DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Main): Motion in One Dimension- 1 | DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics PDF Download
AIEEE Corner
Subjective Questions (Level 1)
Basic Definitions
Ques 1: A car moves with 60 km/h in first one hour and with 80 km/h in next half an hour. Find:
(a) total distance travelled by the car,
(b) average speed of car in total 1.5 hours.
Ans: (a) 100 km
(b) 66.67 kmh-1
Sol: (a) D = v1t1 + v2 t2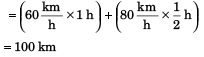
(b) Average speed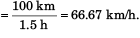
Ques 2: A particle moves in a straight line with initial velocity 4 m/s and a constant acceleration of 6 m/s2. Find the average velocity of the particle in a time interval from
(a) t = 0 to t = 2s
(b) t = 2s to t = 4s.
Ans: (a) 10 ms-1
(b) 22 ms-1
Sol: (a) Displacement in first two seconds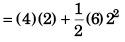
= 20 m
∴ Average velocity = 20m/2s = 10m/s
(b) Displacement in first four seconds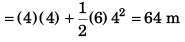
∴ Displacement in the time interval
t = 2s to t = 4s
= 64 - 20
= 44 m
∴ Average velocity = 44m/2s = 22 m/s.
Ques 3: A particle is projected upwards from the roof of a tower 60 m high with velocity 20 m/s. Find:
(a) the average speed and
(b) average velocity of the particle upto an instant when it strikes the ground. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Ans: (a) 16.67 ms-1
(b) 10 ms-1(downwards)
Sol: Let the particle takes t time to reach ground.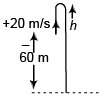
∴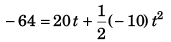
i.e., 5t2 - 20t - 64 = 0
t = 6.1 s
If the particle goes h meter above tower before coming down
0 = (20)2 + 2 (-10) h
⇒ h = 20 m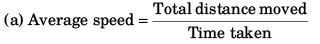
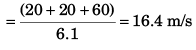
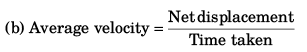

= 9.8 m/s (downwards)
Ques 4: A block moves in a straight line with velocity v for time t0. Then, its velocity becomes 2v for next t0 time. Finally its velocity becomes 3v for time T. If average velocity during the complete journey was 2.5 v, then find T in terms of t0.
Ans: T = 4 t0
Sol: Average velocity 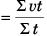
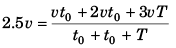
∴ 5t0 + 2.5T = 3t0 + 3T
or T = 4t0
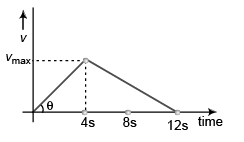
Ques 5: A particle starting from rest has a constant acceleration of 4 m/s2 for 4 s. It then retards uniformly for next 8 s and comes to rest. Find during the motion of particle:
(a) average acceleration,
(b) average speed,
(c) average velocity.
Ans: (a) zero
(b) 8 ms-1
(c) 8 ms-1
Sol: (a) Average acceleration 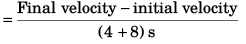
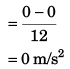
(b) As the particle did not return back distance travelled in 12 s
= Displacement at 12 s
∴ Average speed = 8 m/s.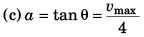
∴ 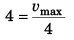 (∵ a = 4 m/s2)
(∵ a = 4 m/s2)
i.e., vmax = 16 m/s
Displacement of particle in 12 seconds
= Area under v-t graph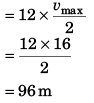
Average velocity 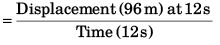
= +8 m/s
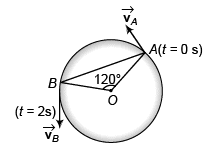
Ques 6: A particle moves in a circle of radius R = 21/22 m with constant speed lm/s. Find:
(a) magnitude of average velocity and
(b) magnitude of average acceleration in 2 s.
