Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Image Formation By Spherical Mirrors (Ray Diagrams)
Image Formation By Spherical Mirrors (Ray Diagrams) - Class 10 PDF Download
FAQs on Image Formation By Spherical Mirrors (Ray Diagrams) - Class 10
| 1. What is the concept of image formation by spherical mirrors? |  |
Ans. Image formation by spherical mirrors refers to the process of how a mirror creates a virtual or real image of an object placed in front of it. This phenomenon is based on the reflection of light rays from the mirror surface, which determines the position, size, and nature of the image formed.
| 2. How do concave mirrors form images? |  |
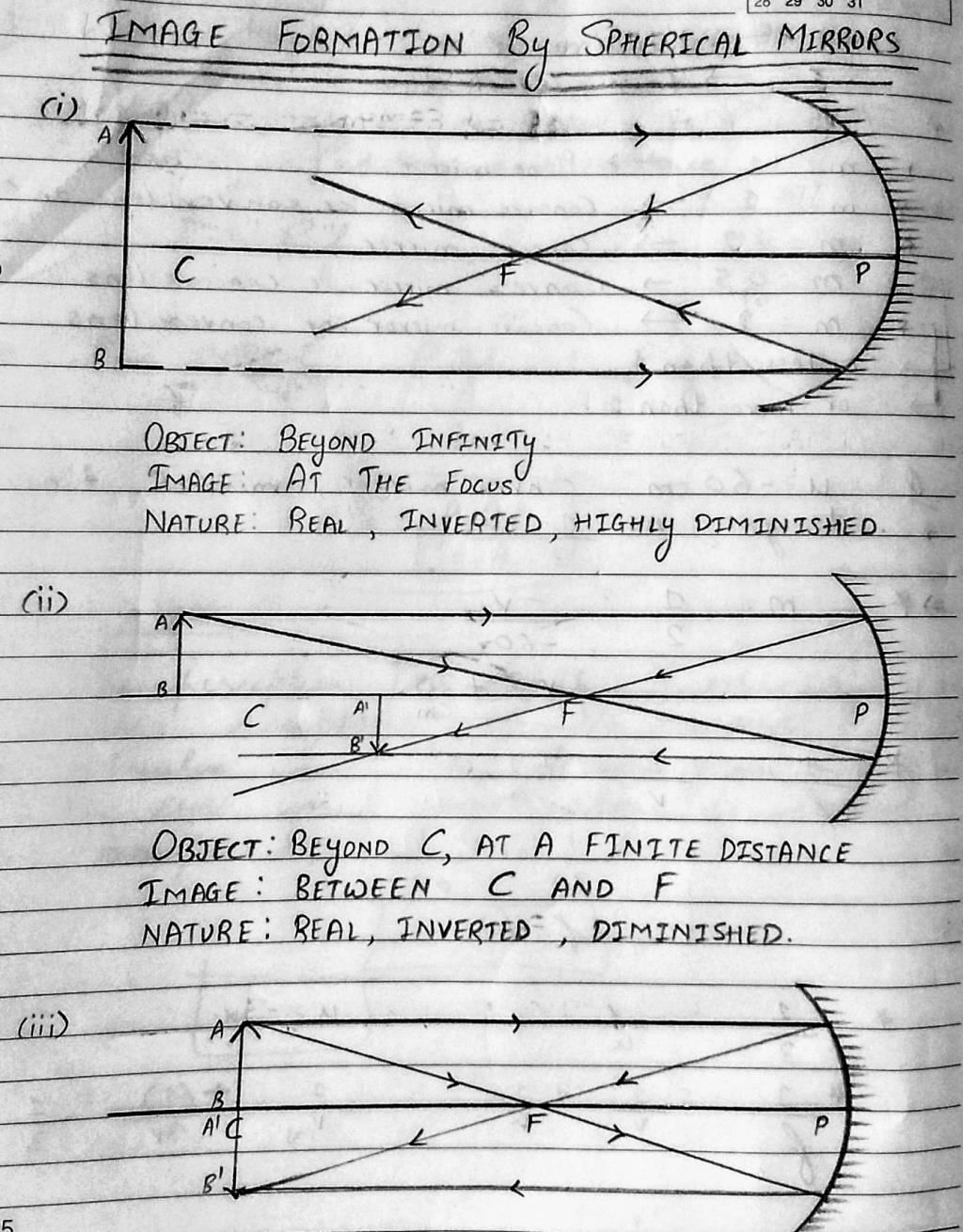
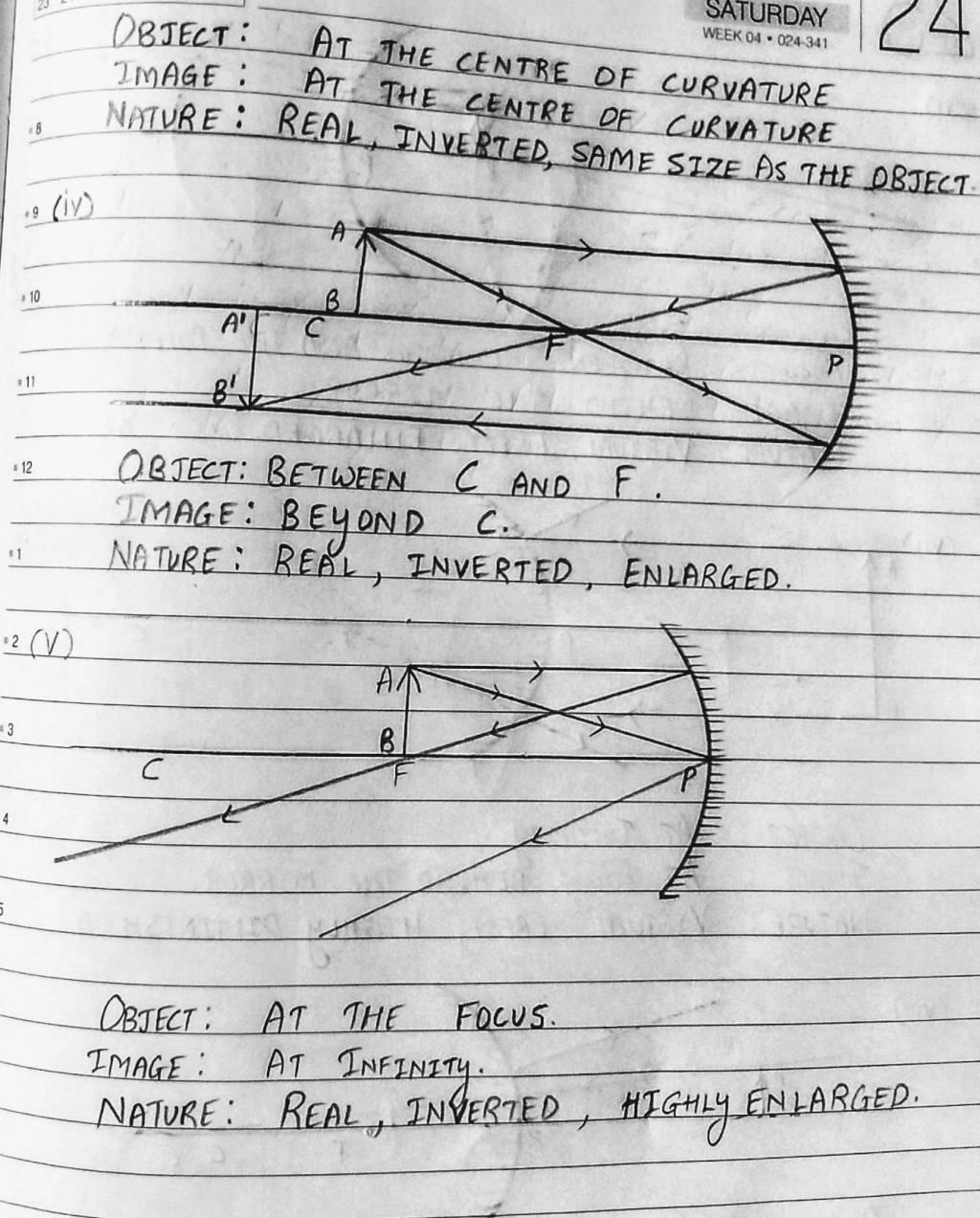
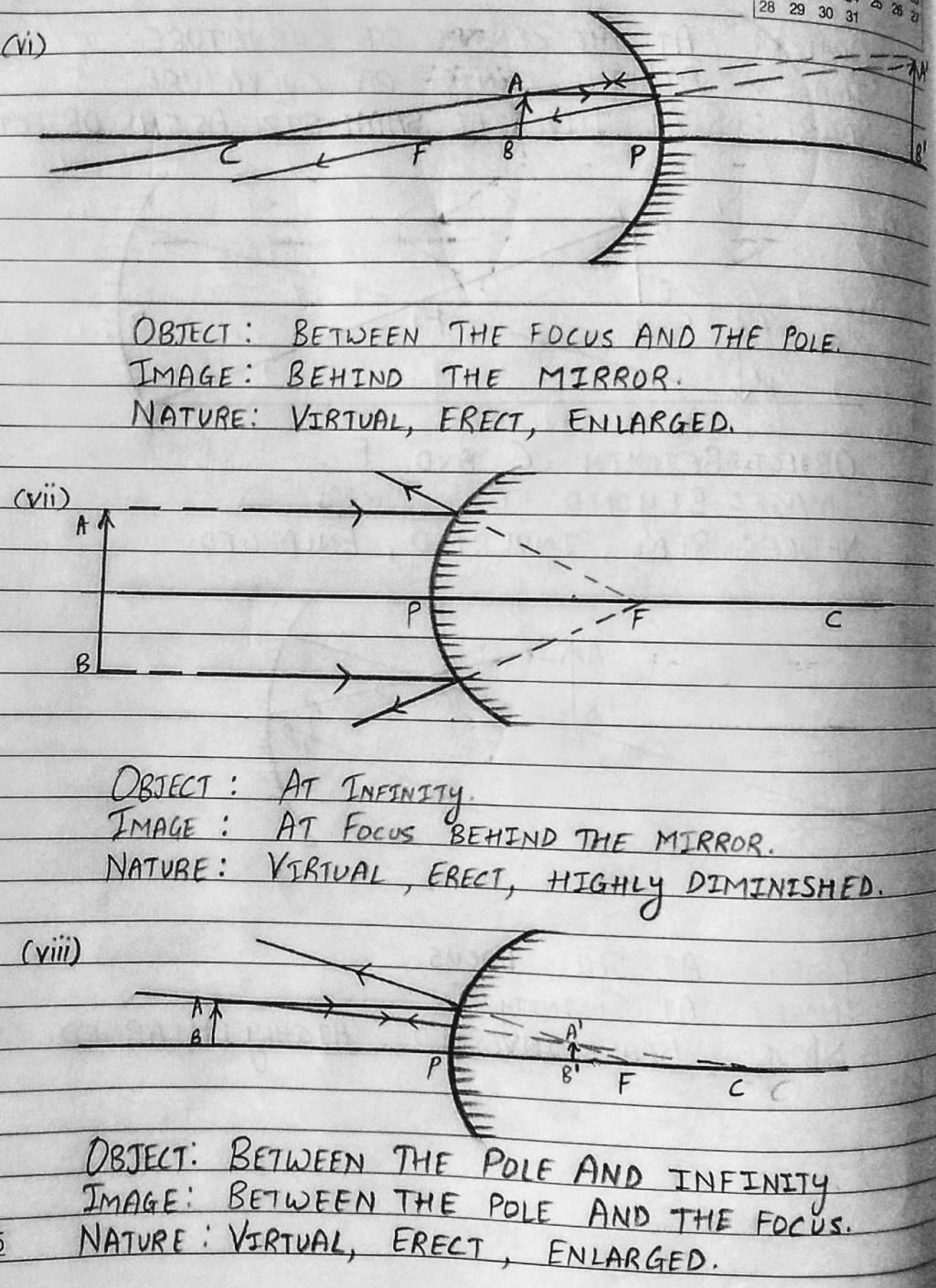
