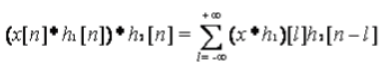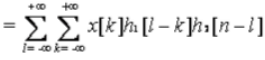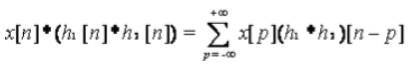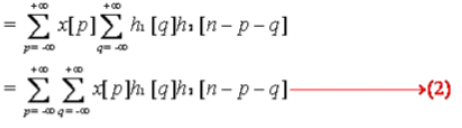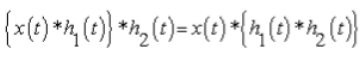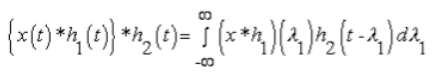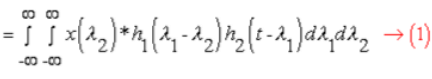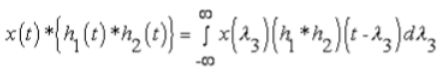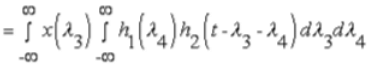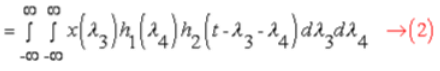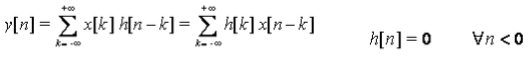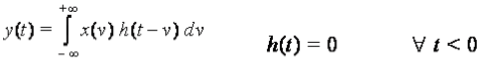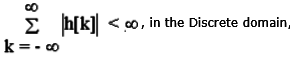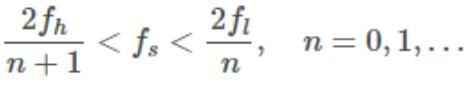Study Notes for Linear Time Invariant System & Sampling Theorem | Signals and Systems - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
Linear Time-Invariant System:
Linear time-invariant systems (LTI systems) are a class of systems used in signals and systems that are both linear and time-invariant. Linear systems are systems whose outputs for a linear combination of inputs are the same as a linear combination of individual responses to those inputs. Time-invariant systems are systems where the output does not depend on when an input was applied. These properties make LTI systems easy to represent and understand graphically.
Linear systems have the property that the output is linearly related to the input. Changing the input in a linear way will change the output in the same linear way. So if the input x1(t) produces the output y1(t) and the input x2(t) produces the output y2(t), then linear combinations of those inputs will produce linear combinations of those outputs. The input {x1(t)+x2(t)} will produce the output {y1(t)+y2(t)}. Further, the input {a1x1(t)+a2x2(t)} will produce the output {a1y1(t)+a2y2(t)} for some constants a1 and a2.
In other words, for a system T over time t, composed of signals x1(t) and x2(t) with outputs y1(t) and y2(t)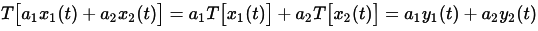
Homogeneity Principle: 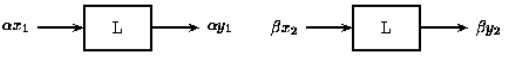
Superposition Principle: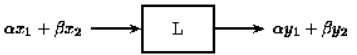
Thus, the entirety of an LTI system can be described by a single function called its impulse response. This function exists in the time domain of the system. For an arbitrary input, the output of an LTI system is the convolution of the input signal with the system's impulse response.
Conversely, the LTI system can also be described by its transfer function. The transfer function is the Laplace transform of the impulse response. This transformation changes the function from the time domain to the frequency domain. This transformation is important because it turns differential equations into algebraic equations, and turns convolution into multiplication.
In the frequency domain, the output is the product of the transfer function with the transformed input. The shift from time to frequency is illustrated in the following image: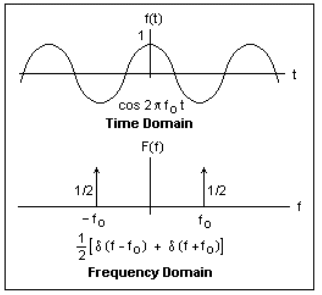
Homogeneity, additivity, and shift invariance may, at first, sound a bit abstract but they are very useful. To characterize a shift-invariant linear system, we need to measure only one thing: the way the system responds to a unit impulse. This response is called the impulse response function of the system. Once we’ve measured this function, we can (in principle) predict how the system will respond to any other possible stimulus.
Introduction to Convolution
Because here’s not a single answer to define what is ? In “Signals and Systems” probably we saw convolution in connection with Linear Time Invariant Systems and the impulse response for such a system. This multitude of interpretations and applications is somewhat like the situation with the definite integral.
To pursue the analogy with the integral, in pretty much all applications of the integral there is a general method at work:
- Cut the problem into small pieces where it can be solved approximately.
- Sum up the solution for the pieces, and pass to a limit.
Convolution Theorem
F(g∗f)(s) = Fg(s)Ff(s)
- In other notation: If f(t)⇔ F(s) and g(t) ⇔ G(s) then (g∗f)(t)⇔ G(s)F(s)
- In words: Convolution in the time domain corresponds to multiplication in the frequency domain.

