Basic Units of Measurement | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
Units of Measurement
Units of Measurement are used to express physical quantities like length, mass, temperature, time, area, and volume. These units help us compare quantities based on a standard reference. Different systems like the Metric System, Imperial System, Traditional Units, and US Customary Units are used worldwide.
From ancient times to today, units have helped us measure everyday things like time worked, water consumed, body weight, height, and distances. In this topic, we explore metric vs imperial units and learn how to measure common quantities using appropriate units, supported by examples for better understanding.
What are Units of Measurement?
- The Units of measurement encompass a set of standard and alternative units employed for quantifying diverse physical attributes.
- Throughout history, various units have been employed to gauge dimensions like length, mass, volume, current, temperature, and more.
- Early on, people relied on informal methods and units of measurement due to the absence of precise tools.
- For instance, measurements of length were often based on body parts such as hand span, foot span, arm span, cubit, pace, and others.
- However, these approaches lacked precision as body parts varied among individuals.
- Consequently, over time, more accurate and reliable units of measurement were developed.
- As a result, the metric system, also known as the International System of Units (called the SI units - the modern form of the metric system), the Imperial system, and US customary units were standardized across the world as the units of measurement to get more accurate results.
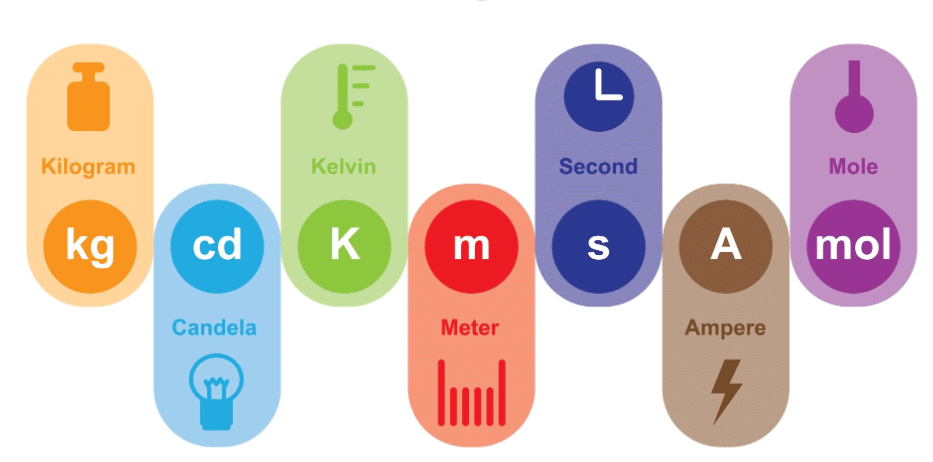
Basic Units of Measurement
Metric Units of Measurement
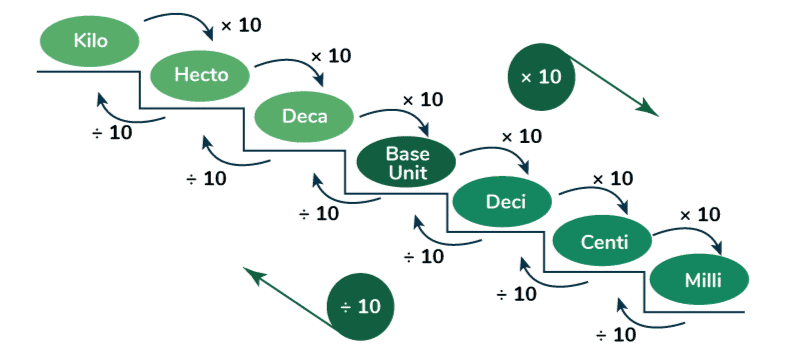
- In the field of mathematics, metric units of measurement serve as standardized units designed for quantifying dimensions such as length, height, weight, area, and capacity (volume).
- These units adhere to the decimal system, employing powers of 10 in their representation.
