Class 12 Geography Solved Paper (2012 Outside Delhi Set-I) - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Ques 1: Define the term 'Population growth'.
Ans: Population growth is an increase in the number of people that reside in a country, state, country, or city. To determine whether there has been population growth, the following formula is used: (Birth rate + migration) - (death rate + migration).
Ques 2: Name the country having the highest sex ratio in the world.
Ans: Latvia.
Ques 3: Define the term 'Tourism'.
Ans: Tourism is an activity done by an individual or a group of individuals, which leads to a motion from a place to another. From a country to another for performing a specific task, or it is a visit to a place or several places for the purpose of entertaining which leads to an awareness of other civilizations and cultures, also increasing the knowledge of countries, cultures, and history.
Ques 4: Give any two examples of quaternary activities.
Ans: (i) Collection of information.
(ii)Production of information.
Ques 5: What is the density of population of India according to 2001 census?
Ans: 325 persons per sq. km.
Ques 6: Which state of India has the lowest percentage of population below poverty line?
Ans: Jammu & Kashmir.
Ques 7: Name any two metropolitan cities of Andhra Pradesh.
Ans: (i) Hyderabad and
(ii) Visakhapatnam.
Ques 8: Which is the eastern terminal city of East-West Corridor?
Ans: Silchar.
Ques 9: Name the railway line that was constructed between Roha in Maharashtra and Mangalore in Karnataka.
Ans: Konkan Railway.
Ques 10: Name any two diseases that are caused by air pollution.
Ans: (i) Disease related to respiratory system like Asthma.
(ii) Allergies.
Ques 11: Define 'Human Geography'. Give four examples of elements of material culture created by human, using the resources provided by nature.
Ans: Human geography is basically the study that deals with human activity in relation to the earth's surface. It shows how human activity affects or is influenced by the surface of the earth. Human geography also shows an interaction between the culture of humans and their land. Examples - Villages, Roads, Railway and Agricultural Farms.
Ques 12: Explain any three features of 'Welfare approach' to 'Human Development'.
Ans: (i) This approach looks human as beneficiaries and targets overall development of human. (ii) This approach argues for higher Government expenditure on Education, Health and Social Sanitation.
(iii) People are not participants, they act as passive recipients.
Ques 13: How do secondary activities add to natural resources? Explain with three examples.
Ans: (i) Secondary activities transform natural resources into valuable products. For example, cotton in the ball has limited use but after its transformation it is used at a large scale.
(ii) Secondary activities are concentrated with manufacturing and processing. For example, Iron can't be used directly from mines. It is manufactured into various useful products.
(iii) Most of the minerals found from natural resources are of limited use in their original form. They become useful for us after transformation done by secondary activities.
Ques 14: Why do people migrate? State the four streams of migration in India.
Ans: People migrate for a better economic and social life. There are two factors which influence the peoples migrate i.e., push factors such as unemployment, poor living conditions, unpleasant climate, etc. and pull factors like better job opportunities and living conditions, peace and stability, security of life, property, etc.
The four streams in which migration takes place:
(i) Rural to rural areas
(ii) Rural to urban areas
(iii) Urban to urban areas
(iv) Urban to rural areas.
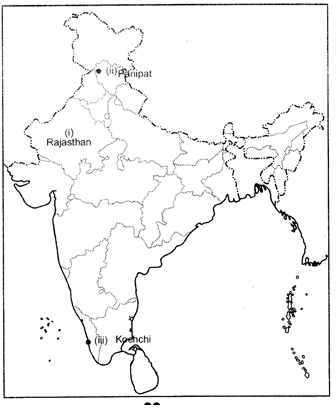
Ques 15: Study the map of India given below and answer the question that follow: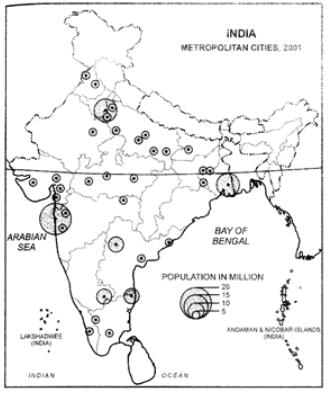
(i) How many metropolitan cities are there in Maharashtra?
(ii) Which one of them is the largest metropolitan city?
(iii) Name the easternmost metropolitan city of India as shown in the map.
Ans: (i) There are 4 metropolitan cities in Maharashtra
(ii) Mumbai
(iii) Kolkata.
