DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Advance): Motion in One Dimension- 5 | DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics PDF Download
Objective Questions (Level 1)
Single Correct Option
Ques 1: A packet is released from a rising balloon accelerating upward with acceleration a. The acceleration of the stone just after the release is
(a) a upward
(b) g downward
(c) (g - a) downward
(d) (g + a) downward
Ans: g downward
Sol: As the packet is detached from rising balloon its acceleration will be g in the downward direction.
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 2: A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the ground. If T1 and T2 are the respective time taken in going up and coming down, and the air resistance is not ignored, then
(a) T1 > T2
(b) T1 = T2
(c) T1 < T2
(d) nothing can be said
Ans: T1 < T2
Sol: While going up: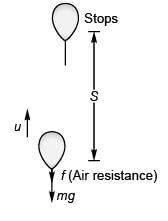
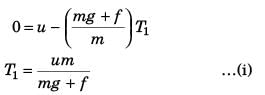
Using v2 = u2 + 2as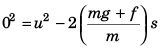
i.e., 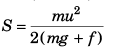
While coming down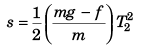
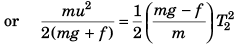
⇒ 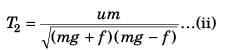
Using Eq. (i) and Eq. (ii)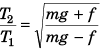
⇒ T2 > T1
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 3: The length of a seconds hand in watch is 1 cm. The change in velocity of its tip in 15 s is
(a) zero 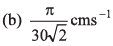
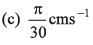
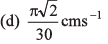
Ans: 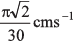
Sol: Angular speed (ω) of seconds hand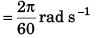
Speed of the tip of seconds hand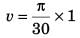 cm/s [∵ v = rω and r = 1 cm]
cm/s [∵ v = rω and r = 1 cm]
As in 15s the seconds hand rotates through 90°, the change in velocity of its tip in 15 s will be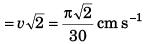
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 4: A particle moving along a straight line travels half of the distance with uniform speed 30 ms-1 and the rem aining half of the distance with speed 60 ms-1. The average speed of the particle is
(a) 45 ms-1
(b) 42 ms-1
(c) 40 ms-1
(d) 50 ms-1
Ans: 40 ms-1
Sol: 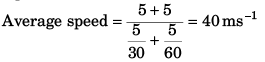
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 5: A boat is moving with a velocity 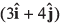 with respect to ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity
with respect to ground. The water in the river is moving with a velocity 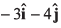 with respect to ground. The relative velocity of the boat with respect to water is
with respect to ground. The relative velocity of the boat with respect to water is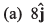
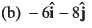
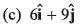
(d) zero
Sol: Relative velocity of boat w.r.t. water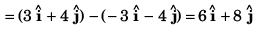
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 6: During the first 18 min of a 60 min trip, a car has an average speed of 11 ms 1. What should be the average speed for remaining 42 min so that car is having an average speed of 21 ms -1 for the entire trip ?
(a) 25.3 ms-1
(b) 29.2 ms-1
(c) 31 ms-1
(d) 35.6 ms-1
Ans: 25.3 ms-1
Sol: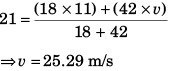
Ques 7: A particle moves along a straight line. Its position at any instant is given by 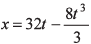 where x is in metre and t in second. Find the acceleration of the particle at the instant when particle is at rest,
where x is in metre and t in second. Find the acceleration of the particle at the instant when particle is at rest,
(a) -16 ms-2
(b) -32 ms-2
(c) 32 ms-2
(d) 16 ms-2
Ans: -32 ms-2
Sol: 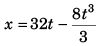
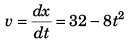 …(i)
…(i)
∴ Particle is at rest when
32 - 8 t2 = 0
i.e., t = 2 s
Differentiating Eq. (i) w.r.t. time t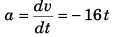
∴ a at time t = 2 s (when particle is at rest)
