An Introduction to the Constitution | Additional Study Material for CLAT PDF Download
What is “Constitution”?
For a school to function properly, there are a set of rules and regulations that are followed. These rules include the discipline, a prescribed uniform, strictly adhered curriculum, a body which regulates student affairs, etc. Similarly, for a country to function properly, there are certain rules and regulations that have to be followed.
The constitution derived from a Latin term “Constitutio’ is considered as the binding and unifying force of a country as it consists of certain rules and regulations for the functioning of a country. It is considered as the supreme law of the land and along with the set of rules and regulations, it also contains the rights and duties of the citizens. This establishes a relationship between the state (a country is also referred as a ‘state’) and its citizens.
There are two types of Constitution:
1. Written Constitution: A written constitution consists of the rules and regulations of a country in a single or more documents. It is precise and certain.
India, United States of America, etc. have adopted the written Constitution
2. Unwritten Constitution: An unwritten Constitution does not contain one single document that bears the rules and regulations of a country. The countries that have adopted unwritten constitution have the provisions in the form of established principles, treaties, conventions, precedents etc. It is not precise or certain.
United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand etc., have unwritten constitutions.
Why is the Constitution, called the “supreme document” of the country?
The Constitution is referred as the supreme document because nobody is above it. This includes both the state and its citizens. On the other hand, the Constitution of a country is the origin of all the other laws of a country. No law can be formulated in contravention to the provisions of the Constitution. The Constitution defines the powers of the three organs of a country viz., Legislature, Executive and Judiciary.
The legislature which has the power to make laws for the country is controlled by the Constitution. The Constitution is considered to be the bible to the legislators for the formulation of other laws. Any law formulated in a manner which is said to be in contradiction to the provisions of the Constitution are considered to be invalid.
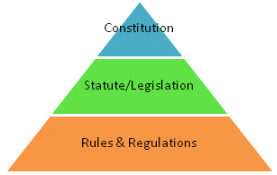
Therefore, unless it is in conformity with the constitution, no law can exist.
THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA
- The Constitution of India was adopted on twenty-sixth November, 1949 and has come into force on twenty-sixth January, 1950.
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar was the Chairman of the drafting committee of the Constitution.
- According to Article 393 of the Indian Constitution, the Constitution is to be referred as the “Constitution of India.”
- The Constitution of India consists of a Preamble, 448 articles, 22 parts and 12 schedules.
What is a preamble?
A preamble is an introduction to a document, which states the purpose of the document.
The Preamble of India is as follows:
“WE, THE PEOPLE OF INDIA, having solemnly
resolved to constitute India into a
SOVEREIGN SOCIALIST SECULAR DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC and
to secure to all its citizens:
JUSTICE, social, economic and political;
LIBERTY of thought, expression, belief, faith and
worship;
EQUALITY of status and of opportunity;
and to promote among them all
FRATERNITY assuring the dignity of the individual
and the unity and integrity of the Nation;
IN OUR CONSTITUENT ASSEMBLY this twenty sixth day of November, 1949, do HEREBY ADOPT,
ENACT AND GIVE TO OURSELVES THIS CONSTITUTION.”
- The Indian Constitution is written and is considered to be the lengthiest Constitution of the world. The Constituent Assembly, which first met on December 9, 1946, took precisely 2 years, 11 months and 18 days to come up with the final draft.
- The Indian constitution grows with time and adapts itself to the needs of the society. Therefore, this requires constant amending of the constitution. The Constitution of India has provisions for its own amendment. However, this amendment power of the Constitution is restricted to a certain extent, thereby making it partly flexible and partly rigid.
- The Constitution of India provides for a parliamentary system of government which contains two levels – The Union (Centre) and the State.
- The Constitution provides for Federal as well as Unitary structure. Therefore, most of the critics consider Indian Constitution to be quasi-federal in nature.
- The Indian Constitution defines the powers of the Union and the State. It also contains provisions limiting the power of the same.
- It provides a set of fundamental rights (Part-III) and fundamental duties (Part IV-A) of the citizens of the Country.
- It provides independent status to the Judiciary and has provisions relating to judicial review
What is judicial review?
It is the power vested in the hands of the judiciary to review the actions of the legislative executive and the judiciary.
12. Apart from the Union and the States, The Constitution of India contains provisions for the Union Territories as well.
13. The Indian Constitution is called as the bag of borrowings, since it has borrowed various features of the Constitution from other countries. Few of the main features are as follows:
(i) Parliamentary type of government: United Kingdom
(ii) Written Constitution: United States of America
(iii) Fundamental rights: United States of America
(iv) Fundamental duties: Russia
(v) Language of the preamble: Australia
(vi) Federal structure: Canada
(vii) Cabinet system of ministers: United Kingdom
(viii) Supreme Court: United States of America
(ix) Judicial review and Independence of Judiciary: United States of America
(x) Preamble: United States of America
(xi) Five year plans: Russia
(xii) Concurrent List: Australia
(xiii) Suspension of fundamental rights during emergency: Weimar Constitution of Germany.
(xiv) Amendment of Constitution: South Africa
(xv) Election commission: United Kingdom
|
1 videos|19 docs|124 tests
|
FAQs on An Introduction to the Constitution - Additional Study Material for CLAT
| 1. What is the purpose of the Constitution? |  |
| 2. How is the Constitution relevant to the CLAT exam? |  |
| 3. What are the key features of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an overview of the amendment process of the Indian Constitution? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of fundamental rights in the Indian Constitution? |  |






















