DC Pandey Solutions: Motion in One Dimension (JEE Main)- 6 | DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics PDF Download
Ques 21: Two objects are moving along the same straight line. They cross a point A with an acceleration a, 2a and velocity 2u, u at time t = 0. The distance moved by the object when one overtakes the other is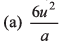
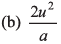
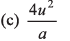
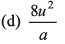
Ans: 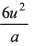
Sol: 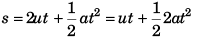
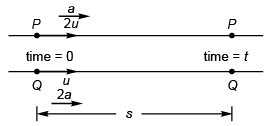
⇒ 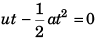
or 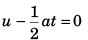
or t = 2u/a
∴ 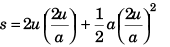
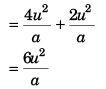
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 22: A cart is moving horizontally along a straight line with constant speed 30 ms-1. A particle is to be fired vertically upwards from the moving cart in such a way that it returns to the cart at the same point from where it was projected after the cart has moved 80 m. At what speed (relative to the cart) must the projectile be fired? (Take g = 10ms-2)
(a) 10 ms-1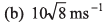
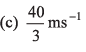
(d) None of these
Ans: 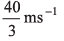
Sol: u = vertical speed (w.r.t. cart) of the particle.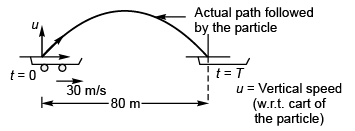
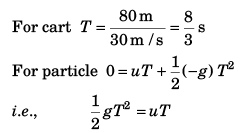
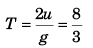
i.e., 2u/10 = 8/3
or 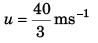
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 23: The figure shows velocity-time graph of a particle moving along a straight line. Identify the correct statement.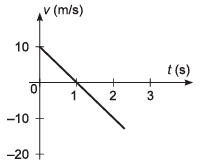
(a) The particle starts from the origin
(b) The particle crosses it initial position at t = 2s
(c) The average speed of the particle in the time interval, 0 < t < 2s is zero
(d) All of the above
Ans: The particle crosses it initial position at t = 2s
Sol: 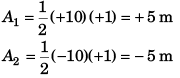
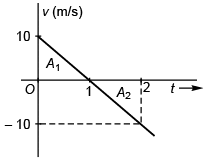
∴ Displacement of particle at time (t = 2)
= (+ 5 m) + (-5 m) = 0 m.
i.e., the particle crosses its initial position at t = 2 s.
Option (b) is correct.
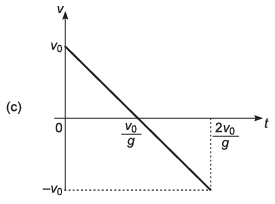
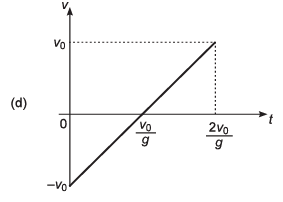
Ques 24: A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity v0. I f the vertical downward direction is considered to be positive, then the correct variation of velocity with time t is represented by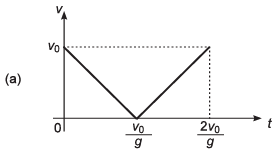
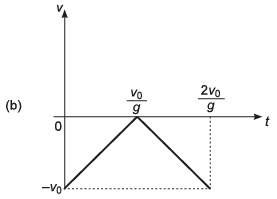
Ans: 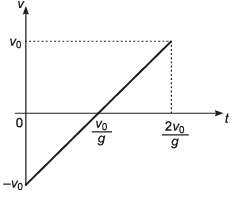
Sol: As downward direction is considered to be + ive, velocity of ball at t = 0 will be - v0.
Thus, option (a) and (c) are incorrect.
Now, as the ball will have +ive acceleration throughout its motion option (b) is also incorrect.
∴ Correct option is (d).