- For the Integral to make sense i.e., to be able to evaluate g(t−x) at points outside the interval from 0 to 1, we need to assume that g is periodic. it is not the issue the present case, where we assume that f(t) and g(t) are defined for all t, so the factors in the integral

Convolving in the Frequency Domain
- In Frequency Domain convolution theorem states that
F(g ∗ f)=Fg ·Ff - Here we have seen that the whole thing is carried out for inverse Fourier transform, as follow:
F−1(g∗f) = F−1g·F−1f
F(gf)(s) = (Fg∗Ff)(s) - Multiplication in the time domain corresponds to convolution in the frequency domain.
By applying Duality Formula
F(Ff)(s)=f(−s) or F(Ff)=f− without the variable.
- To derive the identity F(gf)=Fg∗Ff, we assume for convenience, h = Ff and k = Fg
then we can write as F(gf)=k∗h - The one thing we know is how to take the Fourier transform of a convolution, so, in the present notation, F(k∗h)=(Fk)(Fh).
But now Fk =FFg = g−
and likewise Fh =FFf = f
So F(k∗h)=g−f− =(gf)−, or gf =F(k∗h)−
Now, finally, take the Fourier transform of both sides of this last equation
FF identity : F(gf)=F(F(k∗h)−)=k∗h =Fg∗Ff
Note: Here we are trying to prove F(gf)(s) = (Fg∗Ff)(s) rather than F(g∗f)=(Ff)(Fg) Because, it seems more “natural” to multiply signals in the time domain and see what effect this has in the frequency domain, so why not work with F(fg) directly? But write the integral for F(gf); there’s nothing you can do with it to get toward Fg∗Ff.
There is also often a general method of convolutions:
- Usually there’s something that has to do with smoothing and averaging,understood broadly.
- You see this in both the continuous case and the discrete case.
Some of you who have seen convolution in earlier courses,you’ve probably heard the expression “flip and drag”
Meaning of Flip & Drag: here’s the meaning of Flip & Drag is as follow
- Fix a value t.The graph of the function g(x−t) has the same shape as g(x) but shifted to the right by t. Then forming g(t − x) flips the graph (left-right) about the line x = t.
- If the most interesting or important features of g(x) are near x = 0, e.g., if it’s sharply peaked there, then those features are shifted to x = t for the function g(t − x) (but there’s the extra “flip” to keep in mind).Multiply f(x) and g(t − x) and integrate with respect to x.
Averaging
- I prefer to think of the convolution operation as using one function to smooth and average the other. Say g is used to smooth f in g∗f. In many common applications g(x) is a positive function, concentrated near 0, with total area 1.

- Like a sharply peaked Gaussian, for example (stay tuned). Then g(t−x) is concentrated near t and still has area 1. For a fixed t, forming the integral

- The last expression is like a weighted average of the values of f(x) near x = t, weighted by the values of (the flipped and shifted) g. That’s the averaging part of the convolution, computing the convolution g∗f at t replaces the value f(t) by a weighted average of the values of f near t.
Smoothing
- Again take the case of an averaging-type function g(t), as above. At a given value of t,( g ∗ f)(t) is a weighted average of values of f near t.
- Then Move t a little to a point t0. Then (g∗f)(t0) is a weighted average of values of f near t0, which will include values of f that entered into the average near t.
- Thus the values of the convolutions (g∗f)(t) and (g∗f)(t0) will likely be closer to each other than are the values f(t) and f(t0). That is, (g ∗f)(t) is “smoothing” f as t varies — there’s less of a change between values of the convolution than between values of f.
Other identities of Convolution
It’s not hard to combine the various rules we have and develop an algebra of convolutions. Such identities can be of great use — it beats calculating integrals. Here’s an assortment. (Lower and uppercase letters are Fourier pairs.)
- (f ·g)∗(h·k)(t) ⇔ (F ∗G)·(H ∗K)(s)
- {(f(t)+g(t))·(h(t)+k(t)} ⇔ {[(F + G)∗(H + K)]}(s)
- f(t)·(g∗h)(t) ⇔ F ∗(G·H)(s)
Properties of Convolution
Here we are explaining the properties of convolution in both continuous and discrete domain
- Associative
- Commutative
- Distributive properties
- As a LTI system is completely specified by its impulse response, we look into the conditions on the impulse response for the LTI system to obey properties like memory, stability, invertibility, and causality.
- According to the Convolution theorem in Continuous & Discrete time as follow:
 For Discrete system.
For Discrete system. & For Continuous System
& For Continuous System
We shall now discuss the important properties of convolution for LTI systems.
1) Commutative property:
- In Discrete time: x[n]h[n] ⇔ h[n]x[n]
Proof: Since we know that y[n] = x[n]h[n]
let us assume n-k = l so,
- So it clear from the derived expression that ⇒ x[n]h[n] ⇔ h[n]x[n]
- In Continuous time:
Proof
We know that
Making the substitution


