Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2012 Delhi Set-I) - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Ques 1: Which continent has the highest growth rate of population?
Ans: Africa.
Ques 2: Define the term 'sex ratio'.
Ans: The ratio between the number of women and men in the population is called the sex ratio. In India sex ratio is calculated by using this formula: Female population/Male population×100
Ques 3: Give any two examples of tertiary activities.
Ans: (i) Trade & Commerce,(ii) Communication Services.
Ques 4: Who is an empowered worker?
Ans: Employee empowerment has been denned in many ways but generally means the process of allowing employees to have input and control over their work, and the ability to openly share suggestions arid ideas about their work and the organization as a whole. Empowered employees are committed, loyal and conscientious.
Ques 5: Define the term 'density of population'.
Ans: Density of population is the measurement of population per unit area or can say it is the ratio between the number of peoples to the size of the land.
Ques 6: Which is the most significant aspect of human development?
Ans: Education and health.
Ques 7: Give the meaning of Human settlement.
Ans: A human settlement is defined as a place inhabited more or less permanently. It includes buildings in which they live or use and the paths and streets over which they travel. It also includes the temporary camps of the hunters and herders. It may consist of only a few dwelling units called hamlets or big cluster of buildings called urban cities.
Ques 8: What are National Highways?
Ans: The National Highways are a network of highways that is managed and maintained by agencies of the Government of India.
Ques 9: Name the head quarter of 'South Central Railway Zone'.
Ans: Secunderabad.
Ques 10: Name any two natural sources of water pollutants.
Ans: (i) Erosion, (ii) Land-slides.
Ques 11: Explain how technology indicates the level of cultural development of society.
Ans: Technology plays an important role in education, health and other social phenomena that directly related, to social development. Technological innovation and Communication Technologies represent a way for developing world nations to foster economic development, improve levels of education and training, as well as address gender issues within society. Less development in technology leads a less developed society.
Ques 12: Explain the key areas of human development.
Ans: The key areas of human development are:
(i) Equity: Equity is the idea of fairness for every person, between men and women; we each have the right to an education and health care.
(ii) Sustainability: Sustainability is the view that we all have the right to earn a living that to sustain our lives and have access to a more even distribution of goods.
(iii) Productivity: Productivity states the full participation of people in the process of income generation.
(iv) Empowerment: Empowerment is the freedom of the people to influence development and decisions that affect their lives.
Ques 13: Explain any three characteristics of 'Foot Loose Industries'.
Ans: (i) It can be placed and located at any location without effect from factors such as resources or transport.
(ii) These industries often have spatially fixed costs.
(iii) They do not have to locate close to raw materials unlike the iron and steel industry.
Ques 14: Explain any three 'push factors' which compel the people to migrate from one area to another area in India.
Ans: Push factors causes people to leave their place of residence or origin. People migrate from rural to urban areas mainly due to poverty, high population pressure on the land, lack of basic infrastructural facilities like health care, education, etc. Apart of these factors natural disasters such as flood, drought, cyclonic storms, earthquakes, tsunami, wars, and local conflicts also given extra puch to migrate.
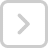
Ques 15: Study the map of India given below carefully and answer the questions that follow: (i) Define the term metropolitan city.
(ii)Which state of India has the largest number of metropolitan cities?
(iii) Name any two northern states of India which have no metropolitan city.
Ans: (i) Metropolitan city is a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories, sharing industry, infrastructure and housing.
(ii) Uttar Pradesh,
(iii) Jammu & Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh.
Ques 16: 'Land use in a region, to a large extent, is influenced by the nature of economic activities carried out in that region' Support the statement giving three examples from India.
Ans: (i) The several types of land resources in India include agricultural land, farmland, barren land, real estate land, commercial land and residential land. Majority of the population of India are engaged in agricultural and allied activities and thus agricultural land accounts for near about 54.7 per cent of the total land area of the country.
(ii) Land has a direct bearing on the productivity of agriculture, unlike other activities.
(iii) In rural areas, aside from its value as a productive factor, land ownership has a social value and serves as a security for credit.
Ques 17: Explain watershed management. What is its aim?