Ans. Concave mirrors are curved inward and have a reflective surface on the inner side. When an object is placed in front of a concave mirror, the light rays from the object reflect off the mirror surface. Depending on the position of the object, a concave mirror can form real or virtual images, which are either magnified or diminished, and can be upright or inverted.
| 3. What are ray diagrams in the context of image formation by spherical mirrors? |  |
Ans. Ray diagrams are graphical representations used to illustrate the formation of images by spherical mirrors. These diagrams show the path of light rays from an object to a mirror and then to the image. By using specific rules and techniques, such as the "principal axis," "incident ray," "reflected ray," and "focal point," ray diagrams help determine the position, size, and nature of the image formed by a mirror.
| 4. How can we determine the nature of the image formed by a spherical mirror? |  |
Ans. The nature of the image formed by a spherical mirror can be determined by considering the position of the object with respect to the mirror's focal point. If the object is placed beyond the focal point, a real image is formed, which is inverted, and can be either magnified or diminished. If the object is placed between the focal point and the mirror, a virtual image is formed, which is erect, magnified, and cannot be obtained on a screen.
| 5. Can convex mirrors form real images? |  |
Ans. No, convex mirrors cannot form real images. Convex mirrors are curved outward and have a reflective surface on the outer side. When light rays from an object are reflected off a convex mirror, they diverge instead of converging. As a result, a convex mirror can only form virtual images, which are always diminished, erect, and cannot be obtained on a screen.
Related Searches