- The contemporary iteration of metric units, known as the International System of Units (SI), is globally acknowledged and embraced.
- Each SI unit is universally defined with a recognized size.
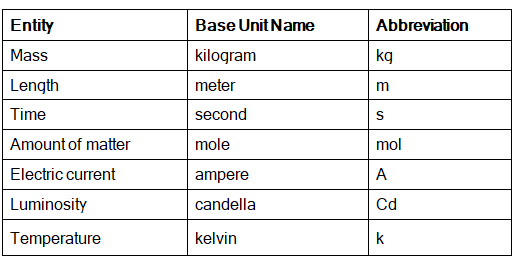
- Let us see some of the commonly used SI units in the table below.
SI Units of Measurement
SI units of measurement are units of the international system of units, also known as the metric system, which is used across the world and each unit has a standard measure.
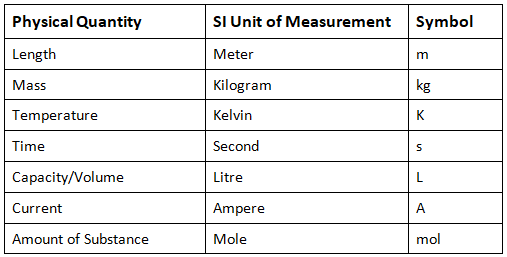
Unit of Measurement List
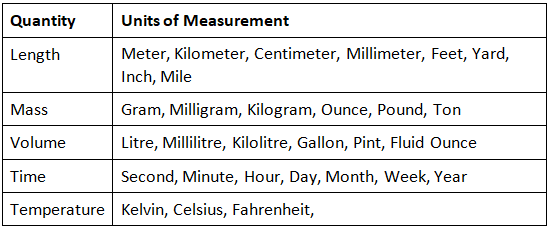
The table above shows the SI units, but we use other units as well to measure the given physical quantities. Let us list some of the commonly used units of measurement below:
- Length - kilometer, meter, centimeter, millimeter
- Mass - kilogram, gram, milligram
- Capacity - kilolitre, litre, milliliter, centilitre
- Time - Minute, Hour, Second, Days, Week, Month, Year
- Temperature - Kelvin, Celsius, Fahrenheit
All the above units for a specific physical quantity can be expressed in terms of each other using the conversion of the units of measurement.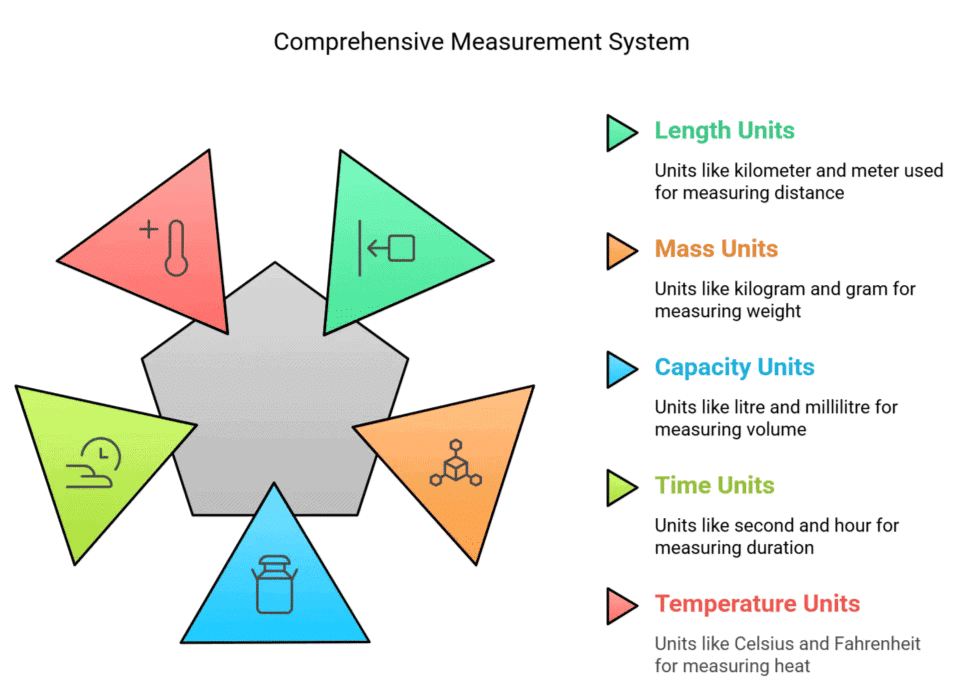
