Types of Elections in India | SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year PDF Download
An electoral system is a set of rules that control how elections and referendums are carried out. Different countries have their own electoral systems for electing members to the legislature.
India uses two types of electoral systems: One is the "First Past the Post" (FPTP) system. The other is the "Proportional Representation with Single Transferable Vote" system, also known as the "List System."
In this article let us understand what is an electoral system, what are the different types of electoral systems and which system is used in India.
What is an electoral system?
- An electoral system is essentially how votes are transformed into seats.
- Every electoral system has three essential components:
- Constituency Size: This indicates the number of lawmakers chosen in one voting area.
- Electoral formula: This is the way to decide who wins a seat.
- Ballot structure: It determines if a voter selects a candidate or a political party and if they pick one choice or rank preferences.
Types of electoral systems
- Plurality/Majority System: Plurality/majority systems are built on the concept that the candidate or party getting the highest number of votes (i.e., more than any other) or a certain number of votes (i.e., 50% plus one—an absolute majority) is declared the victor.
- Single-member districts (e.g., FPTP, alternative vote, or the two-round system) or multi-member districts can be utilized in such a system.
Proportional Representation 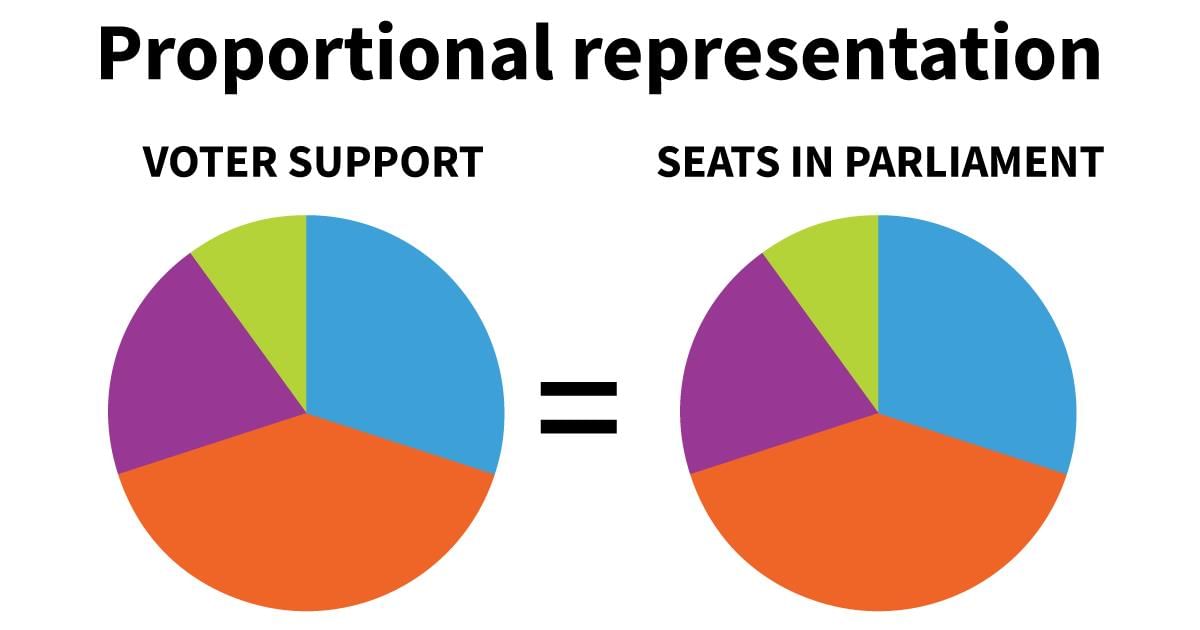
- The system of proportional representation (PR) in elections aims to translate a party's total votes into a corresponding share of seats in the elected body.
- For instance, a party securing 30% of the votes will likely secure about 30% of the seats.
- All PR systems necessitate the presence of multi-member districts.
- The two primary PR systems are List PR and single transferable vote.
Mixed System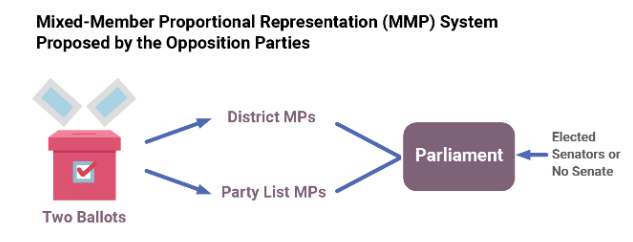
- In a mixed system, voters' choices determine who gets elected using two different methods: PR and majority/plurality.
- There are two kinds of mixed systems: parallel systems and mixed-member proportional systems.
Electoral Systems Practiced in India
First Past The Post (FPTP) System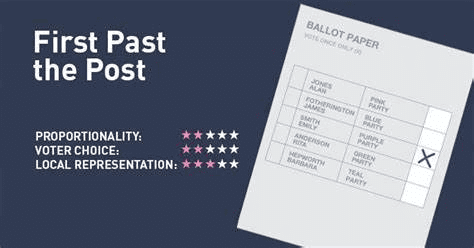
- This is commonly seen in most of the elections conducted throughout India like choosing representatives for the State Assembly, Lok Sabha, and Panchayats.
- Each voter has the ability to vote only once for any candidate in the running or opt for None Of The Above (NOTA).
- Here, the candidate who receives the highest number of votes emerges as the winner.
Proportional Representation with means of Single Transferable Vote
- This system is utilized for selecting the President, Vice President, Members of the Rajya Sabha, and Members of the State Legislative Council.
- It can involve either a single or multiple-member constituency, and the victor is chosen based on a predefined formula.
- The candidate is declared the winner only if they attain the required minimum number of votes.
- The formula to determine the number of votes required to win in this type of election is :

Conclusion
The Indian election system has been highly praised for the way it has been set up. However, there are issues within the system. Even though the Election Commission is working to make sure elections are fair, there are still problems. Some of these problems include using illegal money, politics involving criminals, politics based on caste, and misusing government resources.
|
1335 videos|1436 docs|834 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Elections in India - SSC CGL Tier 2 - Study Material, Online Tests, Previous Year
| 1. What are the types of elections in India and the world? |  |
| 2. How is the Lok Sabha election process carried out in India? |  |
| 3. What is the reservation of seats for SCs and STs in the Lok Sabha elections? |  |
| 4. How is the Rajya Sabha election process different from the Lok Sabha election process in India? |  |
| 5. What are the qualifications for membership of Parliament in India? |  |

















