General Properties of Embryonic Development- 2 | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Gastrulation in discoblastula:
In discoblastula, gastrulation takes place by two methods:
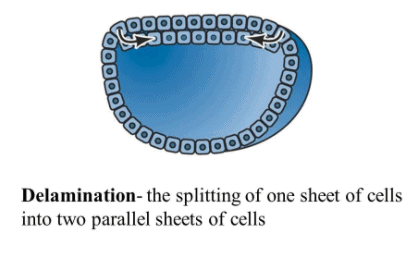
(i) Delamination : In delamination all the blastomere of blastoderm undergoes division. As a result new blastomere form and new blastomere fall on the floor of subgerminal cavity. So embryo become double layered. Upper layer of blastomere is called epiblast and lower-layer of blastomere is called hypoblast. Hypoblast differentiates in endoderm.
(ii) Polyinvaginations : All the blastomere of epiblast undergo division to form new blastomere and new blastomere fall in sub-germinal cavity form different direction and fill the sub-germinal cavity. Blastomere which fill the sub-germinal cavity are collectively called chorda-mesoderm. (chorda mesoderm forms mesoderm) Blastomeres which are left outside i.e. blastomere of epiblast form ectoderm. In such blastulas no new cavity is formed during gastrula stage i.e. archenteron formation does not occur during gastrula stage.
SPECIAL POINTS
1. The growth phase is the longest phase during male gametogenesis. But in human oogenesis, maturation phase is longest.
2. The acrosome of sperm are produced by golgibodies.
3. The smallest sperm is of crocodile and its size is 0.02 mm & largest sperm is of Discoglossus (2mm)
4. 74 days are required to complete the cycle of spermatogenesis in human being.
5. In 1 ml of semen, 20 to 120 millions of sperms are present in human being.
6. Deficiency in the number of sperms result in sterility which is known as oligospermia.
7. Absence of sperms in semen is known as azoospermia.
8. Formation of yolk in oogenesis takes place in the growth phase.
9. Largest egg is of Ostrich ( 16 cm long with its shell).
10. Although normal number of sperm are present in semen but if these are completely non motile. This condition is known as necrospermia.
11. Smallest egg in birds is of humming bird.
12. Due to high mortality rate in lower animals, the production of egg is more.
13. Sequence of egg production is as follows.
Mammals < Aves < Reptiles < Amphibian < Pisces.
14 Cat and rabbit both are induced ovulator.
15. The life span of eggs in female reproductive organs in human being is 48 hrs.
16. The nucleus of egg is known as germinal vesicle.
17. At the age of 45-50 yrs. in female the ovulation process will stop which is known as menopause.
18. The spermiation (release of sperms from sertoli cells) in all sertoli cells occurs simultaneously.
19. Cortical granules are absent in rat.
20. Mosaic type of cleavage is found in the parasite Echinococcus granulosus.
Special features of some animals :
(a) Sperms of some animals are not having flagella : eg.
(1) Ascaris - sperm is amoeboid
(2) Cray fish - star shaped, tail less sperm
(3) In crab and lobster the sperm are tail less and have three sharp processes.
(b) Biflagellated sperm :
eg. In toad fish (Opsansus) head of many sperms unite together and form sperm boats.
In Gastropods, the sperms are hexaflagellated.
Smallest sperm - Crocodile (0.02 mm)
Largest sperm - Discoglossus (2 mm) in chordates and Drosophila in entire animal kingdom.
Shape of head part of sperms :
(i) Spherical - eg Teleostei
(ii) Lance shaped - eg Amphibia and Reptiles
(iii) Spiral end - eg. Birds
(iv) Spoon shaped - eg. Mammals (in man)
(v) Hook like - eg. Rat.
Germinal layers and their derivatives
The following description gives an account of the respective organs formed by the three germ layers. Most of the organs are the product of combination of more than one germ layers.
Organs derived from ectoderm
1. Skin(epidermis) and their pigment cells.
2. Mucosal membrane of lips, cheek, gums, basal portion of mouth, some part of palate, nasal apertures.
3. Lower part of anal canal.Fig: View of Anal canal
4. Glans penis.
5. Labia majora and outer part of labia minora.
6. Anterior epithelium of cornea, epithelium of conjunctiva, ciliary body and iris of eyes.
7. Outer face of tympanic membrane, epithelium of labyrinth.
8. Glands:
(i) Exocrine-
(A) Sweat glands
(B) sebaceous glands
(C) parotid glands
(D) mammary glands
(E) lacrimal glands;
(ii) Endocrine-
(A) Hypophysis cerebri
(B) adrenal medulla
9. Hairs, nails, enamel of teeth
10. Lens of eyes.
11. Nervous system.
Derivatives of mesoderm
1. Connective tissues, superficial and deep fascia, ligaments, tendons, dermis of skin. (from dermatome)
2. Specialized connective tissues like adipose tissue, reticular tissues, bones, cartilages.
3. Teeth.
4. All muscles.
5. Heart, all blood vessels and blood cells.
6. Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, posterior urethra of female, upper glandular part of prostate.
7. Ovaries, uterine tubes.
8. Testes, epididymis, vas deferens and seminal vesicle, ejaculatory duct.
9. Pleural cavities, peritoneal cavity and pericardial cavity.
10. Joints.
11. Cornea, sclera, choroid ciliary body and iris related material.
12. Microglia, duramater etc.
Derivatives of endoderm
1. Epithelial part of mouth, some part of palate, tongue, tonsils, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestine, upper part of anal canal.
2. Pharyngo-tympanic tube, middle ear, inner face of tympanic membrane.
3. Respiratory tract.
4. Gall bladder, pancreatic duct.
5. Major portion of urinary bladder, complete urethra of female except posterior part, complete urethra of male except anterior and posterior part.
6. Whole inner part of vagina including inner face of labia minora.
7. Glands:
(i) Exocrine-
(A) Liver
(B) Pancreas
(ii) Endocrine-
(A) Thyroid
(B) parathyroid
(C) thymus
(D) islets of Langerhans In addition to the above, the glands of gastrointestinal tract, major part of prostate etc. are also formed by endoderm.
|
26 videos|312 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on General Properties of Embryonic Development- 2 - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are the general properties of embryonic development? |  |
| 2. How does cell division contribute to embryonic development? |  |
| 3. What is cell differentiation and why is it important in embryonic development? |  |
| 4. How does morphogenesis contribute to embryonic development? |  |
| 5. What is pattern formation and why is it significant in embryonic development? |  |
