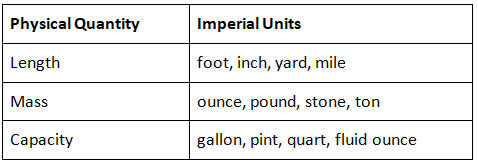
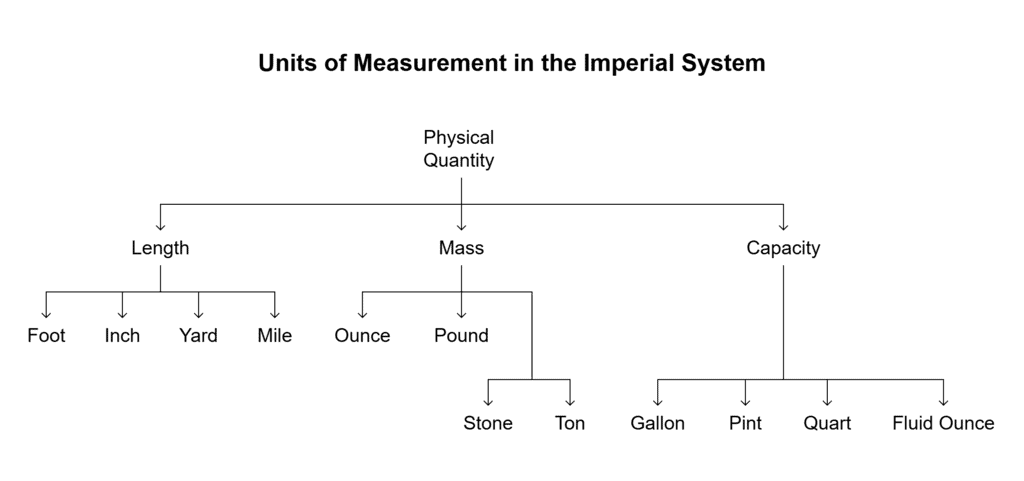
Imperial Units of Measurement
- Imperial units of measurement originate from the British Imperial System, which is the system of weights and measures utilized in Great Britain.
- In contrast to metric units, the imperial system employs distinct units for quantifying physical attributes such as length, mass, volume, and area.
- Let us go through imperial units of measurement in the table below:
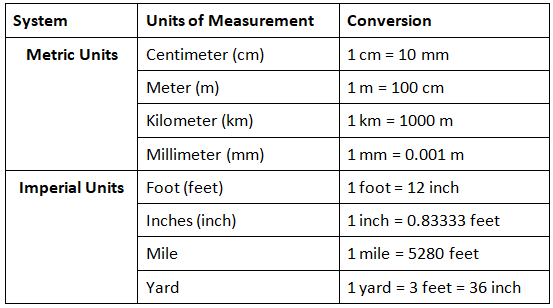
Units of Measurement for Length
- Length is a measurable physical attribute indicating the extent of an object in space.
- It encompasses various aspects, including the distance covered and height.
- All units of measurement for different physical quantities fall under the same category.
- The conversion method allows expressing each unit of length in terms of others, given their standardized values.
- Below, we'll explore commonly used metric and imperial units of length along with their interrelations.