Ans: Watershed management is the study of the relevant characteristics of a watershed aimed at the sustainable distribution of its resources and the process of creating and implementing plans, programs, and projects to sustain and enhance watershed functions that affect the plant, animal, and human communities within a watershed boundary. Features of a watershed that agencies seek to manage include water supply, water quality, drainage, storm water runoff, water rights, and the overall planning and utilization of watersheds. Landowners, land use agencies storm water management experts, environmental specialists, water use surveyors and communities all play an integral part in the management of a watershed.
Ques 18: Describe the uneven distribution of mineral and energy resources in India by giving suitable examples.
Ans: In India the distribution of minerals has not been even. These are mainly confined in the peninsular region of the country leaving aside the Northern Great Plains and the Himalayan region almost devoid of mineals, Jharkhand, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Karnataka, West Bengal, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu states have large potentials of mineral resources in the country.
Most of the deposits of iron ore found in the Achaean rocks of Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu; of manganese in Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Maharashtra; of mica in Jharkhand, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan and Karnataka; of bauxite in Jharkhand, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat; of cyanide in Jharkhand, Bihar and Sillimanite in Meghalaya. The states of Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir and West Bengal are deficient in mineral resources.
Ques 19: Study the diagram showing the location of a major steel plant given below and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify this steel plant and write its name.
(ii) Name the source of lime stone for this plant.
(iii) What is the source of coal for this plant?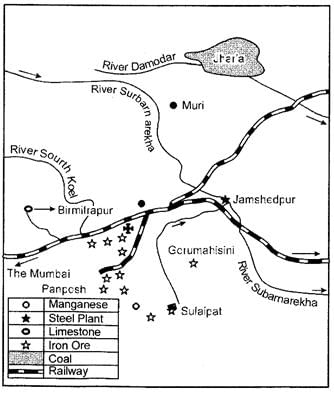 Ans: (i) Tata Iron and Steel Plant (TISCO)
Ans: (i) Tata Iron and Steel Plant (TISCO)
(ii) Birmitrapur
(iii) Jharia.
Ques 20: Explain any three problems caused by urban waste disposal in India.
Ans: (i) Localized environmental health problems such as inadequate household water and sanitation and indoor air pollution.
(ii) City - regional environmental problems such as ambient air pollution, inadequate waste management and pollution of rivers, lakes and coastal areas.
(iii) Extra - urban impacts of urban activities such as ecological disruption and resource depletion in a city?s hinterland, and emissions of acid precursors and greenhouse gases.
(iv) Regional or global environmental burdens that arise from activities outside a city?s boundaries, but which will affect people living in the city.
Ques 21: Describe any five characteristics of the economic activities of hunting and gathering practiced in the world.
Ans: The characteristics of economic activities of hunting and gathering practiced in the world are:
(i) Gathering and hunting are the oldest economic activities of known. These are carried out at different levels with different orientations.
(ii) Gathering is carried out in the regions having harsh climatic conditions. It involves primitive societies who extract both plant and animals to satisfy their needs for fool, shelter and clothing.
(iii) This type of activity requires less capital investment and operates at very low level of technology.
(iv) The yield of activity requires less capital investment and operates at very low level of technology.
(v) The yield per person is very low and little or no surplus is produced.
(vi) Gathers and hunters collected valuable products such as leaves, bark of trees, medicinal plants and after simple processing they sell the products in the markets.
Ques 22: State any three characteristics of water transport. Why is traffic far less on the Cape of good Hope Route?? Give two reasons.
Ans: (i) Water transport has dominated in transport services for centuries on long sea trips until the emergence of air transport. Nowadays, ships have been designed to be much faster to be more competitive.
(ii) The routes are mostly natural so it is less costly than other mode of transportation.
(iii) It requires less maintenance. The main cause for less traffic in Cape of Good Hope route is the limited development of South America and Africa.
Ques 23: Explain any five bases of international trade.
Ans: The basis of International Trade are:
(i) Difference in national resources: The resources are unevenly distributed due to the differences in their physical make up i.e. geology, relief soil, and the climate.
(ii) Population factors: Under these factors, the size, distribution and diversity of people between countries affect the type and volume of goods.