 so x[t]*h[t] ⇔ h[t]*x[t]
so x[t]*h[t] ⇔ h[t]*x[t]
2. Distributive Property
By this Property we will conclude that convolution is distributive over addition.
- Discrete time: x[n]{α h1[n] + βh2[n]} = α {x[n] h1[n]}+ β{x[n] h2[n]} α & β are constant.
- Continuous Time: x(t){α h1(t) + βh2(t)} = α{x(t)h1(t)} + β {x(t)h2(t)} α & β are constant.
3. Associative Property
- Discrete Time y[n] = x[n]*h[n]*g[n]


Proof:

- In Continuous Time:






Let Substitute λ3 = λ2
λ4 = λ1 - λ2
then the jacobian for the above transformation is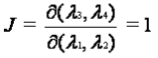
4. Invertibility
A system is said to be invertible if there exist an inverse system which when connected in series with the original system produces an output identical to input .
(x*δ)[n]= x[n]
(x*h*h-1)[n]= x[n]
(h*h-1)[n]= (δ)[n]
5. Causality
- Discrete Time

- Continuous Time

6. Stability
- Discrete Time

- Continuous Time

Sampling Theorem
- Simply the sampling can be defined as: Sampling a signal: Analog → Digital conversion by reading the value at discrete points.
- A band limited continuous time signal with highest frequency (bandwidth) fm hertz can be uniquely recovered from its samples provided that the sampling rate fs is greater than or equal to 2fm samples per second.
- The basic concept of Sampling Theory is the decomposition of a signal into various frequencies.

Aliasing & Anti-aliasing
- Aliasing is such an effect of violating the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theory. During sampling the base band spectrum of the sampled signal is mirrored to every multifold of the sampling frequency. These mirrored spectra are called alias.
- The easiest way to prevent aliasing is the application of a steep sloped low-pass filter with half the sampling frequency before the conversion. Aliasing can be avoided by keeping Fs>2Fmax.
- Since the sampling rate for an analog signal must be at least two times as high as the highest frequency in the analog signal in order to avoid aliasing. So in order to avoid this ,the analog signal is then filtered by a low pass filter prior to being sampled, and this filter is called an anti-aliasing filter. Sometimes the reconstruction filter after a digital-to-analog converter is also called an anti-aliasing filter.
Condition For Sampling
- Consider a signal that has lowest frequency component Fl and highest frequency component Fh. According to the theory of Band pass sampling, this signal can be sampled and successfully recovered if sampled at a frequency (Fs) twice the difference between highest and lowest frequency.
that is, Fs = 2⋅(Fh−Fl) - The above condition is not generally true that a band pass signal can be sampled and recovered without error if fs>2B is satisfied, where B=fh−fl is the signal's bandwidth. This condition is just necessary but not sufficient.
- So we must be make sure that the aliased spectra do not overlap. This results in the following condition on the sampling frequency

- The above condition can only be satisfied for n = 0, so you get the familiar Nyquist sampling theorem where fs must be greater than twice the highest frequency of the signal: fs>2fh.
- The lowest possible sampling frequency is obtained for the largest integer n such that the last equation is still satisfied.
This maximum value of n is given by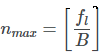
- where B=fh−fl is the bandwidth.
|
42 videos|53 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Study Notes for Linear Time Invariant System & Sampling Theorem - Signals and Systems - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is a linear time-invariant system? |  |
| 2. How can a linear time-invariant system be characterized? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the sampling theorem in signal processing? |  |
| 4. How does the sampling theorem relate to linear time-invariant systems? |  |
| 5. Can a linear time-invariant system violate the sampling theorem? |  |

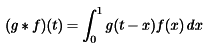
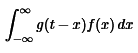
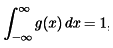
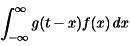
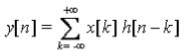 For Discrete system.
For Discrete system.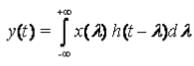 & For Continuous System
& For Continuous System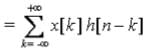
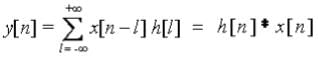
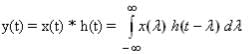
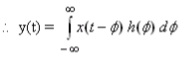
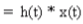 so x[t]*h[t] ⇔ h[t]*x[t]
so x[t]*h[t] ⇔ h[t]*x[t]