Ans: 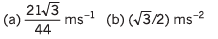
Sol: (a) Radius (R) of circle = 21/22 m
∴ Circumference of circle = 2πR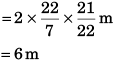
Speed (v) of particle = 1 m/s
∴ Distance moved by particle in 2 s = 2 m
Thus, angle through which the particle moved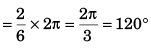
Magnitude of Average velocity 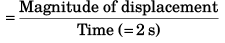
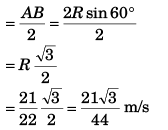
(b) Magnitude of average acceleration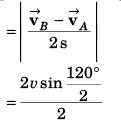
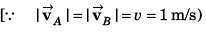
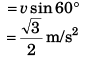
Ques 7: A particle is moving in x-y plane. At time t = 0, particle is at (1m, 2m) and has velocity 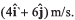 At t = 4 s, particle reaches at (6m, 4m) and has velocity
At t = 4 s, particle reaches at (6m, 4m) and has velocity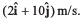 In the given time interval, find:
In the given time interval, find:
(a) average velocity,
(b) average acceleration and
(c) from the given data, can you find average speed?
Ans: 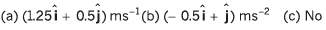
Sol: Position vector at t = 0 s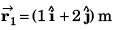
Position vector at t = 4 s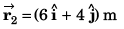
(a) Displacement from t = 0 s to t = 4 s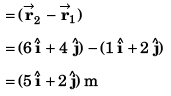
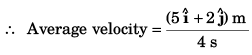
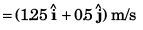
(b) Average acceleration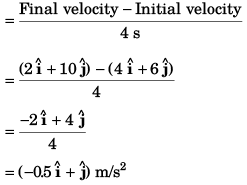
(c) We cannot find the average speed as the actual path followed by the particle is not known.
Uniform acceleration
(a) One dimensional motion
Ques 8: Two diamonds begin a free fall from rest from the same height, 1.0 s apart. How long after the first diamond begins to fall will the two diamonds be 10 m apart? Take g = 10 m/s2.
Ans: 1.5 s
Sol: If at time t the vertical displacement between A and B is 10 m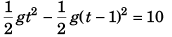
or t2 - (t - 1)2 = 2
or t2 - (t2 - 2t + 1) = 2
or 2t = 3
t = 1.5 s
Ques 9: Two bodies are projected vertically upwards from one point with the same initial velocity v0. The second body is projected t0 s after the first. How long after will the bodies meet?
Ans: 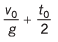
Sol: The two bodies will meet if
Displacement of first after attaining highest point = Displacement of second before attaining highest point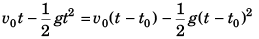
or 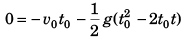
or 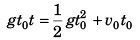
or 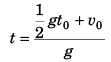
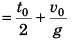
Ques 10: A stone is dropped from the top of a tower. When it crosses a point 5 m below the top, another stone is let fall from a point 25 m below the top. Both stones reach the bottom of the tower simultaneously. Find the height of the tower. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Ans: 45 m
Sol: 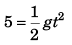
⇒ t = 1s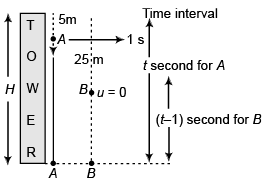
For A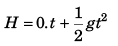
or 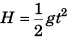 …(i)
…(i)
For B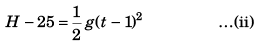
or 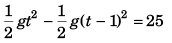
[Substituting value of H from Eq. (i)]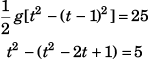
2t - 1 = 5
⇒ t = 3 s
Substituting t = 3 s in Eq. (i)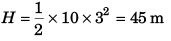
Ques 11: A point mass starts moving in a straight line with constant acceleration. After time t0 the acceleration changes its sign, remaining the same in magnitude. Determine the time t from the beginning of motion in which the point mass returns to the initial position.
Ans: (3.414) t0
Sol:
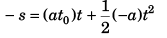
∴ 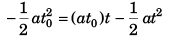
or 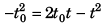
or 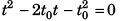
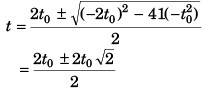
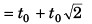 (- ive sign being absurd)
(- ive sign being absurd)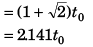
From the begining of the motion the point mass will return to the initial position after time 3.141t0.
Ques 12: A football is kicked vertically upward from the ground and a student gazing out of the window sees it moving upwards past her at 5.00 m/s. The window is 15.0 m above the ground. Air resistance may be ignored. Take g = 10 m/s2.
(a) How high does the football go above ground?
(b) How much time does it take to go from the ground to its highest point?