(iii) Stage of economic development: The nature of items traded undergoes changes due to the stage of economic development of country. As in agriculturally important countries, agro products are exchanged for manufactured goods.
(iv) Extent of foreign investment: Foreign investment helps in trading for the developing countries where lack of capital affects the development of mining, oil drilling, heavy engineering, lumbering, and plantation agriculture.
(v) Transport: Inadequate and inefficient means of transport restricted trade to only local area, but better transport and better means of refrigeration and preservation expand the trade internationally.
Ques 24: Explain and five problems of rural settlements in the developing countries of the world.
Ans: Major problem of rural settlements in the developing countries of the world are:
(i) Rural settlements in the developing countries have poor infrastructure facilities.
(ii) Supply of water to rural settlements in developing countries is not adequate. People in villages, particularly in mountains and arid areas have to walk along distances to fetch drinking water.
(iii) Water borne diseases such as cholera and jaundice are common problem because of lack of safe drinking water and unhygienic conditions.
(iv) Villages are adversely affected by conditions of drought and flood. This in turn affects the crop cultivation.
(v) The absence of toilet and garbage disposal facilities cause health related problems.
(vii) Most houses have no proper ventilation.
(viii) Unmetalled roads and lack of modern communication network causes difficulties in providing emergency services.
(ix) It is also difficult to provide adequate health and educational infrastructure for large rural population. The problem is particularly serious where houses are, scattered over a large area.
Ques 25: 'Despite the setback, caused by the partition.., India ports continued to grow after the independence'. Support the statement with examples.
Ans: Before independence, the British Government used the ports as suction points of the resources from their hinterlands. After independence, it was expected that the country's independence will reverse the process, but the partition of the country snatched away two very important ports i.e. Karachi port went to Pakistan and Chittagong port to the erstwhile east-Pakistan now Bangladesh.
Despite this major setback, Indian ports continued to grow after the independence. Kandla in Kuch was the first port built up soon after independence to relieve the augmented pressure on Bombay port, following the loss of Karachi port to Pakistan. Later on Government of India took initiatives to develop 12 highly equipped ports in India. Today we have 185 minor and 12 major ports.
Today Indian Ports are handling large volume of domestic as well as overseas trade. The capacity of Indian ports increased from 20 million tons cargo in 1951 to 500 million tons at present. The experience of operating berths through PPPs at some of the major ports in India has been quite successful. It has, therefore, been decided to expand the programme and allocate new berths to be constructed through PPPs. A model concession agreement is being formulated for this purpose.
Ques 26: (a) In the given political Outline Map of the World, the following four features are shown:
A. The major area of commercial livestock rearing.
B. The major Sea Port.
C. The major Air Port.
D. The Mega City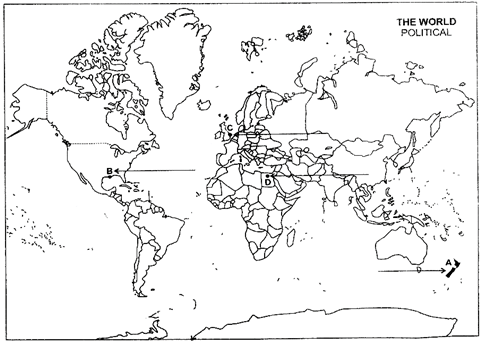 (b) In the given political Outline Map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols:
(b) In the given political Outline Map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols:
(i) The state having the smallest area.
(ii)The iron mine of Karnataka.
(iii) A software Technology Park located in Himachal Pradesh.
Ans: (a)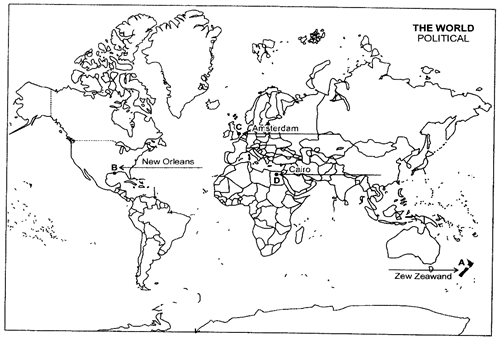 (b)
(b)