Class 9 History Chapter 1 Question Answers - The French Revolution
Q.1. What is the name of the national anthem of France?
Ans. It is named La Marseillaise'. It was composed by the poet Roget de L'lsle. It was sung for the first time by volunteers from Marseilles as they marched into Paris and so got its name.
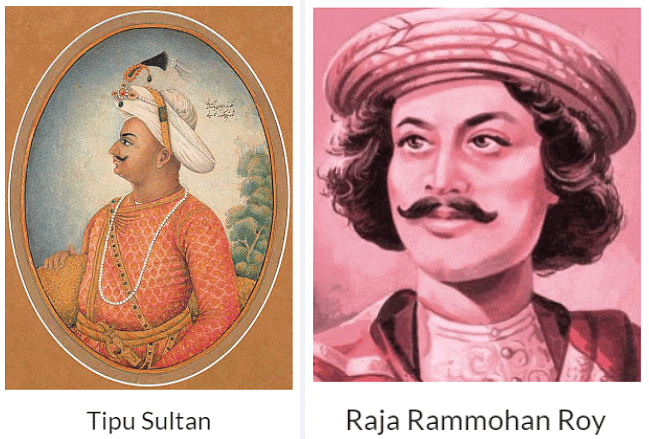
 La Marseillaise'Q.2. Which Indian individuals responded to the ideas coming from revolutionary France?
La Marseillaise'Q.2. Which Indian individuals responded to the ideas coming from revolutionary France?
Ans. Tipu Sultan and Raja Rammohan Roy are two examples of Indian individuals who responded to the ideas coming from revolutionary France.
Q.3. A large number of Jacobins came to be known as 'Sans-culottes'. What did this term mean?
Ans. A large group among the Jacobins decided to start wearing long striped trousers similar to those worn by dock workers. This was to set themselves apart from the fashionable sections of society, especially nobles, who wore knee breeches. These Jacobins came to be known as the ''sans-culottes', literally meaning 'those without knee breeches'.
 The Jacobin era of clothing.Q.4. Which rights were the 'natural and inalienable' rights according to the French Constitution?
The Jacobin era of clothing.Q.4. Which rights were the 'natural and inalienable' rights according to the French Constitution?
Ans. The Constitution began with a declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen. These rights were the right to life, freedom of speech, freedom of opinion, equality before the law, etc.
Q.5. Identify the symbols that stand for liberty, equality, and fraternity.
Ans. Liberty:- The broken chain and the Phrygian cap.
Equality:- The winged woman and the Law tablet.
Fraternity:- The bundle of rods or fasces and Blue - white - red.
 Symbolism of the French Revolution
Symbolism of the French Revolution
Q.6. How were some basic rights set forth in Olympe de Gouges different from the Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen?
Ans. The manifesto drafted by Olympe de Gouges mentions women and equality throughout its text, mentioning women first in all places. The Declaration of the Rights of Man and citizen does not mention women at all, it only talks about men. Manifesto drafted by Olympe de Gouges
Manifesto drafted by Olympe de Gouges
Q.7. What was the immediate cause of the French Revolution?
Ans. Due to bad harvest, the prices of bread rose and often, bakers hoarded the bread. The angry women who could not get bread after long hours in the queues stormed into the shops. The king ordered troops and on 14th July the agitated crowd stormed and destroyed the Bastille.
Q.8. Who was Mirabeau?
Ans. Mirabeau was born into a noble family and was a representative of a third estate who delivered speeches to the crowds assembled at Versailles. He was born into a noble family but was convinced of the need to do away with a society of feudal privilege.
 H.G. Mirabeau
H.G. Mirabeau
Q.9. Which proposal of the third estate was rejected by the Estates General?
Ans. The third estate demanded that voting should be conducted by the assembly as a whole, in which each member would have one vote. But the king rejected this proposal, and therefore, members of the third estate walked out of the assembly in protest.
Q.10. How was the meeting of Estates General called by Louis XVI attended by three Estates?
Ans. The first and the second estates sent 300 representatives each, who were seated in rows facing each other on two sides, while the 600 members of the third estate had to stand at the back.
Q.11. Who was Rousseau?
Ans. Rousseau was a French philosopher who carried the idea of Locke forward, proposing a form of government based on a social contract between people and their representatives.

Q.12. What were the views of John Locke in inspiring the people for the French Revolution?