Ques 16: 'Land resource is more crucial to the livelihood of the people depending on agriculture'. Support this statement with any three suitable arguments.
Ans: (i) The several types of land resources in India include agricultural land, farmland, barren land, real estate land, commercial land and residential land. Majority of the population of India are engaged in agricultural and allied activities and thus agricultural land accounts for near about 54.7 percent of the total land area of the country.
(ii) Land has a direct bearing on the productivity of agriculture, unlike other activities.
(iii) In rural areas, besides its value as a productive factor, land ownership has a social value and serves as a security for credit.
Ques 17: Describe any three key features of India's 'National Water Policy', 2002.
Ans: According to National Water Policy 2002:
(i) Water resources available to the country should be brought within the category of utilisable.
(ii) Non-conventional methods for utilization of water such as through inter-basin transfers, artificial recharge of ground water and desalination of brackish or sea water as well as traditional water conservation practices like rainwater harvesting, including root-top rainwater harvesting, need to be practiced to further increase the unlizable water resources. Promotion of frontier research and development, in a focused manner, for these techniques is necessary.
(iii) Water resources development and. management will have to be planned for a hydrological unit such as drainage basin as a whole or tor a sub-basin, multi - sectorally, taking into account surface and ground water for sustainable use incorporating quantity and quality aspects.
Ques 18: Describe three broad belts of minerals in India.
Ans: Minerals are generally concentrated in three broad belts in India:
(i) The North-Eastern plateau region: This belt covers Chotanagpur (Jharkhand), Odisha plateau, West-Bengal and some parts of Chhattisgarh.
(ii) The South-Western plateau region: Karnataka, Goa, Tamilnadu and Kerala comes under this region. 1 his belt is rich in ferrous metals, bauxite also contains high trade iron-ore, manganese and limestone.
(iii) The North-Western region: This belt exists in Aravali (Raj as than) and some parts of Gujarat Ra) as than is rich in building stones, sand stone, granite, marble and gypsum. Dolomite and limestone provide raw materials for cement industry. Gujarat is known for its petroleum deposits.
Ques 19: Study the diagram showing the location of a major steel plant of India, given below and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Identify and name the steel plant.
(ii) In which state of India is this plant located?
(iii) Name the source of iron ore for this plant.
Ans: (i) Bhilai Steel Plant
(ii) Chhattisgarh
(iii) Dalli - Rajahara Hills
Ques 20: Explain any three problems faced by slum dwellers in India.
Ans: The three problems faced by slum dwellers in India are:
(i) The areas in which they live (dilapidated houses) are over crowed having narrow street pattern prone to serious hazards from fire.
(ii) Lack of basic amenities like drinking water, light, and toilet facilities. They are also faced by poor ventilation, and poor hygienic conditions.
(iii) Moreover, the population of slum workers is low paid, high risk prone, in unorganized sectors of the urban economy.
Ques 21: Explain any five features of nomadic herding in the world.
Ans: Nomadic herding is a primitive subsistence activity. Basic features of nomadic herding are:
(i) In this activity, herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport. (ii) They move from one place to another along with their livestock, depending on the amount and quality of pastures and water.
(iii) Each nomadic community occupies a well-identified territory as a matter of tradition. (iv) A wide variety of animals is kept in different regions.
(v) The process of migration from plain areas to pasture on mountains during summers and again from mountain pastures to plain areas during winters.
(vi) Nomadic herding as a way of life is declining because of natural disasters such as droughts, loss of land area due to development and degradation, and pressure from governments to lead a settled existence.
Ques 22: Explain the merits and demerits of road transport in the world.
Ans: Merits:
(i) Road transport provides convenient service to people. Goods can be conveniently transported from sender to the receiver.
(ii) Road transport or automobiles like truck, motor etc. are the best means for transporting perishable goods. They can carry such goods to the destination within shorter time at lower cost.
(iii) Road transport is more flexible than other means of transport. If any road is blocked, the road automobiles like truck, bus can be taken through alternative ways. They do not need fixed road like railway line.
Demerits:
(i) The means of road transport like bus, trucks etc. are not suitable in travelling or transporting goods to long distance.
(ii) The service of road automobiles such as bus, trucks etc. are nor reliable. They have neither certain route nor fixed time.
(iii) Road transport is risky. Sudden accident may happen. Necessary security arrangement cannot be made against such accident.
