Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science Class 10 > Overview: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Overview: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Magnetism
- A magnet attracts iron or iron-like substances.
- Electric currents create magnetic effects.
- Electromagnets and electric motors use the magnetic effect of electric current, while electric generators use the electric effect of moving magnets.
- Passing an electric current through a metallic conductor can deflect a compass needle.
Properties of Magnets
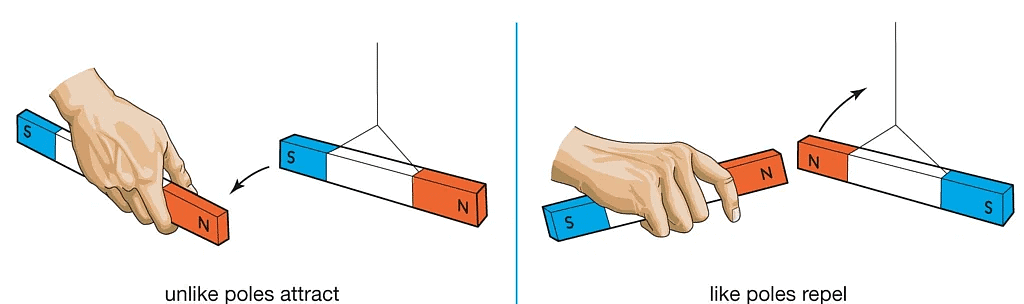
- Every magnet has two poles: North and South.
- Like poles repel each other, and unlike poles attract each other.
- A freely suspended bar magnet aligns itself in a nearly north-south direction with its north pole pointing north.
Characteristics of Magnetic Field Lines
- Field lines originate from the North pole and terminate at the South pole.
- Field lines are closed curves.
- Field lines are closer in a stronger magnetic field.
- Field lines never intersect.
- Inside a magnet, the field lines go from South to North.
- The degree of closeness of field lines indicates the relative strength of the magnetic field.
Magnetic Field of a Bar Magnet
- Hans Christian Oersted first stated that electric current has a magnetic field.
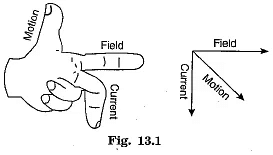
- Right Hand Thumb Rule determines the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor.
- Magnetic field lines form concentric circles around a straight conductor carrying current.
- The magnetic field strength is proportional to the current and inversely proportional to the distance from the conductor.
Magnetic Field due to Current through a Circular Loop
- Magnetic field lines form concentric circles around a circular current-carrying conductor.
- The strength of the magnetic field depends on the current, distance from the conductor, and the number of turns in the coil.
- Magnetic fields of multiple loops add up because of the directions of current in each loop.
Solenoid
- A solenoid is a coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wound closely in a cylindrical form.
- Its magnetic field is similar to that of a bar magnet.
- The magnetic field is uniform inside the solenoid with parallel field lines.
- The direction of the magnetic field is from North to South outside the solenoid and from South to North inside.
- A solenoid can be used to magnetize magnetic materials like soft iron.
Electromagnets vs. Permanent Magnets
- Electromagnets are temporary magnets that can be easily demagnetized, while permanent magnets cannot.
- Electromagnets allow variable strength and polarity, while permanent magnets have fixed properties.
Question for Overview: Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentTry yourself: What creates the magnetic effect in electromagnets and electric motors?View Solution
Force on a Current-Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field
- André-Marie Ampère suggested that a magnetic field exerts an equal and opposite force on a current-carrying conductor.
- The displacement in the conductor is maximal when the current direction is perpendicular to the magnetic field.
- The direction of force is reversed when the direction of current is reversed.
- Fleming's Left Hand Rule helps determine the direction of force.
Electric Motors
- Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- They use a rotating coil of insulated copper wire in a magnetic field to generate motion.
- A split-ring commutator reverses the direction of the current and force on the coil, ensuring continuous rotation.
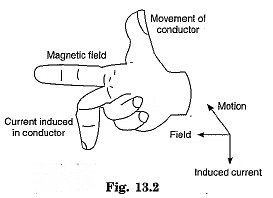
Electric Generator
- Electric generators convert mechanical energy into electricity.
- They use a rotating rectangular coil in a magnetic field to induce a current.
- A split-ring commutator or slip rings are used to control the direction of the induced current, leading to either direct or alternating current.
- Generators produce electrical energy.
Domestic Electric Circuits
- Electric circuits have live (positive, red insulation), neutral (negative, black insulation), and earth (green insulation) wires.
- In India, the potential difference between live and neutral wires is 220 V.
- Safety devices include fuses, earth wires, and MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) to prevent electrical accidents.
The document Overview: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current | Science Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Science Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Overview: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Science Class 10
| 1. What is magnetism? |  |
Ans. Magnetism is a phenomenon that arises from the force between objects with magnetic fields. It is the property of certain materials to attract or repel each other based on the arrangement of their atoms' magnetic fields.
| 2. What are the magnetic effects of electric current? |  |
Ans. The magnetic effects of electric current refer to the creation of a magnetic field around a conductor when an electric current passes through it. This phenomenon is utilized in various applications such as electromagnets, electric motors, and generators.
| 3. How does an electromagnet work? |  |
Ans. An electromagnet is a temporary magnet created by passing an electric current through a coil of wire. When the current flows, it generates a magnetic field around the coil, which can attract or repel magnetic materials. The strength of the electromagnet can be controlled by adjusting the current.
| 4. What is the relationship between magnetism and electricity? |  |
Ans. Magnetism and electricity are closely related phenomena. Electric current produces a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field induces an electric current in a conductor. This relationship is described by electromagnetic induction, which forms the basis for many electrical devices and technologies.
| 5. How are magnetic fields produced by electric currents used in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Magnetic fields produced by electric currents have numerous applications in everyday life. They are used in electric motors to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, in generators to produce electricity, in transformers to change voltage levels, and in various medical imaging technologies such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging).
Related Searches






