Ans. Locke sought to refute the doctrine of the divine and absolute right of the monarch in his book "Two Treatises Of Government".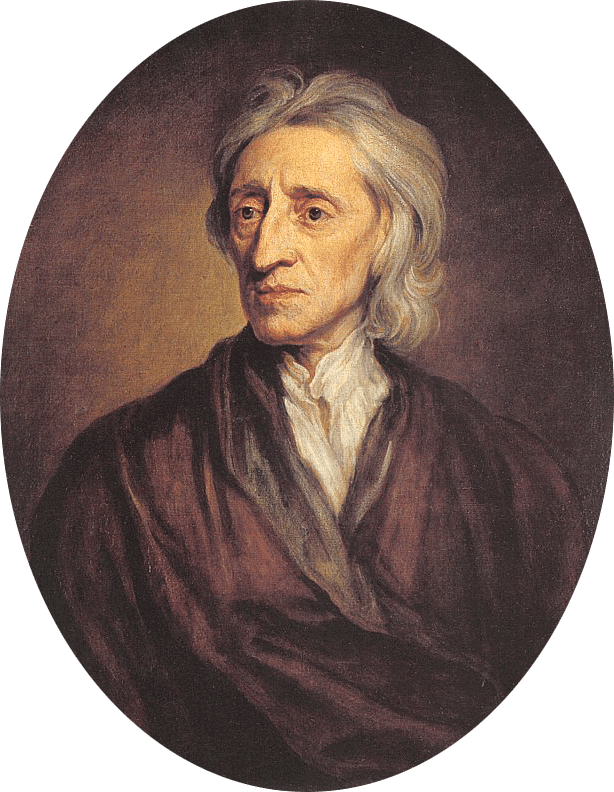 Locke
Locke
Q.13. Which social groups emerged as 'middle class' in 18th century France?
Ans. The social groups who earned their wealth through expanding overseas trade and from the manufacture of goods such as woollen and silk textiles that were either exported or bought by the richer members of society emerged as the middle class.
Q.14. Who formed the First and Second Estates of French Society?
Ans. The clergy and the nobility were the members of the first and second estates, respectively. They enjoyed certain privileges by birth and were also exempted from paying taxes to the state from the first and second estates, respectively.
Q.15. Why did the French government increase the taxes?
Ans. To meet its regular expenses, such as the cost of maintaining an army, the court, and running government offices or universities, the state was forced to increase taxes.
Q.16. How did the American War of Independence add more debt to France?
Ans. The French army supported thirteen colonies of America in their war of independence against Great Britain. It added more than one billion livres (units of currency in France) that had risen to more than two billion livres with interest.
Q.17. Why was the treasury empty when Louis XVI ascended the throne?
Ans. Long years of war had drained the financial resources of France, and along with it was the cost of maintaining an extravagant court at the immense Palace of Versailles.
Q.18. What do you know about the 'Estates General'?
Ans. The Estates General was a political body to which the three estates sent their representatives. In France of the Old Regime, the monarch did not have the power to impose taxes, rather he had to call a meeting of the Estates General to pass the proposals for new taxes. However, it was the monarch alone who could decide when to call a meeting of this body.
 Estates GeneralQ.19. Elucidate the contribution of Mirabeau in the formation of the National Assembly.
Estates GeneralQ.19. Elucidate the contribution of Mirabeau in the formation of the National Assembly.
Or
What was the contribution of Mirabeau to the formation of the National Assembly?
Ans. Mirabeau was born into a noble family but was convinced to do away with feudal privileges. On 20 June, the third estate assembled in the hall of an indoor tennis court in the grounds of Versailles. Mirabeau brought out a journal and delivered powerful speeches to the crowds assembled at Versailles.
Q.20. When did France become a Republic?
Ans. The newly elected assembly was called the Convention. On 21st Sep. 1792, it abolished the monarchy and declared France a republic. A republic is a form of government where the people elect the government, including the head of the government. There is no hereditary monarch.
Q.21. Based on the French Constitution of 1791, who were known as 'active citizens'?
Or
Who all got the right to vote for the National Assembly?
Ans. Based on the French Constitution of 1791, Only men of 25 years of age paid taxes equal to at least three days of a labourer’s wage. They were called ‘active citizens’ and were entitled to vote.
Q.22. When was the National Assembly recognized?
Ans. Louis XVI finally accepted the National Assembly in July 1789 and on 4th Aug 1789, the assembly passed a decree abolishing the feudal system of obligations and taxes.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 History Chapter 1 Question Answers - The French Revolution
| 1. What were the main causes of the French Revolution? |  |
| 2. What was the significance of the Storming of the Bastille? |  |
| 3. How did the French Revolution impact the monarchy? |  |
| 4. What were the main outcomes of the French Revolution? |  |
| 5. How did the Enlightenment influence the French Revolution? |  |






