Ques 25: A boy standing in an elevator accelerating upward throws a ball upward with a velocity v0. The ball returns in his hands after a time t. The acceleration of the lift is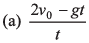
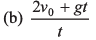
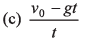
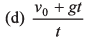
Ans: 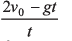
Sol: Let acceleration of lift = a (upwards)
Displacement of ball in time t = Displacement of lift in time t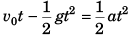
or 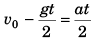
∴ 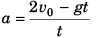
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 26: A body starts moving with a velocity v0 = 10ms-1. It experiences a retardation equal to 0.2v2. Its velocity after 2s is given by
(a) +2 ms-1
(b) +4 ms-1
(c) -2 ms-1
(d) +6 ms-1
Ans: +2 ms-1
Sol: a = -0.2 v2
∴ 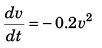
or 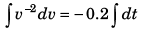
or 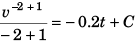
or 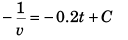
Now, at t = 0, v = 10 m/s (given)
∴ 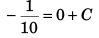
i.e., 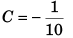
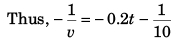
∵ For velocity v at time t (= 2 s)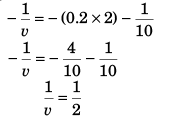
⇒ v = + 2 m/s.
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 27: Two trains are moving with velocities v1 = 10 ms-1 and v2 = 20 ms-1 on the same track in opposite directions. After the application of brakes if their retarding rates are a1 = 2 ms-2 and a2 = 1 ms-2 respectively, then the minimum distance of separation between the trains to avoid collision is
(a) 150 m
(b) 225 m
(c) 450 m
(d) 300 m
Ans: 225 m
Sol: For displacement (S1) of train 1 before coming to rest
02 = (10)2 + 2 (-2) S1
i.e., S1 = 25 m
For displacement (S2) of train 2 before coming to rest
02 = (20)2 + 2 (-1) S2
i.e., S2 = 200 m
∴ Smin = S1 + S2
= 225 m
Option (b) is correct
Ques 28: Two identical balls are shot upward one after another at an interval of 2s along the same vertical line with same initial velocity of 40 ms-1. The height at which the balls collide is
(a) 50 m
(b) 75 m
(c) 100 m
(d) 125 m
Ans: 75 m
Sol: Let the balls collide after time t the first ball is shot.
∴ displacement (S) of ball 1 at time t
= displacement (S) of ball 2 at time (t - 2)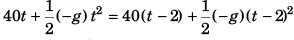
or 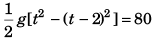
or (t + t - 2) (t - t + 2) = 16
or 2t - 2 = 8
or t = 5 s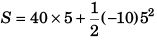
= 200 - 125
= 75 m
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 29: A particle is projected vertically upwards and reaches the maximum height H in time T. The height of the particle at any time t will be
(a) g (t - T)2
(b) H - g (t —T )2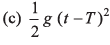
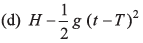
Ans: 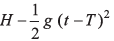
Sol: 0 = u - gT
i.e., u = gT …(i)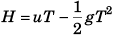 …(ii)
…(ii)
and 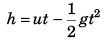 …(iii)
…(iii)
Substracting Eq. (ii) from Eq. (iii),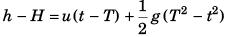
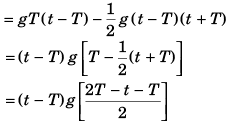
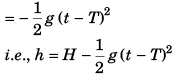
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 30: A particle m oves along the curve 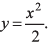 Here x varies with time as
Here x varies with time as 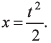 Where x and y are measured in metre and t in second. At t = 2s, the velocity of the particle (in ms-1) is
Where x and y are measured in metre and t in second. At t = 2s, the velocity of the particle (in ms-1) is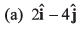
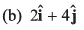
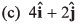
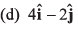
Ans: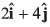
Sol: 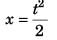
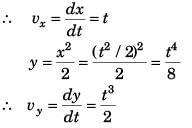
Ques 31: If the displacement of a particle varies w ith time as √x = t + 3
(a) velocity of the particle is inversely proportional to t
(b) velocity of particle varies linearly with t
(c) velocity of particle is proportional to √t
(d) initial velocity of the particle is zero
Ans: velocity of particle varies linearly with t
Sol: 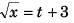
i.e., x = t2 + 6t + 3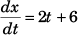
i.e., v ∝ t
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 32: The graph describes an airplane’s acceleration during its take-off run. The airplane’s velocity when it lifts off at t = 20 s is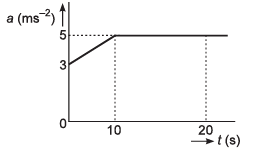
(a) 40 ms-1
(b) 50 ms-1
(c) 90 ms-1
(d) 180 ms-1
Ans: 90 ms-1
Sol: Aeroplane’s velocity at time t (= 20 s)
= Area under curve (t-a graph)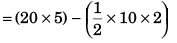
= 90 m/s
Ques 33: A particle moving in a straight line has velocity-displacement equation as 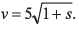 Here v is in ms-1 and sin metre. Select the correct alternative.