Ques 23: Explain any five bases of international trade in the world.
Ans: The bases of International Trade are:
(i) Difference in national resources: The resources are unevenly distributed due to the differences in their physical make up i.e., geology, relief soil, and the climate.
(ii) Population factors: Under these factors, the size, distribution and diversity of people between countries affect the type and volume of goods.
(iii) Stage of economic development: The nature of item traded undergoes changes due to the stage of economic development of the country. As in agriculturally important countries, agro products are exchanged for manufactured goods.
(iv) Extent of foreign investment: Foreign investment helps in trading for the developing countries where lack of capital affects the development of mining, oil drilling, heavy engineering, lumbering, and plantation agriculture.
(v) Transport: Inadequate and inefficient means of transport restricted trade to only local areas, but better transport and better means of refrigeration and preservation expand the trade internationally.
Ques 24: Classify the human settlements of the world into two types, by their shape. Explain any two features of each type.
Ans: A human settlement is defined as a place inhabited more or less permanently. It includes buildings in which they live or use and paths and streets over which they travel. It also includes the temporary camps of the hunters and herders. It may consist of only a few dwelling units called hamlets or big cluster of buildings called urban cities. Settlements can also be classified on the basis of shape and pattern into:
(i) Compact settlements:
1. In these settlement houses are built very close to each other.
2. Such settlements are found in river valleys and fertile plains.
3. The people are closely tied and share common occupations.
(ii). Dispersed settlements:
1. In these settlements houses are built far apart from each other.
2. These settlements consist of one or two houses and cultural feature such as a church or a temple binds the settlement together.
3. Such settlements are found over hills, plateau and highlands.
Ques 25: 'Air transport plays an important role in the international trade?. Support the statement.
Ans: Air transport is of recent origin in the development of transport system of a country. It is gift is 20th century to the world. The second world ware has stimulated the growth of air transport and it has made progress in the recent years because it is the fattest way of transporting of goods. The transport of goods through airways is costly and therefore it is designated to carry costly goods of small quantity. Air transport does not give emphasis on construction of tracks like railways. As no capital investment in surface track is needed, it is a less costly mode of transport.
Air transport is regarded as the only means of transport in those areas which are not easily accessible to other modes or transport. It is therefore accessible to all areas regardless the obstruction of land. Air transport is free from physical barriers because it follows the shortest and direct routes where seas, mountains and forests do not obstruct. Air transport offers numerous advantages for international trade such as:
(i) Delivers items quickly over long distances.
(ii) Gives the high levels of security for sensitive items.
(iii) Be used for a range of goods.
Ques 26: (a) In the given political outline map of the world, the following four features are shown:
A. The country having the lowest rank in Human Development Index in 2003.
B. An area of subsistence gathering.
C. Terminal station of Trans-Siberian Railway,
D. A major sea-port of Australia.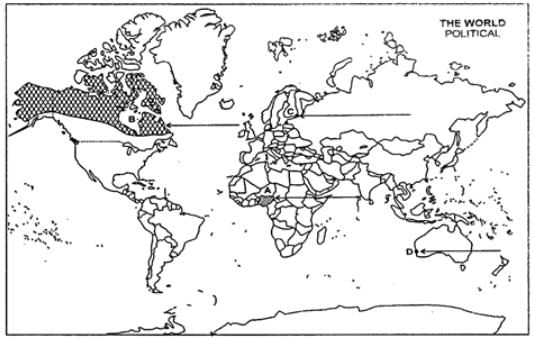 (b) In the given political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols:
(b) In the given political outline map of India, locate and label the following with appropriate symbols:
(i) The state having the largest area.
(ii) The oil refinery located in Haryana.
(iii) A metropolitan city of Kerala (2001).
Ans: (a)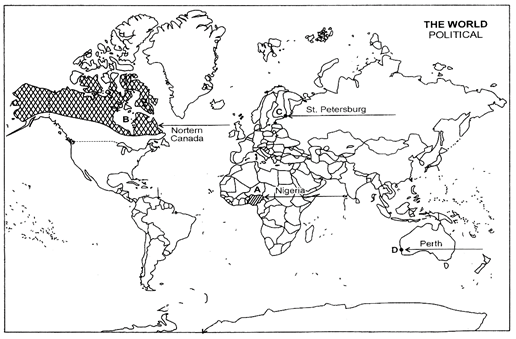 (b)
(b)