Ans: (a) 16.25 m (b) 1.8 s
Sol: 52 = u2 + 2 (-10)15
⇒ u2 = 325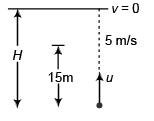
(a) For H
02 = u2 + 2(-10) H
i.e., 20H = 325
or H = 16.25 m
(b) For t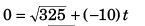
∴ 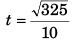
= 1.8 s
Ques 13: A car moving with constant acceleration covered the distance between two points 60.0 m apart in 6.00 s. Its speed as it passes the second point was 15.0 m/s.
(a) What is the speed at the first point?
(b) What is the acceleration?
(c) At what prior distance from the first was the car at rest?
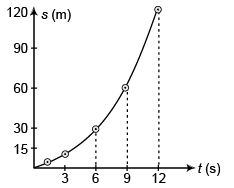
(d) Graph s versus t and v versus t for the car, from rest (t = 0).
Ans: (a) 5 ms-1
(b)1 .6 7 ms-2
(c) 7.5 m
Sol: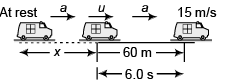
(a) 152 = u2 + 2a x 60 …(i)
and 15 = u + a x 6 …(ii)
Substituting the value of 6a from Eq. (ii) in Eq. (i)
225 = u2 + 20 (15 - u)
i.e., u2 - 20 u + 75 = 0
(u - 15)(u - 5) = 0
∴ u = 5 m/s
(15 m/s being not possible)
(b) Using Eq. (ii)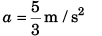
(c) u2 = 02 + 2ax
i.e.,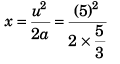
= 7.5 m
(d)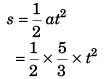
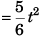 …(iii)
…(iii)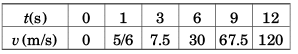
Differentiating Eq. (iii) w.r.t. time t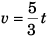
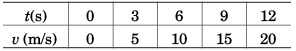
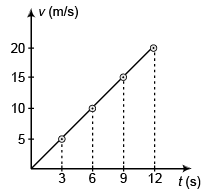
Ques 14: A train stopping at two stations 4 km apart takes 4 min on the journey from one of the station to the other. Assuming that it first accelerates with a uniform acceleration x and then that of uniform retardation y, prove that 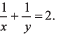
Sol: 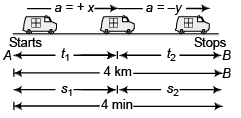
Journey A to P
vmax = 0 + xt1 …(i)
and 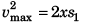 …(ii)
…(ii)
Journey P to B
0 = vmax + (- y) t2 …(iii)
and 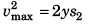 …(iv)
…(iv)
⇒ 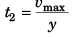
∴ 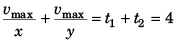
or 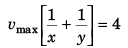 …(v)
…(v)
From Eq. (ii) and Eq. (iv)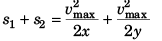
or 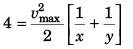 …(vi)
…(vi)
Dividing Eq. (vi) by Eq. (v)
vmax = 2
Substituting the value of vmax in Eq. (v)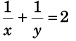 (Proved)
(Proved)
Ques 15: A particle moves along the x-direction with constant acceleration. The displacement, measured from a convenient position, is 2m at time t = 0 and is zero when t = 10s. If the velocity of the particle is momentary zero when t = 6 s, determine the acceleration a and the velocity v when t = 10s.
Ans: 0.2 ms-2, 0.8 ms-1
Sol: Let acceleration of the particle be a using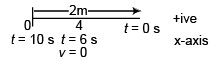
v = u + at
0 = u + a6
∴ 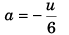
(a) At t = 10 s, s = - 2 m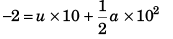
or -2 = (-6a) 10 + 50a
or -10a = - 2
or a = 0.2 m/s2
(b) v(at t = 10 s) = u + a 10
= - 6a + 10a
= 4 a
= 0.8 m/s
(b) Two or three dimensional motion
Ques 16: Net force acting on a particle of mass 2 kg is 10 N in north direction. At t = 0, particle was moving eastwards with 10 m/s. Find displacement and velocity of particle after 2 s.
Ans: 10√5 m at cos-1(2) from east towards north, 10√2 ms-1 at 45° from east towards north.
