Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Force and Pressure
Q1: Explain contact and non-contact forces. Give two examples for each.
Ans:
Contact forces: Forces that act only when there is physical contact between two interacting objects is known as Contact forces.
Example:
- Muscular force: This is the force we can exert with our bodies by using our muscles, e.g., pull etc.
- Frictional force: The force acting against the relative motion of surfaces in contact is called frictional force or friction.
 Friction Force and Tension Force
Friction Force and Tension Force
Non-contact forces: Forces that can act without physical contact between objects, i.e. those that can act from a distance, are called non-contact forces or field forces.
Example:
- Magnetic force: Magnets exert forces of attraction or repulsion on other magnets
- Electrostatic force: The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or uncharged body is known as electrostatic force.
 Gravitational Force and Electrostatic Force
Gravitational Force and Electrostatic Force
Q2: (a) How can friction be reduced?
(b) How can it be increased? Give examples.
Ans: Reducing Friction
- By using wheels and ball bearings. The use of wheels between surfaces moving over each other reduces friction. Ball bearings have small balls of steel between steel surfaces. Because of the balls, the steel surfaces can easily move over each other.
- By polishing the rubbing surfaces, they are smooth.
- Use a suitable lubricant, like oil (for light machinery) or grease (for heavy machinery). This helps because fluid friction is less than solid friction.
- Friction due to air (air resistance) or water is reduced by using streamlined shapes in airplanes or ships. A streamlined shape is narrow in front and broader at the back. Birds and aquatic animals have streamlined shapes that hold them in flying or swimming.
Increasing Friction
- Sand and gravel are strewn on slippery ground during the rainy season to increase friction. It is then easier to walk on the ground.
- By making the moving surfaces rough, e.g. tyres have designs and patterns with grooves on the surface to increase resistance with the road. This prevents the slipping of the tyres on a wet road.
- To increase friction, spikes are provided in the soles of shoes used by players and athletes.
Q3: Do liquids and gases exert pressure on the walls of the container in all directions? Give an example to justify your statement.
Ans: Liquid and gases exert pressure on the walls of the container. For example, If we take a plastic bottle and drill four holes near the bottom of the bottle at the same height. After filling the water in that bottle, we observe that water comes out of the holes and falls at the same distance. This shows that liquid exerts pressure on the walls of the container in all directions.
Similarly, we cannot inflate a balloon with holes because the air inside the balloon exerts pressure in all directions. Hence, we can say that gases exert pressure on the walls of the container in all directions.
Q4: Why is it easy to push a nail into a wooden plank by the pointed end?
Ans: It is easy to push a nail into a wooden plank by a pointed end because the smaller the area, the larger the surface pressure for the same force. The area of the pointed end of the nail is much smaller than that of its head. The same force, therefore, produces a pressure sufficient to push the pointed end of the nail into the wooden plank.
Q5: Read the Table and try to identify the action as push or pull.
Ans: Table Identifying Actions as Push or Pull
S. No. | Description of the situation | Action: (Pushing/ pulling/ picking/ hitting/ lifting/lowering/ flying/ kicking/ throwing | Action can be grouped as a | ||||
|
|
| shutting/flicking) |
| push | pull | |
1. | Moving a book placed on a table | Pushing | Pulling | Lifting | — | Yes | Yes |
2. | Opening or shutting a door | Pulling | Pushing | Lifting | Lowering | Yes | Yes |
3. | Drawing a bucket of water from a well | Pulling | Lifting | Lowering | — | — | Yes |
4. | A football player taking a penalty kick | Kicking | Flying | — | — | Yes | — |
5. | A cricket ball hit by a batsman | Hitting | Flying | — | — | Yes | — |
6. | Moving a loaded cart | Pulling | — | — | — | — | Yes |
7. | Opening a drawer | Pulling | — | — | — | — | Yes |
Q6: Read the Table and complete it.
Ans: Table Studying the Effect of Force on Objects
Description of situation | How to apply force | Action of force | |||
Change in state of motion | Change in shape | ||||
Yes | No | Yes | No | ||
A lump of dough on a plate | Pressing it down with your hands | — | No | Yes | — |
Spring fixed to the seat of bicycle | By sitting on the seat | - | No | Yes | - |
A rubber band suspended from a hook/nail fixed on a wall | By hanging a weight or by pulling its free end | Yes | - | Yes | - |
A plastic or metal scale placed between two bricks | By putting a weight at the centre of the scale | - | No | Yes | - |
Q7: What are the various effects of force on different objects?
Ans: The various effects of force are:
- A force can make an object move from rest.
- It can change the speed of a moving object.
- It can bring about a change in the shape of an object.
- It can change the direction of motion of an object.
- It can cause some or all of these effects.
Q8: What are contact forces? State different types of contact forces.
Ans: The forces that come into play only when two objects come in contact with each other are called contact forces.
Some contact forces are:
- Muscular force: The forces resulting from the action of muscles are known as muscular forces. Muscular force is a contact force because it comes into play when two objects, come in contact.
- Force of friction: When a body moves, a force equal and opposite to the direction of motion is exerted on that moving body. This force is called the force of friction. It is also a contact force because it is exerted when two surfaces come in contact.
Q9: What are non-contact forces? Explain different types of non-contact forces.
