameter of colloidal particles vary between (1-1000) nm.
Q.35 What is Kraft temperature?
Answer: The specific temperature at which micelles formation takes place is called Kraft temperature.
Q.36 Explain critical micelle concentration.
Answer: A particular concentration at which micelle formation takes place is called CMC.
Q.37 Give one example of a peptising agent.
Answer: may be used as peptising agent.
Q.38 Name the method used for the purification of colloidal solution.
Answer: Method used for the purification of colloids are (i) Dialysis (ii) Electro-dialysis (iii) Ultrafiltration.
Q.39 The value of colligative properties of colloids are very small. Why?
Answer: Colloidal particles being larger aggregates, the number of particles in a colloidal solution is small as compared to the true solution. Hence, the value of the colligative property is small.
Q.40 Which property of colloid was used to set up a microscope?
Answer: Tyndall effect was used to set up a microscope.
Q.41 On which property colour of colloids depends?
Answer: The wavelength of light scattered by the dispersed particles, depends on the size of colloidal particles.
Q.42 On what factors Brownian movement of a colloid depends?
Answer: Brownian movement of colloids depends upon the size of the particles and the viscosity of the solution.
Q.43 How Brownian movement is responsible for the stability of colloids?
Answer: The Brownian movement has a stirring effect that does not permit the particles to settle and thus is responsible for the stability of sols.
Q.44 Define Zeta potential.
Answer: The potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opposite charge of the colloidal system is called Zeta potential.
Q.45 What is Helmholtz electrical double layer?
Answer: The combination of the two layers of opposite charges around the colloidal particles is called Helmholtz electrical double layer.
Q.46 Define coagulating value.
Answer: The minimum concentration of an electrolyte in millimoles prelature required to cause precipitation of a sol is called coagulating value.
Q.47 Why lyophilic sols are more stable than lyophobic sols?
Answer: Lyophilic sols are more stable than lyophobic sols because lyophilic colloids are extensively solvated i.e. colloidal particles are covered by a layer of the liquid in which they are dispersed.
Q.48 What are protective colloids? Which type of colloids are used as protective colloids?
Answer: The colloids which protect other colloids from the electrolytes are called protective colloids. A lyophilic colloid is used as a protective colloid of lyophobic colloid.
Q.49 What are emulsions?
Answer: The colloidal system in which dispersed phase and dispersion medium both are liquid is called emulsion.
Q.50 What are various type of emulsions?
Answer: Emulsions are of two types Oil dispersed in water (o/w type) Water dispersed in oil (w/o type)
|
361 videos|822 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Questions: Surface Chemistry - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is surface chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are some common examples of surface chemistry in everyday life? |  |
| 3. How does surface chemistry play a role in catalysis? |  |
| 4. What are some techniques used to study surface chemistry? |  |
| 5. How can surface chemistry impact environmental issues? |  |
