Here v is in ms-1 and sin metre. Select the correct alternative.
(a) Particle is initially at rest
(b) Initially velocity of the particle is 5 m/s and the particle has a constant acceleration of 12.5 ms-2
(c) Particle moves with a uniform velocity
(d) None of these
Ans: Initially velocity of the particle is 5 m/s and the particle has a constant acceleration of 12.5 ms-2
Sol: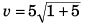 …(i)
…(i)
At s = 0 (i.e., initially),
velocity of particle = 5 m/s
Option (b) is correct.
Differentiating equation (i) w.r.t. s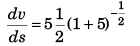
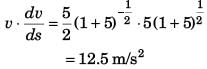
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 34: A particle is thrown upwards from ground. It experiences a constant resistance force which can produce a retardation of 2 ms-2. The ratio of time of ascent to time of descent is (g = 10 ms-2)
(a) 1 : 1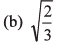
(c) 2/3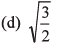
Ans: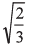
Sol: See answer to question no. 2.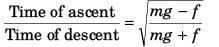
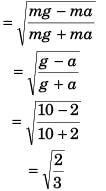
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 35: A river is flowing from west to east with a speed of 5 m min-1. A man can swim in still water with a velocity 10 m min-1. In which direction should the man swim so as to take the shortest possible path to go to the south?
(a) 30° east of south
(b) 30° west of south
(c) South
(d) 30° west of north
Ans: 30° west of south
Sol: 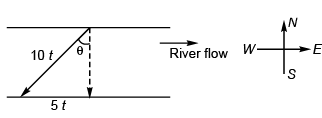
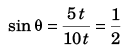
⇒ θ = 30°
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 36: A body of mass 10 kg is being acted upon by a force 311 and an opposing constant force of 32 N. The initial speed is 10 ms-1. The velocity o f body after 5 s is
(a) 14.5 ms-1
(b) 6.5 ms-1
(c) 3.5 ms-1
(d) 4.5 ms-1
Ans: 6.5 ms-1
Sol: Fnet = 3t2 - 32
i.e., manet = 3 t2 - 32
or 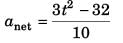
or anet = 0.3 t2 - 3.2
or 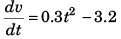
or 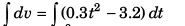
or 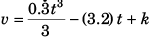
or v = 0.1t3 - (3.2) t + k
Now, at t = 0, v = 10 m/s
∴ 10 = k
Thus, v = 0.1 t3 - (3.2) t + 10
∴ at t = 5 s
v = 0.1 (5)3 - (3.2) (5) + 10
= 12.5 - 16.0 + 10
= 6.5 m/s Option (b) is correct.
Ques 37: A stone is thrown vertically upwards. When stone is at a height half of its maximum height, its speed is 10 ms-1; then the maximum height attained by the stone is (g = 10 ms-2)
(a) 25 m
(b) 10 m
(c) 15 m
(d) 20 m
Ans: 10 m
Sol: u2 = 2 gH
⇒ 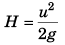
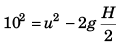
⇒ u2 = 100 + gH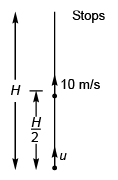
Thus,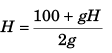
or gH = 100
⇒ H = 10 m
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 38: A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the ground and a student gazing out of the window sees it moving upward past him at 10 ms-1. The window is at 15 m above the ground level. The velocity of ball 3 s after it was projected from the ground is [Take g = 10ms-2]
(a) 10 m/s, up
(b) 20 ms-1, up
(c) 20 ms-1, down
(d) 10 ms-1, down
Ans: 10 ms-1, down
Sol:
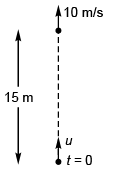
102 = u2 - 2g x 15
100 = v2 - 2 x 10 x 15
i.e., u = 20 m/s
Now, v = u - gt = 20 - 10 x 3
= 20 - 10 × (3)
= - 10 m/s, downward
Option (d) is correct.
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Motion in One Dimension (JEE Main)- 6 - DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics
| 1. What is motion in one dimension? |  |
| 2. What is JEE Main? |  |
| 3. Who is DC Pandey? |  |
| 4. How can DC Pandey's book help in JEE Main preparation? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions related to motion in one dimension in JEE Main? |  |
