Sol:
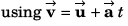
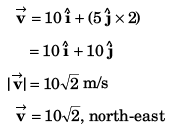
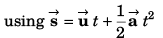
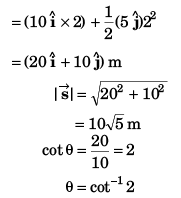
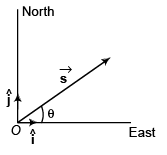
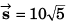 m at cot-1(2) from east to north.
m at cot-1(2) from east to north.
Ques 17: At time t = 0, a particle is at (2m, 4m). It starts moving towards positive x-axis with constant acceleration 2 m/s2 (initial velocity = 0). After 2 s an acceleration of 4 m/s2 starts acting on the particle in negative y-direction also. Find after next 2 s:
(a) velocity and
(b) coordinates of particle.
Ans: 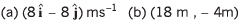
Sol: 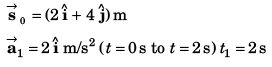
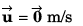
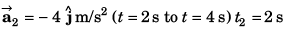
(a) Velocity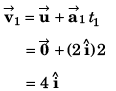
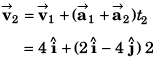
or 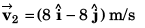
(b) Co-ordinate of particle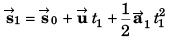
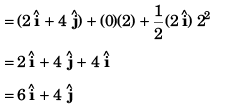
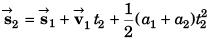
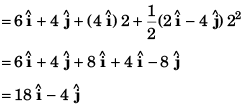
Co-ordinate of the particle [18 m, - 4 m]
Ques 18: A particle moving in x-y plane is at origin at time t = 0. Velocity of the particle is 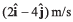 and acceleration is
and acceleration is 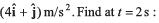
(a) velocity of particle and
(b) coordinates of particle.
Ans: 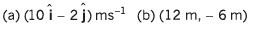
Sol: 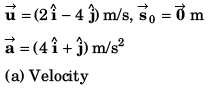
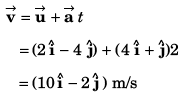
(b) Co-ordinates of the particle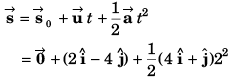
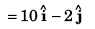
∴ Co-ordinates of particle would be [10 m , - 2 m]
Ques 19: A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 with a velocity of 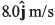 and moves in the x-y plane with a constant acceleration of
and moves in the x-y plane with a constant acceleration of 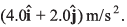 At the instant the particle’s x-coordinate is 29 m, what are:
At the instant the particle’s x-coordinate is 29 m, what are:
(a) its y-coordinate and
(b) its speed ?
Ans: (a) 45 m (b) 22 ms-1
Sol: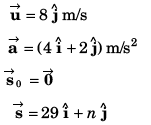
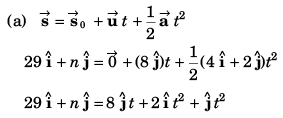
Comparing the coefficients of 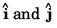
29 = 2t2 …(i)
and n = 8t + t2 …(ii)
⇒ 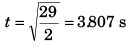
Substituting value of t in Eq. (ii)
n = 8 x 3.807 + (3.807)2
= 44.95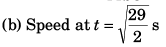
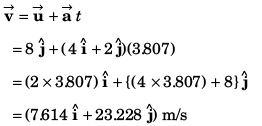
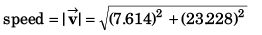
= 24.44 m/s
Ques 20: At time t = 0, the position vector of a particle moving in the x-y plane is 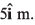 By time t = 0.02 s, its position vector has become
By time t = 0.02 s, its position vector has become 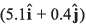 m determine the magnitude vav of the average velocity during this interval and the angle θ made by the average velocity with the positive x-axis.
m determine the magnitude vav of the average velocity during this interval and the angle θ made by the average velocity with the positive x-axis.
Ans: 20.6 ms-1, tan-1(4)
Sol:
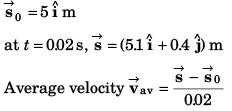
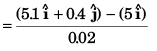
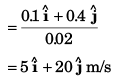
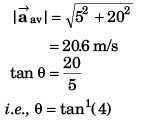
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Main): Motion in One Dimension- 1 - DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics
| 1. What is motion in one dimension? |  |
| 2. How is displacement different from distance? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between speed and velocity? |  |
| 4. How is average velocity calculated? |  |
| 5. What is the equation of motion for an object moving with constant acceleration? |  |






