= - (16) x (2) = -32 m/s2
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 8: A car starts from rest and accelerates at constant rate in a straight line. In the first second the car covers a distance of 2 m. The velocity of the car at the end of second (sec) will be
(a) 4.0 ms-1
(b) 8.0 ms-1
(c) 16 ms-1
(d) None of these
Ans: 8.0 ms-1
Sol: For first one second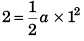
⇒ a = 4 m/s2
Velocity at the end of next second
v = (4) x (2) = 8 m/s
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 9: A particle is moving along x-axis whose position is varying with time according to the relation x = - 3t + t3 where x is in metre and t is in second. The displacement of particle for t = 1 s to t = 3 s is
(a) +16 m
(b) -16 m
(c) +20 m
(d) -20 m
Ans: +20 m
Sol: x = - 3t + t3
∴ displacement at time t (= 1 s)
= - 3(1) + (1)3 = - 2 m
and displacement at time t (= 3 s)
= - 3(3) + (3)3 = 18 m
And as such displacement in the time interval (t = 1 s to t = 3 s)
= (18 m) - (- 2 m)
= + 20 m
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 10: The acceleration of a particle is increasing linearly with time t as bt. The particle starts from the origin with an initial velocity v0. The distance travelled by the particle in time t will be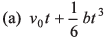
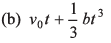
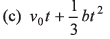
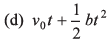
Ans: 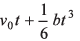
Sol: Acceleration α = bt
∴ 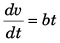
or 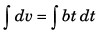
or 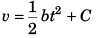
Now, at t = 0, v = v0
∴ C = v0
i.e., 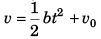
or 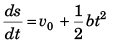
or 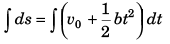
or 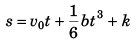
At t = 0, s = 0,
∴ k = 0
⇒ 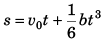
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 11: Water drops fall at regular intervals from a tap 5 m above the ground. The third drop is leaving the tap, the instant the first drop touches the ground. How far above the ground is the second drop at that instant, (g = 1 0 ms-2)
(a) 1.25 m
(b) 2.50 m
(c) 3.75 m
(d) 4.00 m
Ans: 3.75 m
Sol: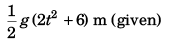
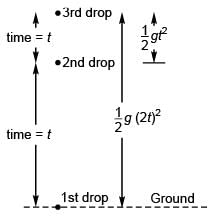
∴ 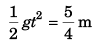
∴ Height of 2nd drop from ground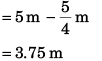
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 12: A stone is dropped from the top of a tower and one second later, a second stone is thrown vertically downward with a velocity 20 ms-1. The second stone will overtake the first after travelling a distance of (g = 10 ms-2)
(a) 13 m
(b) 15 m
(c) 11.25 m
(d) 19.5 m
Ans: 11.25 m
Sol: 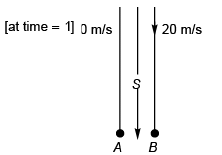
[At time = t - 1]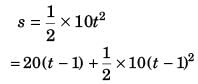
or t2 = 4 (t - 1) + (t2 - 2t + 1)
or 2t - 3 = 0
or 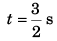
∴ 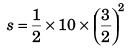
= 11.25 m
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 13: When a ball is thrown up vertically with velocity v0, it reaches a maximum height of h. If one wishes to triple the maximum height then the ball should be thrown with velocity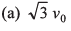
(b) 3 v0
(c) 9 v0
(d) 3/2 v0
Ans: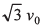
Sol: 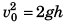 and u2 = 2g (3h)
and u2 = 2g (3h)
∴ 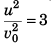
or u = v0√3
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 14: A particle moves in the x-y plane with velocity vx = 8t - 2 and vy = 2. If it passes through the point x = 14 and y = 4 at t = 2 s, the equation of the path is
(a) x = y2 - y + 2
(b) x = y2 - 2
(c) x = y2 + y - 6
(d) None of these
Ans: x = y2 - y + 2
Sol: vx = 8t - 2
∴ 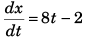
or ∫ dx = ∫ (8 t - 2) dt
or x = 4t2 - 2t + k1
Now at t = 2, x = 14
∴ 14 = 4 × 22 - (2) 2 + k1
i.e., k1 = 2
Thus, x = 4 t2 - 2t + 2 …(i)
Further, vy = 2
i.e., 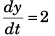