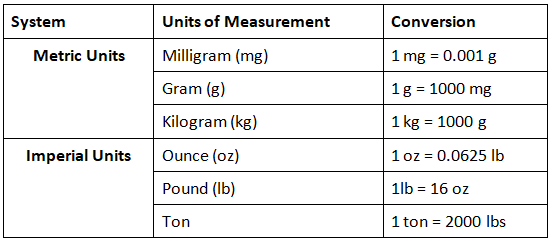
Units of Measurement for Mass
Mass is a physical quantity that tells how heavy or light an object is. It is also commonly called the weight of the object. The SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg).
The table below shows the different and commonly used units of measuring mass in the metric and imperial systems, along with their conversions:
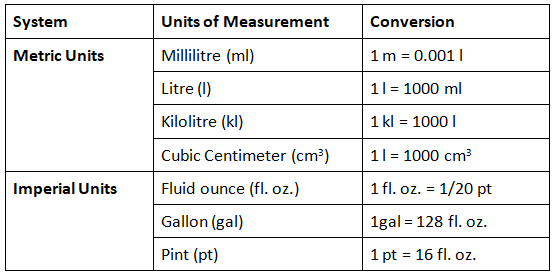
Units of Measurement for Volume
- Volume, referred to as capacity, denotes the space occupied or the maximum space an object possesses.
- The liter (L) serves as the SI unit for volume.
- Additionally, volume measurements can be articulated using cubic length units like cubic centimeter (cm³) or cubic meter (m³).
- Let us go through some of the commonly used units of measurement of volume in the table below:
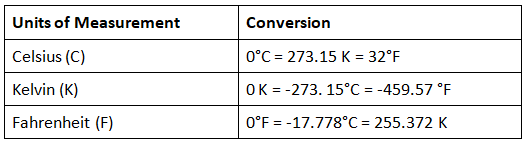
Units of Measurement for Temperature
- Temperature is a physical characteristic that indicates the degree of heat or coldness present in an object or the surrounding environment.
- The three primary units used to measure temperature are Celsius, Kelvin, and Fahrenheit, with Kelvin being the designated SI unit for temperature measurement.
- The table given below shows the different units of measuring temperature and their conversion.
 Generally, for the conversion of temperature, we use the formula C/5 = (F - 32) / 9 = (K - 273.15) / 5. This formula helps to express the temperature in different units.
Generally, for the conversion of temperature, we use the formula C/5 = (F - 32) / 9 = (K - 273.15) / 5. This formula helps to express the temperature in different units.
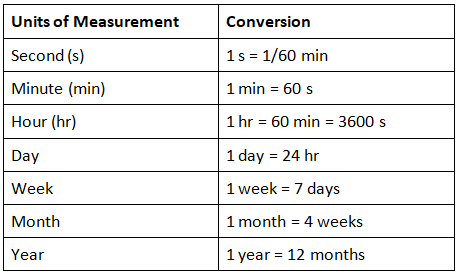
Units of Measurement of Time
- Time is a measure that tells about the time taken to complete a process or travel from one point to another.
- It is an ongoing process of continuous events.
- We measure time in three units: seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months, and years.
- The table given below describes these units and their relation to each other.
 These units of measurement of time are standard and are followed all across the world.
These units of measurement of time are standard and are followed all across the world.
Units of Measurement Chart
Now that we have discussed the different units of measurement used across different systems of measurement, let us summarize the units in a chart below for a quick review:
Important Notes on Units of Measurement
- The units of measurement are the units that are used to represent physical quantities like length, mass, temperature, current, area, volume, intensity, etc.
- We use two systems of units of measurement - metric and imperial.
- In the early days, hand span, arm span, and foot span were used as units of measurement.
|
365 videos|701 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Units of Measurement - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What are Units of Measurement? |  |
| 2. What are the Basic Units of Measurement? |  |
| 3. What are Metric Units of Measurement? |  |
| 4. What are SI Units of Measurement? |  |
| 5. What are Imperial Units of Measurement? |  |






