Ans. The forces that can be exerted from a distance without establishing contact are called non-contact forces. Some non-contact forces are:
- Magnetic force: The force exerted by a magnet on another magnet or some other magnetic substance like iron is called magnetic force. Like poles of a magnet repel each other, unlike poles of a magnet attract each other without contact. So, it is called non-contact force.
- Electrostatic force: The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or uncharged body is called electrostatic force. The electrostatic force also acts without directly contacting other charged or uncharged bodies. So, it is also a non-contact force.
- Force of gravity: Earth pulls everything or body towards it. The force of attraction exerted by the earth on any object is called the force of gravity. This is also a non-contact force as it acts from a distance.
Q10: What is force? Name different types of forces.
Ans. A push or pull on an object is called force. There are the following types of forces:
- Muscular force
- Force of friction
- Magnetic force
- Force of gravity
- Electrostatic force
Q11: Prove that the force of friction depends on the nature of the two surfaces in contact.
Ans. Collect the following things: A thick book, nylon cloth, gunny cloth, plastic sheet, jute cloth, and sandpaper. Place the book on each of the materials and slide it on the floor one by one. If your book slides off the plastic sheet or nylon cloth, use adhesive tape to stick it firmly on the surface of the book.
You will observe that the different materials offer different amounts of resistance to sliding.
This activity shows that the force of friction depends on the nature of the surface in contact. In general, a smooth surface offers less friction than a rough surface.
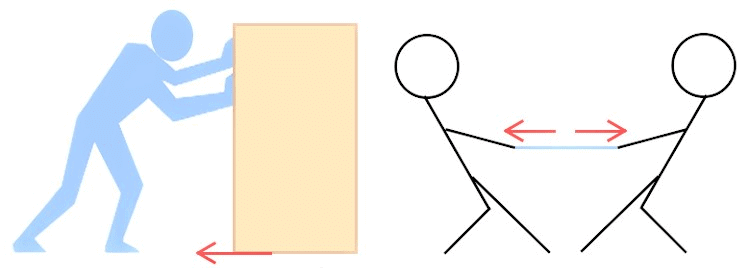
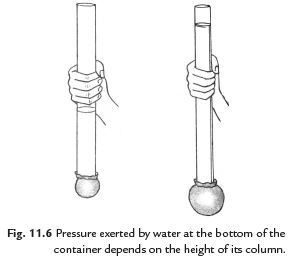
Q12: Prove that the pressure exerted by water at the bottom of the container depends on the height of its column.
Ans. Take a transparent glass tube or plastic pipe. Also, take a piece of a thin sheet of good quality rubber. Stretch the rubber sheet tightly over one end of the pipe. Hold the pipe in the middle, keeping it in a vertical position. Pour some water into the pipe. Note the height of the water column in the pipe. Pour some more water. Observe, the bulge in the rubber sheet and the height of the water column in the pipe.
Repeat this process a few more times. You observe that as the height of the water column increases, the bulge in the rubber sheet also increases.
Q13: Show that a liquid exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Ans. Take a plastic bottle. Fix a cylindrical glass tube a few cm long near its bottom. You can do so by slightly heating one end of the glass tube and then quickly inserting it near the bottom of the bottle. Make sure that water does not leak from the joint. If there is any leakage, seal it with molten wax. Cover the mouth of the glass tube with a thin rubber sheet. Now, fill the bottle up to half with water. We observe the bulge in the rubber sheet. Pour some more water into the bottle. We see more bulges in the rubber sheet. This activity indicates that water exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
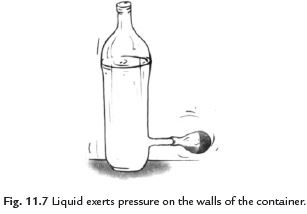
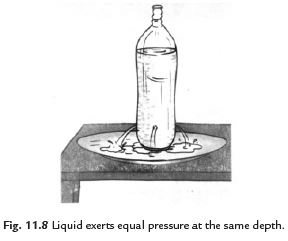
Q14: Explain that liquids exert equal pressure at the same depth.
Ans. Take an empty plastic bottle. Drill four holes all around near the bottom of the bottle. Make sure that all the holes are at the same height from the bottom. Now, fill the bottle with water. We observe that different streams of water coming out of the holes fall at the same distance from the bottle. This observation indicates that liquids exert equal pressure at the same depth.
Q 15: What experiment was performed to prove that air has pressure?
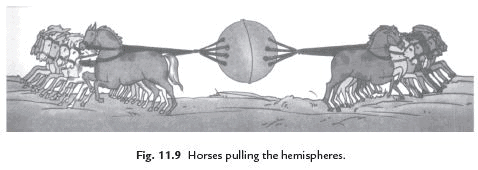
Ans. Otto von Guericke, a German Scientist, invented a pump in the 17th century to extract air out of a vessel. He demonstrated the force of the air pressure. He joined two hollow metallic hemispheres of 51 cm diameter each and pumped air out of them. Then, he employed eight horses on each hemisphere to pull them apart. So great is the force of air pressure that the hemispheres could not be pulled apart.
|
92 videos|296 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Question Answers - Force and Pressure
| 1. What is the difference between force and pressure? |  |
| 2. How is force measured? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of forces? |  |
| 4. How does pressure affect objects? |  |
| 5. How can pressure be increased or decreased? |  |

