or ∫ dy = ∫ 2 dt
or y = 2t + k2
Now, at t = 2, y = 4
∴ k2 = 0
Thus, y = 2t …(ii)
Substituting t = y/2 in Eq. (i),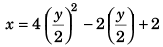
or x = y2 - y + 2
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 15: The horizontal and vertical displacements of a particle moving along a curved line are given by x = 5t and y = 2t2 + 1. Time after which its velocity vector makes an angle o f 45° with the horizontal is
(a) 0.5 s
(b) 1 s
(c) 2 s
(d) 1.5 s
Ans: 1 s
Sol: x = 5t and y = 2t2 + t
∴ 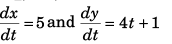
Now, 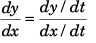
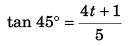
⇒ t = 1 s
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 16: The height y and the distance x along the horizontal plane of a projectile on a certain planet (with no surrounding atmosphere) are given by y = (8t - 5 t2) metre and x = 6t metre where t is in second. The velocity of projection is
(a) 8 ms-1
(b) 6 ms-1
(c) 10 ms-1
(d) data insufficient
Ans: 10 ms-1
Sol: y = 8t - 5t2 and x = 6t
∴ 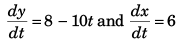
At t = 0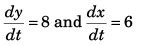
∴ Velocity of projection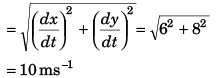
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 17: A ball is released from the top of a tower of height h metre. It takes T second to reach the ground. What is the position of the ball in T/3 second?
(a) h/9 metre from the ground
(b) (7h/9) metre from the ground
(c) (8h/9) metre from the ground
(d) (17h/18)metre form the ground
Ans: (8h/9) metre from the ground
Sol: 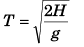
∴ 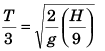
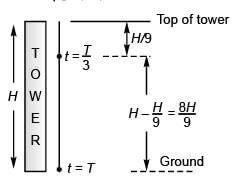
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 18: An ant is at a comer of a cubical room of side a. The ant can move with a constant speed u. The minimum time taken to reach the farthest comer of the cube is
(a) 3a/u 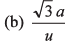
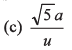
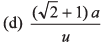
Ans: 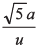
Sol: Distance of farthest corner from one corner
= a + a + a = 3 a
∴ Time taken = 3a/u
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 19: A lift starts from rest. Its acceleration is plotted against time. When it comes to rest its height above its starting point is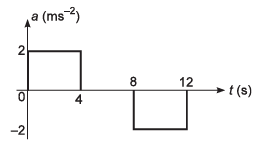
(a) 20 m
(b) 64 m
(c) 32 m
(d) 36 m
Ans: 64 m
Sol: Time-velocity graph of the given time-acceleration graph will be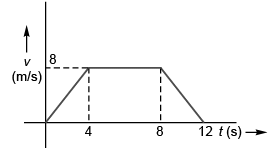
∴ Height of lift above the starting point when it comes to rest
= Area under t-v graph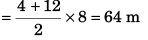
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 20: A lift performs the first part of its ascent with uniform acceleration a and the remaining with uniform retardation 2a. If t is the time of ascent, find the depth of the shaft.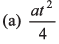
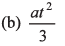
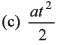
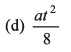
Ans: 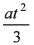
Sol: 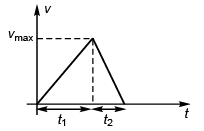
In time interval t1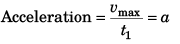
In time interval t2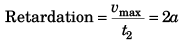
∴ 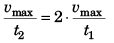
i.e., t1 = 2t2
Now t1 + t2 = t
∴ 2t2 + t2 = t
or t2 = t/3
Depth of shaft = Displacement of lift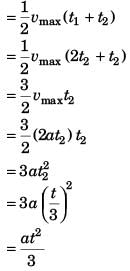
Option (b) is correct.
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Advance): Motion in One Dimension- 5 - DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics
| 1. What is the concept of motion in one dimension in physics? |  |
| 2. How is motion in one dimension different from motion in multiple dimensions? |  |
| 3. What are the key equations used to describe motion in one dimension? |  |
| 4. How is the concept of motion in one dimension applicable in real life? |  |
| 5. How can the DC Pandey JEE book help in understanding motion in one dimension for the JEE Main exam? |  |
















